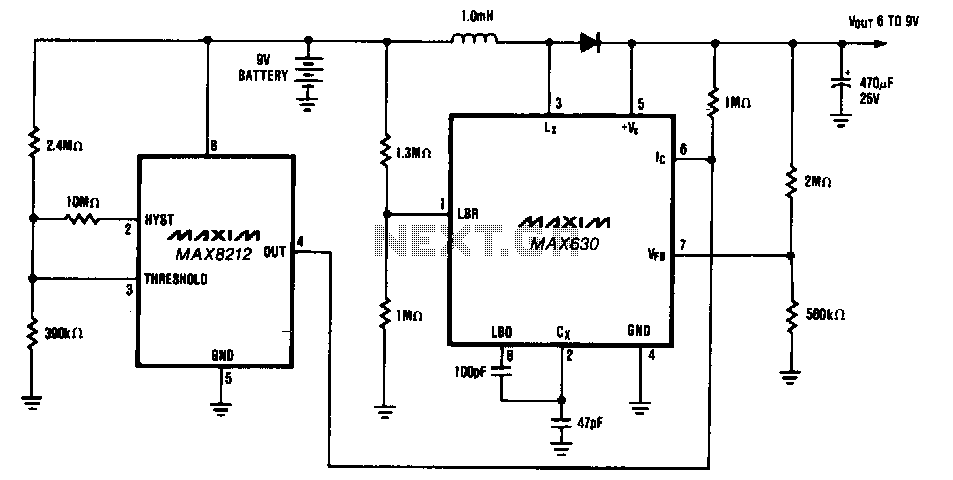
Low Battery Cut off and Overload Protection Circuit
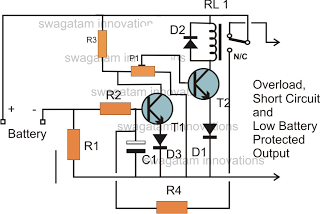
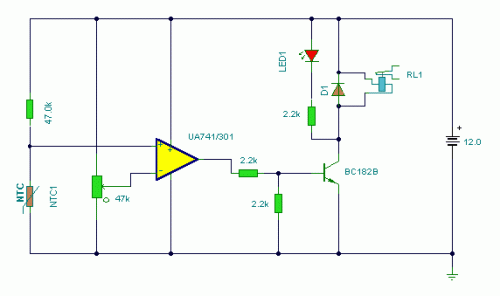
The battery voltage must pass through resistor R1 before reaching the output load. As a result, the current flowing through R1 is proportionately transformed into a voltage across it. When the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold, the base current of transistor T2 decreases sufficiently, preventing it from maintaining the relay in conduction, which subsequently switches it OFF along with the load.
The described circuit operates as a voltage monitoring and control system. The primary component, R1, serves as a current-limiting resistor that influences the voltage drop across itself based on the current flowing through it. This voltage drop is critical for regulating the operation of transistor T2, which functions as a switch for the relay controlling the load.
When the battery voltage is at an acceptable level, the current through R1 produces a sufficient base current for T2, allowing it to remain in the 'ON' state. In this state, T2 activates the relay, completing the circuit to the load and enabling its operation. However, as the battery voltage declines and crosses a predetermined threshold, the base current of T2 diminishes. This reduction leads to T2 transitioning to the 'OFF' state, which interrupts the current flow to the relay and consequently disconnects the load.
The design ensures that the load is only powered when the battery voltage is above the critical threshold, thereby preventing potential damage to the load from insufficient voltage conditions. This circuit is particularly useful in battery-powered applications where load protection and power management are essential for prolonging battery life and ensuring reliable operation. Proper selection of R1 and the characteristics of T2 are crucial for achieving the desired voltage threshold and response time in this monitoring system.The battery voltage has to pass through R1 before reaching the load at the output and therefore the current passing through it is proportionately transformed into voltage across it. When the battery voltage falls beyond a certain low voltage threshold, the base current of T2 becomes sufficiently low such that its no longer able to hold the relay i
nto conduction and switches it OFF and also the load. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a voltage monitoring and control system. The primary component, R1, serves as a current-limiting resistor that influences the voltage drop across itself based on the current flowing through it. This voltage drop is critical for regulating the operation of transistor T2, which functions as a switch for the relay controlling the load.
When the battery voltage is at an acceptable level, the current through R1 produces a sufficient base current for T2, allowing it to remain in the 'ON' state. In this state, T2 activates the relay, completing the circuit to the load and enabling its operation. However, as the battery voltage declines and crosses a predetermined threshold, the base current of T2 diminishes. This reduction leads to T2 transitioning to the 'OFF' state, which interrupts the current flow to the relay and consequently disconnects the load.
The design ensures that the load is only powered when the battery voltage is above the critical threshold, thereby preventing potential damage to the load from insufficient voltage conditions. This circuit is particularly useful in battery-powered applications where load protection and power management are essential for prolonging battery life and ensuring reliable operation. Proper selection of R1 and the characteristics of T2 are crucial for achieving the desired voltage threshold and response time in this monitoring system.The battery voltage has to pass through R1 before reaching the load at the output and therefore the current passing through it is proportionately transformed into voltage across it. When the battery voltage falls beyond a certain low voltage threshold, the base current of T2 becomes sufficiently low such that its no longer able to hold the relay i
nto conduction and switches it OFF and also the load. 🔗 External reference