Low Voltage Adjustable Reference Supply
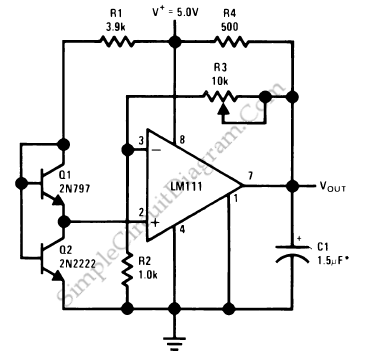
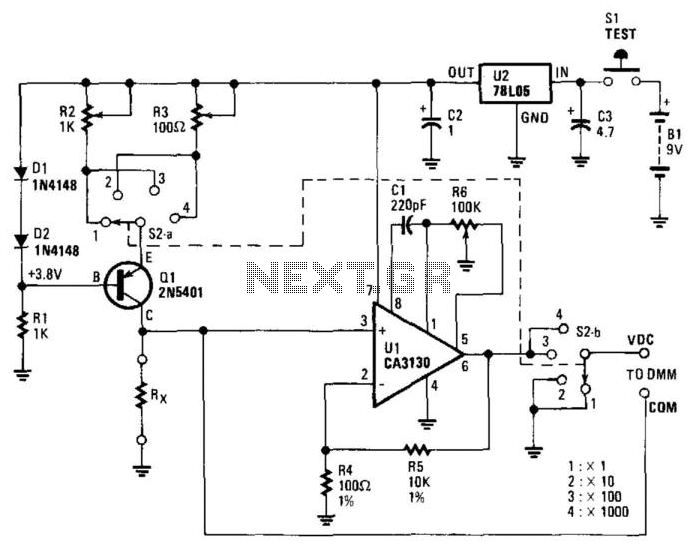
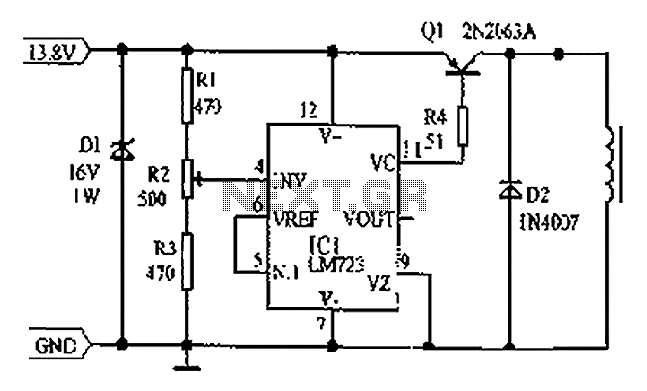
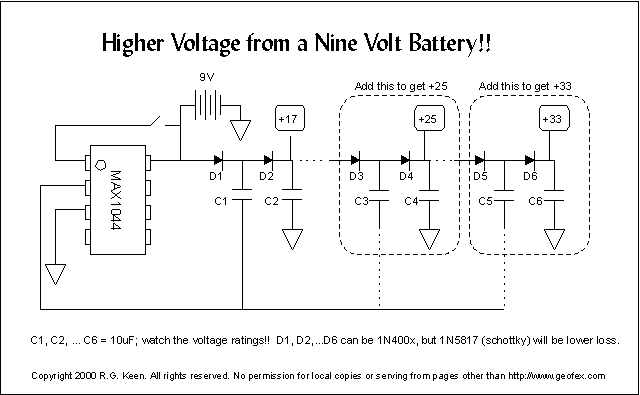
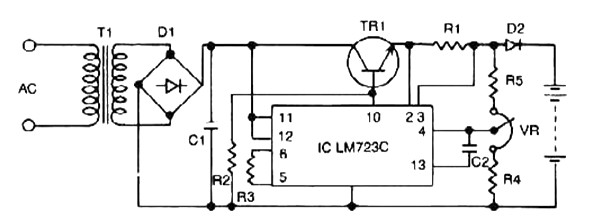
A low voltage reference is essential for providing an offset source or biasing, or simply serving as a reference for a comparator. Its adjustable feature should be compatible with this circuit.
A low voltage reference circuit is designed to deliver a stable and precise voltage output that remains unaffected by variations in power supply and temperature. This type of circuit is crucial in applications where accurate voltage levels are required for biasing transistors, setting reference points for comparators, or providing a stable voltage source for analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
The typical architecture of a low voltage reference circuit includes a voltage reference diode or bandgap reference, which ensures a stable output voltage. The circuit may also incorporate a series of resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the output. An adjustable feature can be achieved by including a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the feedback loop, allowing the user to fine-tune the output voltage according to specific requirements.
For implementation, the low voltage reference circuit can be powered by a stable supply voltage, and the output can be connected to various components that require a reference voltage. The design should take into consideration the load current and the desired output voltage range to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, a low voltage reference circuit is a critical component in many electronic systems, providing reliable voltage levels for biasing and reference purposes, with adjustable features to meet specific circuit needs.Low voltage reference is important to provide offset source or biasing, or just a reference for comparator, and its adjustable feature should suit this circuit.. 🔗 External reference
A low voltage reference circuit is designed to deliver a stable and precise voltage output that remains unaffected by variations in power supply and temperature. This type of circuit is crucial in applications where accurate voltage levels are required for biasing transistors, setting reference points for comparators, or providing a stable voltage source for analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
The typical architecture of a low voltage reference circuit includes a voltage reference diode or bandgap reference, which ensures a stable output voltage. The circuit may also incorporate a series of resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the output. An adjustable feature can be achieved by including a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the feedback loop, allowing the user to fine-tune the output voltage according to specific requirements.
For implementation, the low voltage reference circuit can be powered by a stable supply voltage, and the output can be connected to various components that require a reference voltage. The design should take into consideration the load current and the desired output voltage range to ensure optimal performance.
In summary, a low voltage reference circuit is a critical component in many electronic systems, providing reliable voltage levels for biasing and reference purposes, with adjustable features to meet specific circuit needs.Low voltage reference is important to provide offset source or biasing, or just a reference for comparator, and its adjustable feature should suit this circuit.. 🔗 External reference