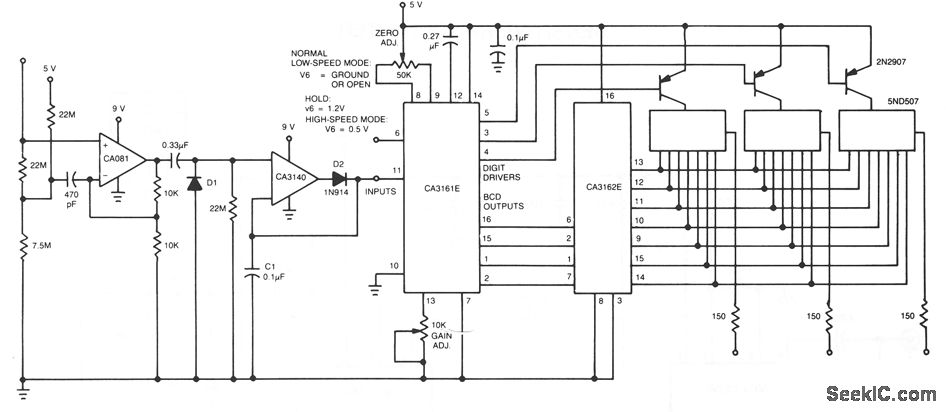
Low-Drift High-Impedance JFET DC Voltmeter
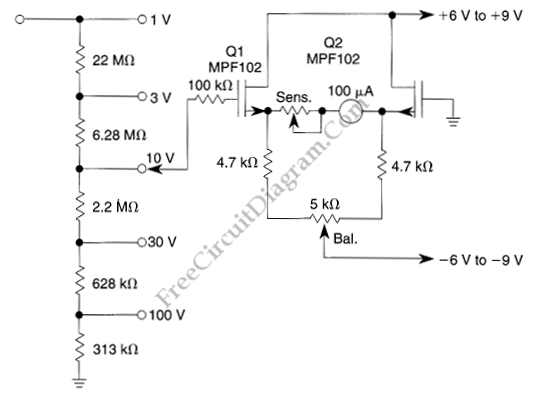
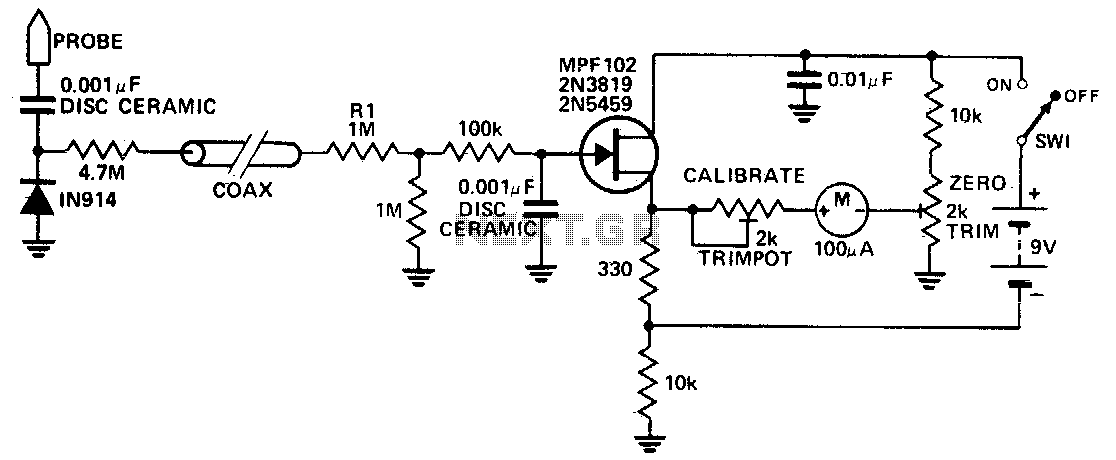
The voltmeter illustrated in the schematic diagram below possesses a very high input impedance. The range selector employs standard voltage divider resistors; however, due to the subsequent preamplifier utilizing JFETs, the divider can be designed with very high resistance series resistors. This DC voltmeter circuit is also characterized by low drift. It incorporates a pair of JFETs, configured in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. The transistors Q1 and Q2 must be matched within 10% for Idss to maintain bridge balance across varying temperatures. Below is the schematic diagram of the circuit:
The described voltmeter circuit is engineered for precision measurement of DC voltages, emphasizing high input impedance to minimize the loading effect on the circuit under test. The use of JFETs (Junction Field-Effect Transistors) in the preamplifier stage is crucial for achieving high input impedance, as JFETs inherently possess high gate resistance. This characteristic allows for the use of high-value resistors in the voltage divider without significantly affecting the measurement accuracy.
The voltage divider configuration is essential for scaling down the input voltage to a level suitable for the JFET input stage. The choice of resistors in the divider must be made carefully, considering thermal stability and drift characteristics to ensure consistent performance. The low drift specification indicates that the circuit is designed to maintain accuracy over time and temperature variations, which is critical for precision applications.
The balanced-bridge configuration of the source-follower amplifier, formed by the two matched JFETs, enhances the circuit's performance by ensuring that any common-mode noise is effectively rejected. Matching Q1 and Q2 within 10% for their drain-source saturation current (Idss) is vital for maintaining the balance of the bridge. This matching minimizes offset voltages and improves the overall stability of the circuit, especially under varying environmental conditions.
In summary, this voltmeter circuit is a sophisticated design that leverages high-impedance JFET technology and a balanced-bridge topology to deliver accurate and stable voltage measurements. The careful selection and matching of components are fundamental to achieving the desired performance characteristics, making it suitable for high-precision applications.The voltmeter shown in the schematic diagram below has very high impedance. The range selector uses conventional voltage divider resistors, but since the following pre amplifier uses JFET, the divider can be designed using very high resistance series resistors. This DC voltmeter circuit also featured with low drift. This circuit uses a pair JFETs, which is configured in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. The Q2 and Q1 must be matched within 10% for Idss that will maintains bridge balance over temperature. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: 🔗 External reference
The described voltmeter circuit is engineered for precision measurement of DC voltages, emphasizing high input impedance to minimize the loading effect on the circuit under test. The use of JFETs (Junction Field-Effect Transistors) in the preamplifier stage is crucial for achieving high input impedance, as JFETs inherently possess high gate resistance. This characteristic allows for the use of high-value resistors in the voltage divider without significantly affecting the measurement accuracy.
The voltage divider configuration is essential for scaling down the input voltage to a level suitable for the JFET input stage. The choice of resistors in the divider must be made carefully, considering thermal stability and drift characteristics to ensure consistent performance. The low drift specification indicates that the circuit is designed to maintain accuracy over time and temperature variations, which is critical for precision applications.
The balanced-bridge configuration of the source-follower amplifier, formed by the two matched JFETs, enhances the circuit's performance by ensuring that any common-mode noise is effectively rejected. Matching Q1 and Q2 within 10% for their drain-source saturation current (Idss) is vital for maintaining the balance of the bridge. This matching minimizes offset voltages and improves the overall stability of the circuit, especially under varying environmental conditions.
In summary, this voltmeter circuit is a sophisticated design that leverages high-impedance JFET technology and a balanced-bridge topology to deliver accurate and stable voltage measurements. The careful selection and matching of components are fundamental to achieving the desired performance characteristics, making it suitable for high-precision applications.The voltmeter shown in the schematic diagram below has very high impedance. The range selector uses conventional voltage divider resistors, but since the following pre amplifier uses JFET, the divider can be designed using very high resistance series resistors. This DC voltmeter circuit also featured with low drift. This circuit uses a pair JFETs, which is configured in a balanced-bridge source-follower amplifier circuit. The Q2 and Q1 must be matched within 10% for Idss that will maintains bridge balance over temperature. Here is the schematic diagram of the circuit: 🔗 External reference