Low Distortion Crystal Oscillator
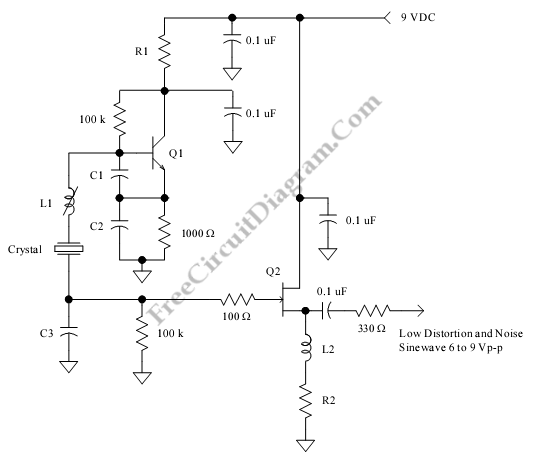
This is a low distortion crystal oscillator circuit. This circuit generates a sine wave that has low phase noise and distortion. This circuit can be used for various applications.
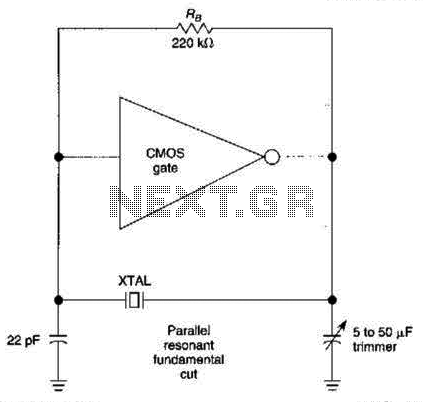
The low distortion crystal oscillator circuit is designed to produce a stable sine wave output with minimal phase noise and distortion, making it suitable for high-precision applications. At the core of the circuit is a quartz crystal, which serves as the frequency-determining element. The crystal's high Q-factor ensures that the oscillator operates at its fundamental frequency with excellent stability.
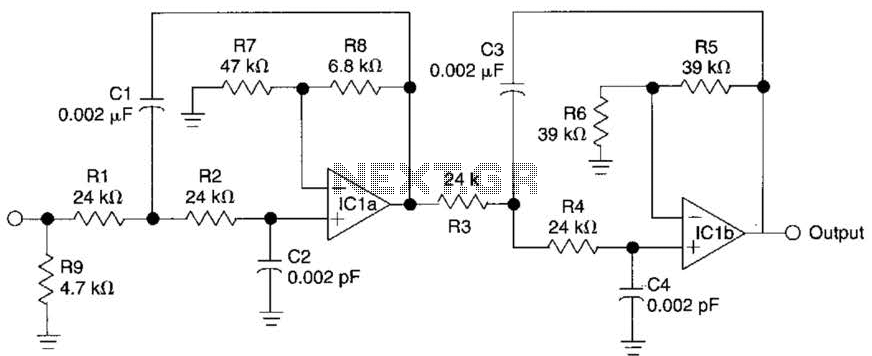
The circuit typically includes an amplifier stage, which boosts the signal generated by the crystal. This stage is often configured as a feedback loop to maintain oscillation. Commonly, a Colpitts or Hartley oscillator configuration is employed, where the feedback network is formed by capacitors and the crystal itself.
To further enhance the performance, additional components may be included, such as low-noise voltage regulators to provide a stable power supply, and filtering capacitors to eliminate high-frequency noise. Output buffering may also be implemented to drive loads without affecting the oscillator's performance.
The output frequency can be adjusted by selecting different crystals or by using variable capacitors in the feedback network. The circuit may also incorporate temperature compensation techniques to maintain frequency stability over varying environmental conditions.
This low distortion crystal oscillator circuit is widely used in telecommunications, audio applications, and precision measurement instruments, where signal integrity is paramount. Its ability to generate clean sine waves makes it an essential component in various electronic systems.This is a Low Distortion Crystal Oscillator circuit. This circuit generate a sinewave that has low phase noise and distortion. This circuit can be used to. 🔗 External reference
The low distortion crystal oscillator circuit is designed to produce a stable sine wave output with minimal phase noise and distortion, making it suitable for high-precision applications. At the core of the circuit is a quartz crystal, which serves as the frequency-determining element. The crystal's high Q-factor ensures that the oscillator operates at its fundamental frequency with excellent stability.
The circuit typically includes an amplifier stage, which boosts the signal generated by the crystal. This stage is often configured as a feedback loop to maintain oscillation. Commonly, a Colpitts or Hartley oscillator configuration is employed, where the feedback network is formed by capacitors and the crystal itself.
To further enhance the performance, additional components may be included, such as low-noise voltage regulators to provide a stable power supply, and filtering capacitors to eliminate high-frequency noise. Output buffering may also be implemented to drive loads without affecting the oscillator's performance.
The output frequency can be adjusted by selecting different crystals or by using variable capacitors in the feedback network. The circuit may also incorporate temperature compensation techniques to maintain frequency stability over varying environmental conditions.
This low distortion crystal oscillator circuit is widely used in telecommunications, audio applications, and precision measurement instruments, where signal integrity is paramount. Its ability to generate clean sine waves makes it an essential component in various electronic systems.This is a Low Distortion Crystal Oscillator circuit. This circuit generate a sinewave that has low phase noise and distortion. This circuit can be used to. 🔗 External reference