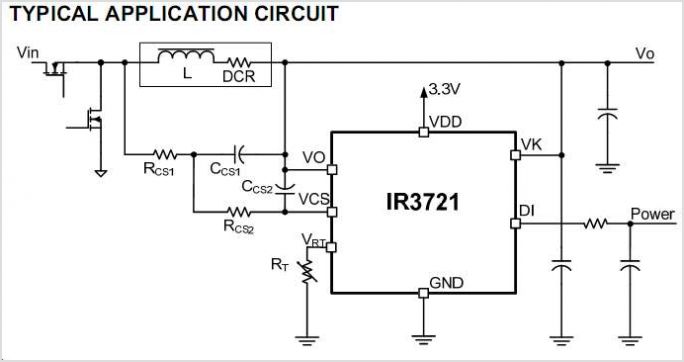
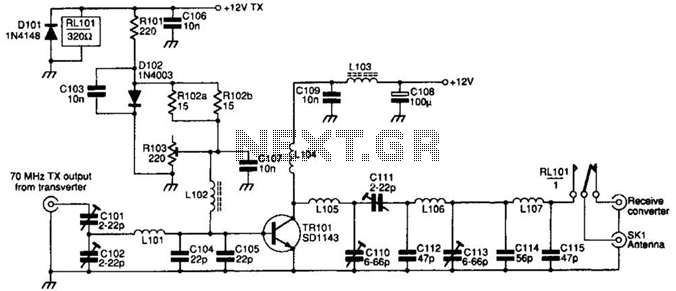
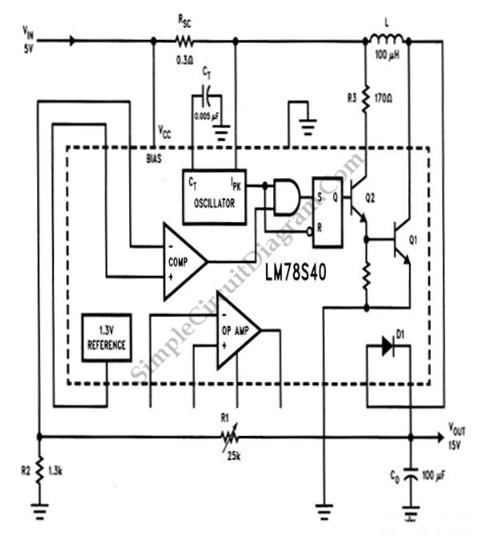
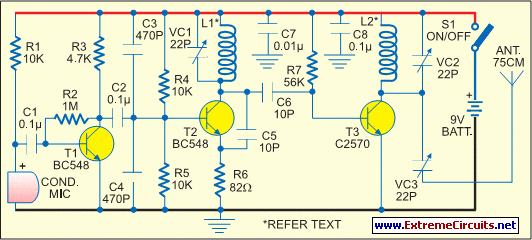
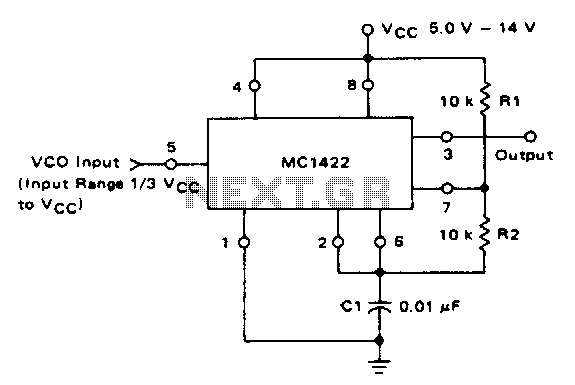
Low Voltage Power Supply Without Transformer
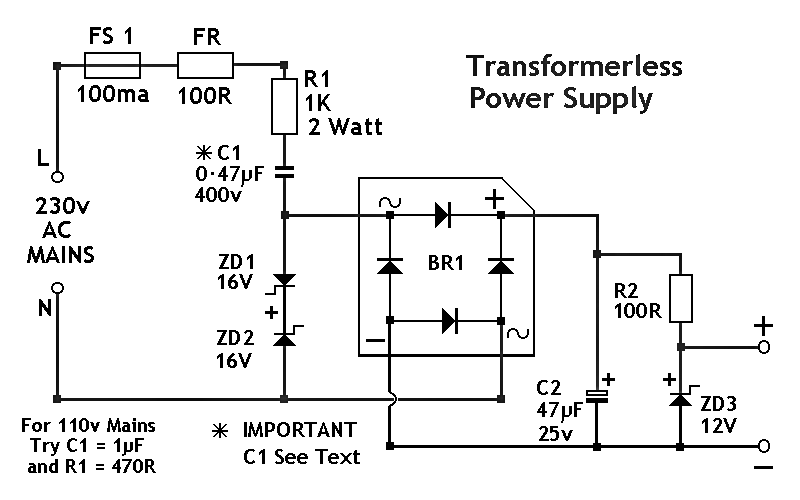
The circuit diagram was designed to create a power supply without utilizing any transformer circuit. This circuit illustrates the advantages as well as the limitations of transformerless power supplies.
The transformerless power supply circuit typically employs a capacitive dropper method or a resistive dropper method to convert AC mains voltage to a lower DC voltage suitable for powering low-power electronic devices. The absence of a transformer reduces the overall size and cost of the circuit, making it an attractive option for compact applications.
In a capacitive dropper circuit, a non-polarized capacitor is placed in series with the AC supply. This capacitor limits the current flowing into the load, allowing for a reduced voltage across the output. The output is then rectified using a diode and smoothed with a capacitor to provide a stable DC voltage. It is essential to select the capacitor value carefully to ensure that the output current remains within safe limits for the intended application.
Alternatively, a resistive dropper circuit uses a resistor in series with the load to limit the current. While this method is simpler, it is less efficient than the capacitive method, as it dissipates power as heat. The output voltage is again rectified and filtered to provide the desired DC output.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Transformerless power supplies are lightweight and cost-effective but may lack the isolation provided by traditional transformer-based power supplies. They also pose safety risks, as the output is directly connected to the mains voltage, necessitating careful design to ensure user safety.
In summary, transformerless power supply circuits are suitable for low-power applications where size and cost are critical factors, but they require careful consideration of safety and performance parameters.The circuit diagram was designed to create a power supply without utilizing any transformer circuit. This circuit illustrates the advantages as well as th.. 🔗 External reference
The transformerless power supply circuit typically employs a capacitive dropper method or a resistive dropper method to convert AC mains voltage to a lower DC voltage suitable for powering low-power electronic devices. The absence of a transformer reduces the overall size and cost of the circuit, making it an attractive option for compact applications.
In a capacitive dropper circuit, a non-polarized capacitor is placed in series with the AC supply. This capacitor limits the current flowing into the load, allowing for a reduced voltage across the output. The output is then rectified using a diode and smoothed with a capacitor to provide a stable DC voltage. It is essential to select the capacitor value carefully to ensure that the output current remains within safe limits for the intended application.
Alternatively, a resistive dropper circuit uses a resistor in series with the load to limit the current. While this method is simpler, it is less efficient than the capacitive method, as it dissipates power as heat. The output voltage is again rectified and filtered to provide the desired DC output.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages. Transformerless power supplies are lightweight and cost-effective but may lack the isolation provided by traditional transformer-based power supplies. They also pose safety risks, as the output is directly connected to the mains voltage, necessitating careful design to ensure user safety.
In summary, transformerless power supply circuits are suitable for low-power applications where size and cost are critical factors, but they require careful consideration of safety and performance parameters.The circuit diagram was designed to create a power supply without utilizing any transformer circuit. This circuit illustrates the advantages as well as th.. 🔗 External reference