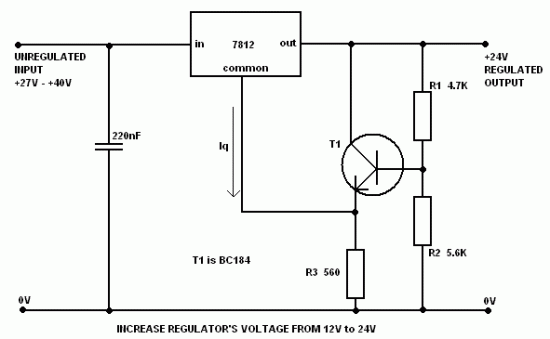
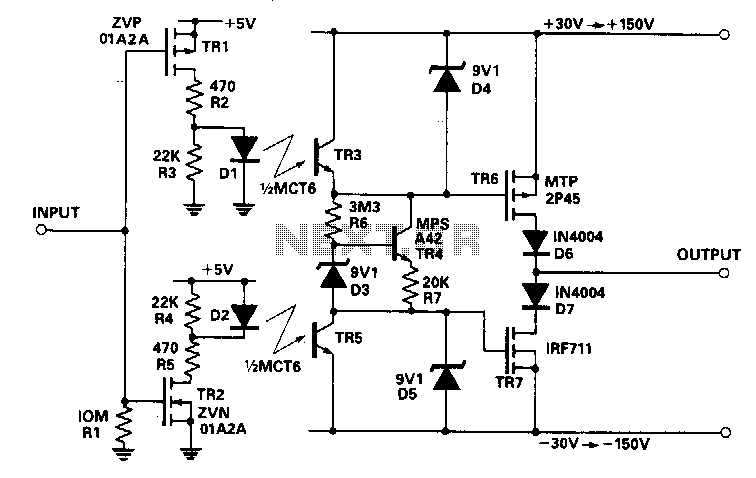
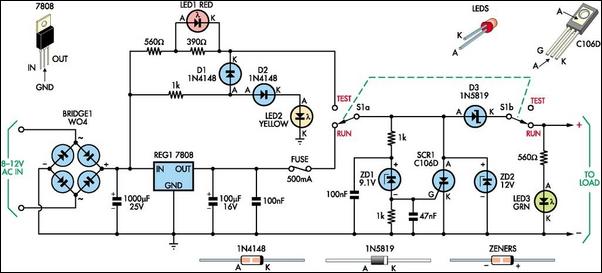
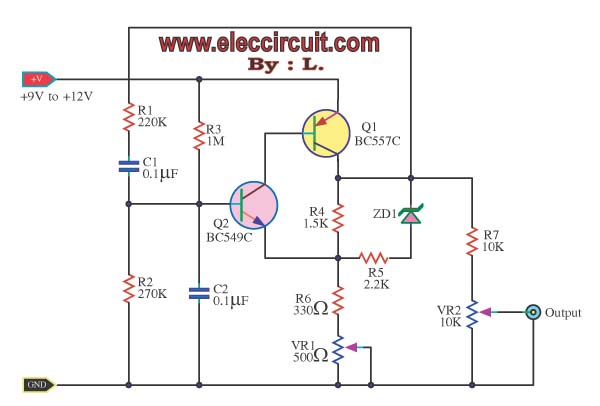
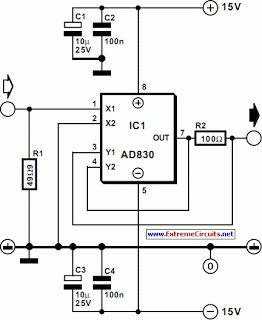
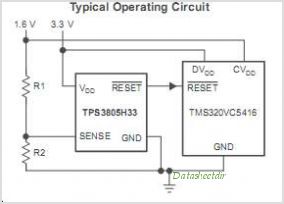
Voltage controlled oscillator
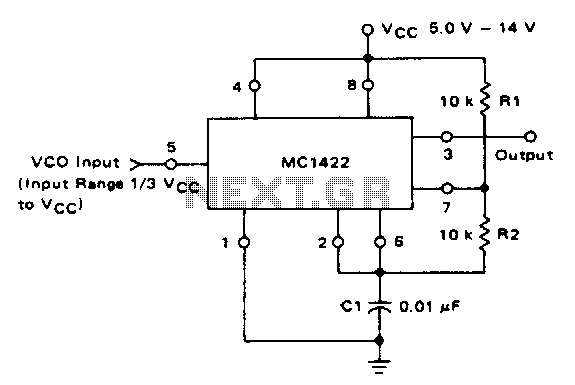
The VCO circuit, which has a nonlinear transfer characteristic, will operate satisfactorily up to 200 kHz. The VCO input range is effective from V% Vcc to Vcc - 2 V, with the highest control voltage producing the lowest output frequency.
The Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates within a frequency range of up to 200 kHz, characterized by its nonlinear transfer function. This nonlinearity can be advantageous in applications where precise frequency modulation is required, as it allows for a broader range of frequency outputs for varying input control voltages.
The input voltage range for the VCO is specified from a percentage of the supply voltage (Vcc) to (Vcc - 2 V). This means that the VCO is designed to accept control voltages that start at a certain percentage of the maximum supply voltage and extend to two volts less than the maximum supply voltage. The relationship between the control voltage and the output frequency is inversely proportional; as the control voltage increases towards Vcc, the output frequency decreases, reaching its minimum output frequency at the highest control voltage level.
In practical applications, this VCO can be utilized in various signal processing tasks, including frequency synthesis, modulation, and demodulation processes. The nonlinear characteristics can be leveraged in designing circuits that require specific frequency responses or in generating complex waveforms. The design considerations for such a VCO may include the selection of appropriate components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers, ensuring that they can handle the specified frequency range and input voltage levels effectively.
For optimal performance, the circuit layout should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the stability and accuracy of the oscillation. The choice of components should also consider thermal stability and power supply decoupling to maintain consistent operation across varying environmental conditions.The VCO circuit, which has a nonlinear transfer characteristic, will operate satisfactorily up to 200 kHz The VCO input range is effective from V% Vcc to Vcc - 2 V, with the highest control voltage producing the lowest output frequency.
The Voltage-Controlled Oscillator (VCO) circuit described operates within a frequency range of up to 200 kHz, characterized by its nonlinear transfer function. This nonlinearity can be advantageous in applications where precise frequency modulation is required, as it allows for a broader range of frequency outputs for varying input control voltages.
The input voltage range for the VCO is specified from a percentage of the supply voltage (Vcc) to (Vcc - 2 V). This means that the VCO is designed to accept control voltages that start at a certain percentage of the maximum supply voltage and extend to two volts less than the maximum supply voltage. The relationship between the control voltage and the output frequency is inversely proportional; as the control voltage increases towards Vcc, the output frequency decreases, reaching its minimum output frequency at the highest control voltage level.
In practical applications, this VCO can be utilized in various signal processing tasks, including frequency synthesis, modulation, and demodulation processes. The nonlinear characteristics can be leveraged in designing circuits that require specific frequency responses or in generating complex waveforms. The design considerations for such a VCO may include the selection of appropriate components such as resistors, capacitors, and operational amplifiers, ensuring that they can handle the specified frequency range and input voltage levels effectively.
For optimal performance, the circuit layout should minimize parasitic capacitance and inductance, which can affect the stability and accuracy of the oscillation. The choice of components should also consider thermal stability and power supply decoupling to maintain consistent operation across varying environmental conditions.The VCO circuit, which has a nonlinear transfer characteristic, will operate satisfactorily up to 200 kHz The VCO input range is effective from V% Vcc to Vcc - 2 V, with the highest control voltage producing the lowest output frequency.