Low current touch switch
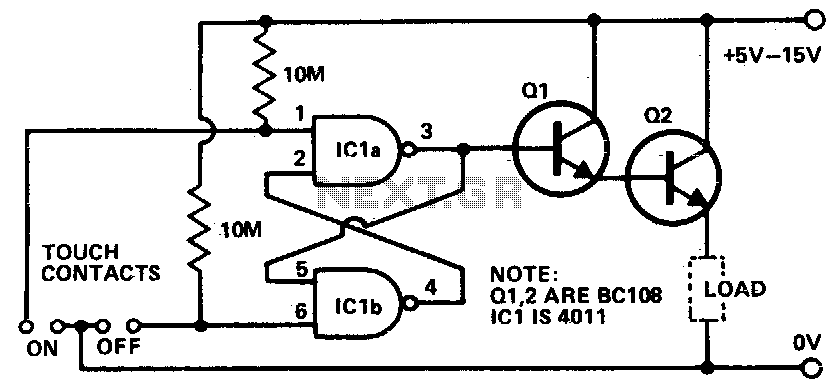
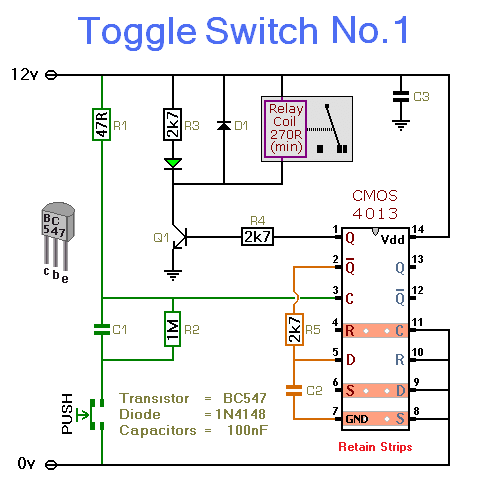
Touching the on contacts with a finger brings pin 3 high, turning on the Darlington pair and supplying power to the load (transistor radio, etc.). Q1 must be a high-gain transistor, and Q2 is chosen for the current required by the load circuit.
The circuit utilizes a Darlington pair configuration, which consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected in such a way that the current amplified by the first transistor (Q1) is further amplified by the second transistor (Q2). This configuration is advantageous for applications requiring high current gain, making it suitable for driving loads such as a transistor radio.
In this setup, the input signal is applied to pin 3, which is connected to the base of Q1. When a finger touches the on contacts, it effectively applies a high voltage to pin 3, causing Q1 to turn on. The base-emitter junction of Q1 becomes forward-biased, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which in turn activates Q2.
Q2 is selected based on the current requirements of the load circuit. It is essential that Q1 is a high-gain transistor to ensure that even a small input current can produce a sufficient output current to drive the load effectively. The output from Q2 can then be used to power devices that require higher currents, such as a small transistor radio.
The design must also consider the power ratings and thermal management of both transistors, especially Q2, which may dissipate significant power depending on the load. Proper biasing resistors and possibly a heat sink for Q2 may be necessary to ensure reliable operation under varying load conditions. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be incorporated to prevent back EMF from inductive loads, ensuring the longevity and stability of the circuit.Touching the on contacts with a finger brings pin 3 high, turning on the Darlington pair and supplying power to the load (transistor radio etc) Ql must be a high gain transistor, and Q2 is chosen for the current required by the load circuit. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a Darlington pair configuration, which consists of two bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) connected in such a way that the current amplified by the first transistor (Q1) is further amplified by the second transistor (Q2). This configuration is advantageous for applications requiring high current gain, making it suitable for driving loads such as a transistor radio.
In this setup, the input signal is applied to pin 3, which is connected to the base of Q1. When a finger touches the on contacts, it effectively applies a high voltage to pin 3, causing Q1 to turn on. The base-emitter junction of Q1 becomes forward-biased, allowing current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which in turn activates Q2.
Q2 is selected based on the current requirements of the load circuit. It is essential that Q1 is a high-gain transistor to ensure that even a small input current can produce a sufficient output current to drive the load effectively. The output from Q2 can then be used to power devices that require higher currents, such as a small transistor radio.
The design must also consider the power ratings and thermal management of both transistors, especially Q2, which may dissipate significant power depending on the load. Proper biasing resistors and possibly a heat sink for Q2 may be necessary to ensure reliable operation under varying load conditions. Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be incorporated to prevent back EMF from inductive loads, ensuring the longevity and stability of the circuit.Touching the on contacts with a finger brings pin 3 high, turning on the Darlington pair and supplying power to the load (transistor radio etc) Ql must be a high gain transistor, and Q2 is chosen for the current required by the load circuit. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713