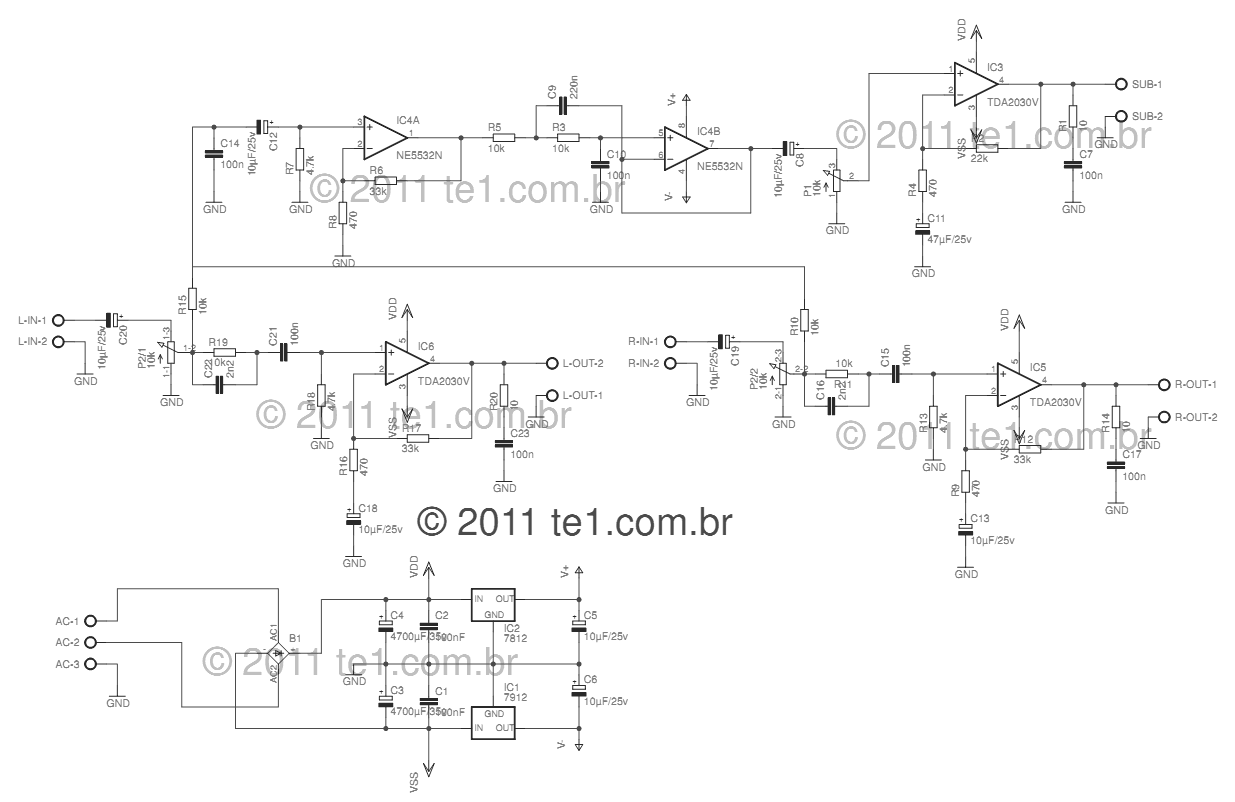
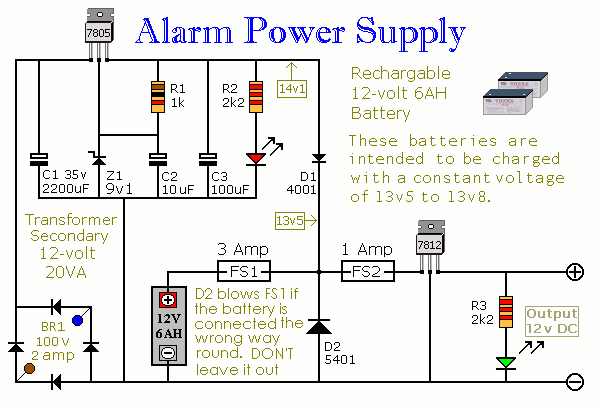
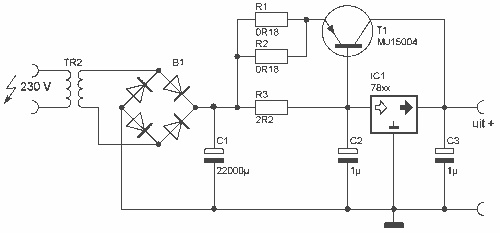
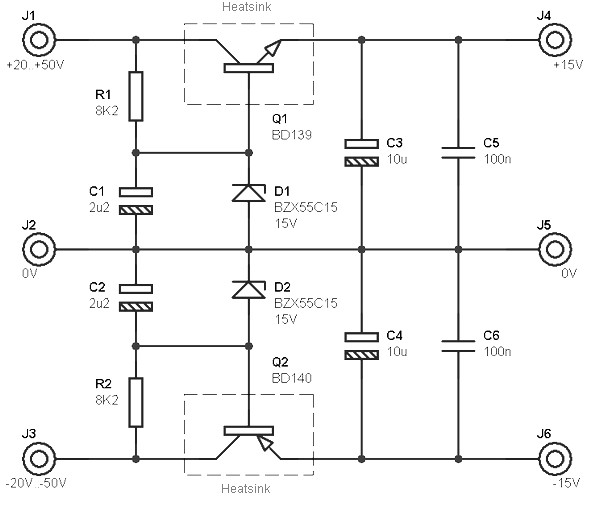
Low-Cost AC Supply
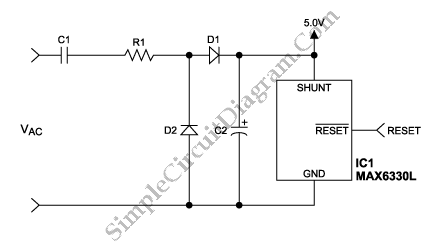
Applying the filtered and rectified AC input to a high-input-voltage linear regulator is the simplest way to produce a low current level from an AC source.
The process of converting an AC source to a low current level using a high-input-voltage linear regulator involves several key steps. Initially, the AC voltage is filtered and rectified to convert it into a usable DC voltage. This is typically accomplished using a combination of diodes and capacitors. The diodes serve to rectify the AC signal, allowing current to flow in only one direction, while the capacitors smooth out the resulting pulsating DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable output.
Once the AC input has been rectified and filtered, the next stage involves feeding this DC voltage into a high-input-voltage linear regulator. The linear regulator is designed to provide a consistent output voltage, irrespective of variations in input voltage or load conditions. The operation of the linear regulator is based on controlling the voltage drop across a pass element, typically a transistor, which dissipates excess voltage as heat.
The selection of the linear regulator must consider the maximum input voltage, output voltage requirements, and the current rating. The regulator should be chosen to ensure that it can handle the filtered DC voltage without exceeding its maximum input specifications. Additionally, thermal management must be addressed, as linear regulators can generate significant heat, especially when there is a large difference between input and output voltages.
The output from the linear regulator provides a low current level suitable for powering sensitive electronic circuits or components that require stable voltage levels. This setup is particularly advantageous in applications where simplicity and low noise are critical, such as in audio equipment or precision measurement devices. Proper bypass capacitors may also be included at the output to further stabilize the voltage and filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, the combination of filtering, rectification, and regulation allows for the effective conversion of AC power into a stable low current DC output, making it a fundamental approach in various electronic applications.Applying the filtered and rectified AC input to a high-input-voltage linear regulator is the simplest way to produce low current level from an AC source.. 🔗 External reference
The process of converting an AC source to a low current level using a high-input-voltage linear regulator involves several key steps. Initially, the AC voltage is filtered and rectified to convert it into a usable DC voltage. This is typically accomplished using a combination of diodes and capacitors. The diodes serve to rectify the AC signal, allowing current to flow in only one direction, while the capacitors smooth out the resulting pulsating DC voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable output.
Once the AC input has been rectified and filtered, the next stage involves feeding this DC voltage into a high-input-voltage linear regulator. The linear regulator is designed to provide a consistent output voltage, irrespective of variations in input voltage or load conditions. The operation of the linear regulator is based on controlling the voltage drop across a pass element, typically a transistor, which dissipates excess voltage as heat.
The selection of the linear regulator must consider the maximum input voltage, output voltage requirements, and the current rating. The regulator should be chosen to ensure that it can handle the filtered DC voltage without exceeding its maximum input specifications. Additionally, thermal management must be addressed, as linear regulators can generate significant heat, especially when there is a large difference between input and output voltages.
The output from the linear regulator provides a low current level suitable for powering sensitive electronic circuits or components that require stable voltage levels. This setup is particularly advantageous in applications where simplicity and low noise are critical, such as in audio equipment or precision measurement devices. Proper bypass capacitors may also be included at the output to further stabilize the voltage and filter out high-frequency noise.
In summary, the combination of filtering, rectification, and regulation allows for the effective conversion of AC power into a stable low current DC output, making it a fundamental approach in various electronic applications.Applying the filtered and rectified AC input to a high-input-voltage linear regulator is the simplest way to produce low current level from an AC source.. 🔗 External reference