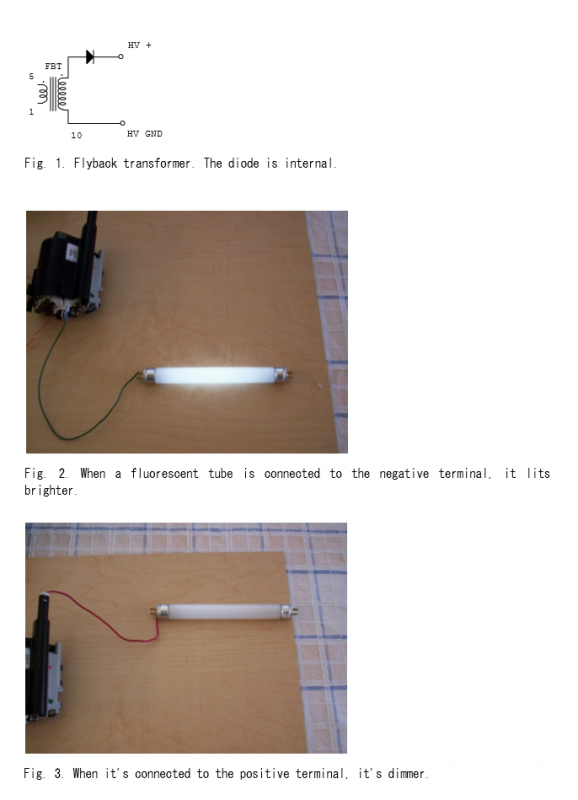
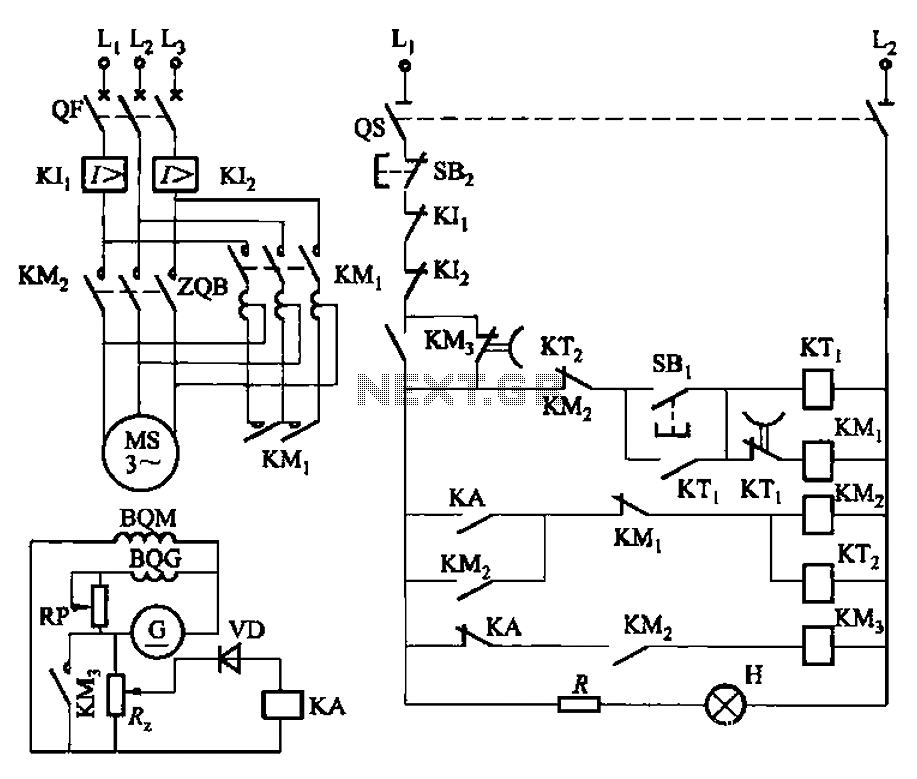
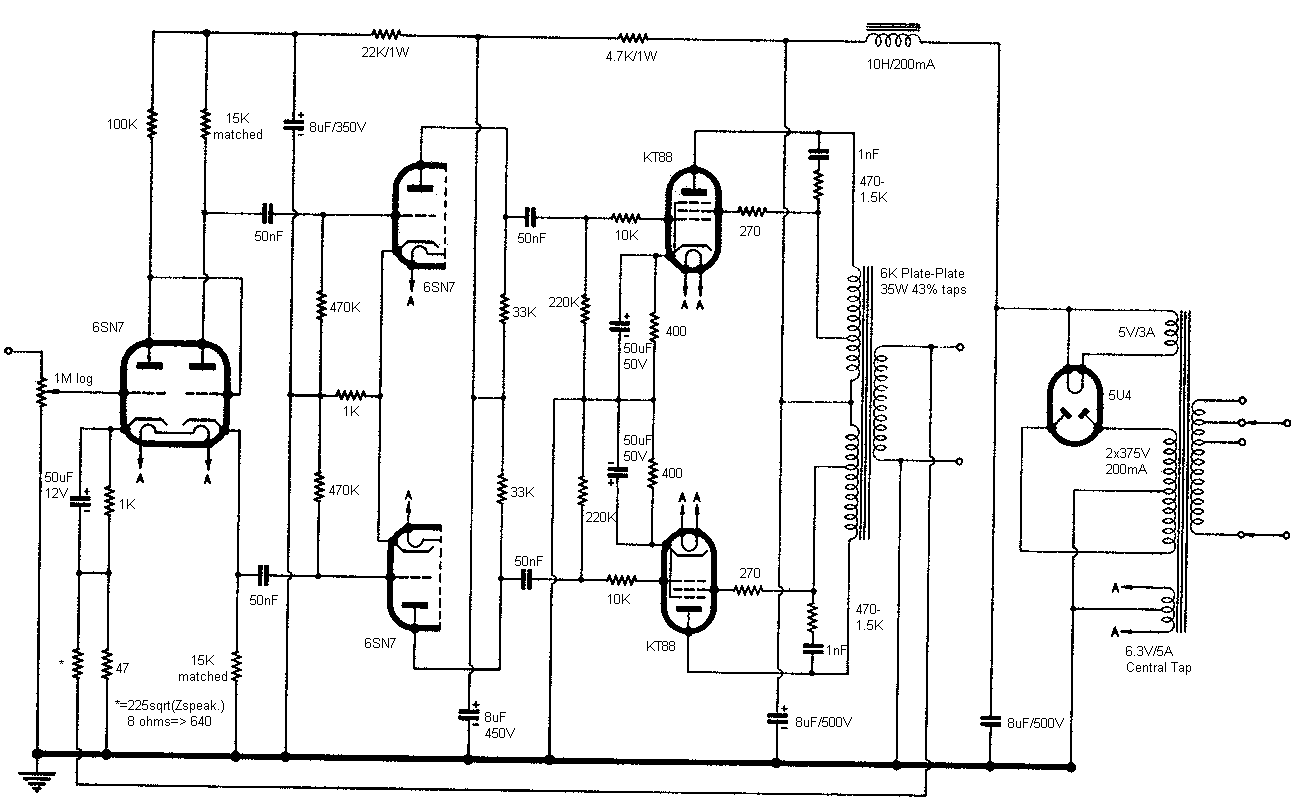
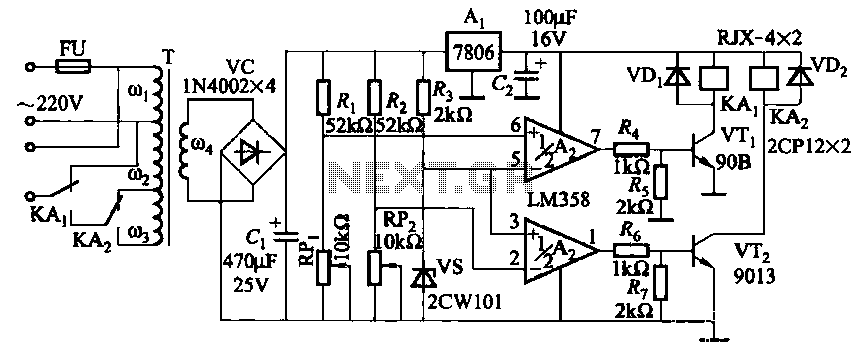
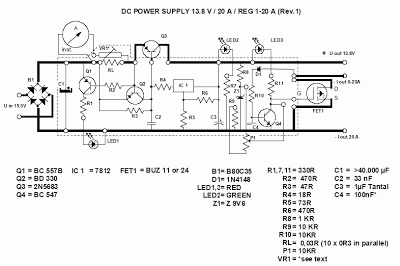
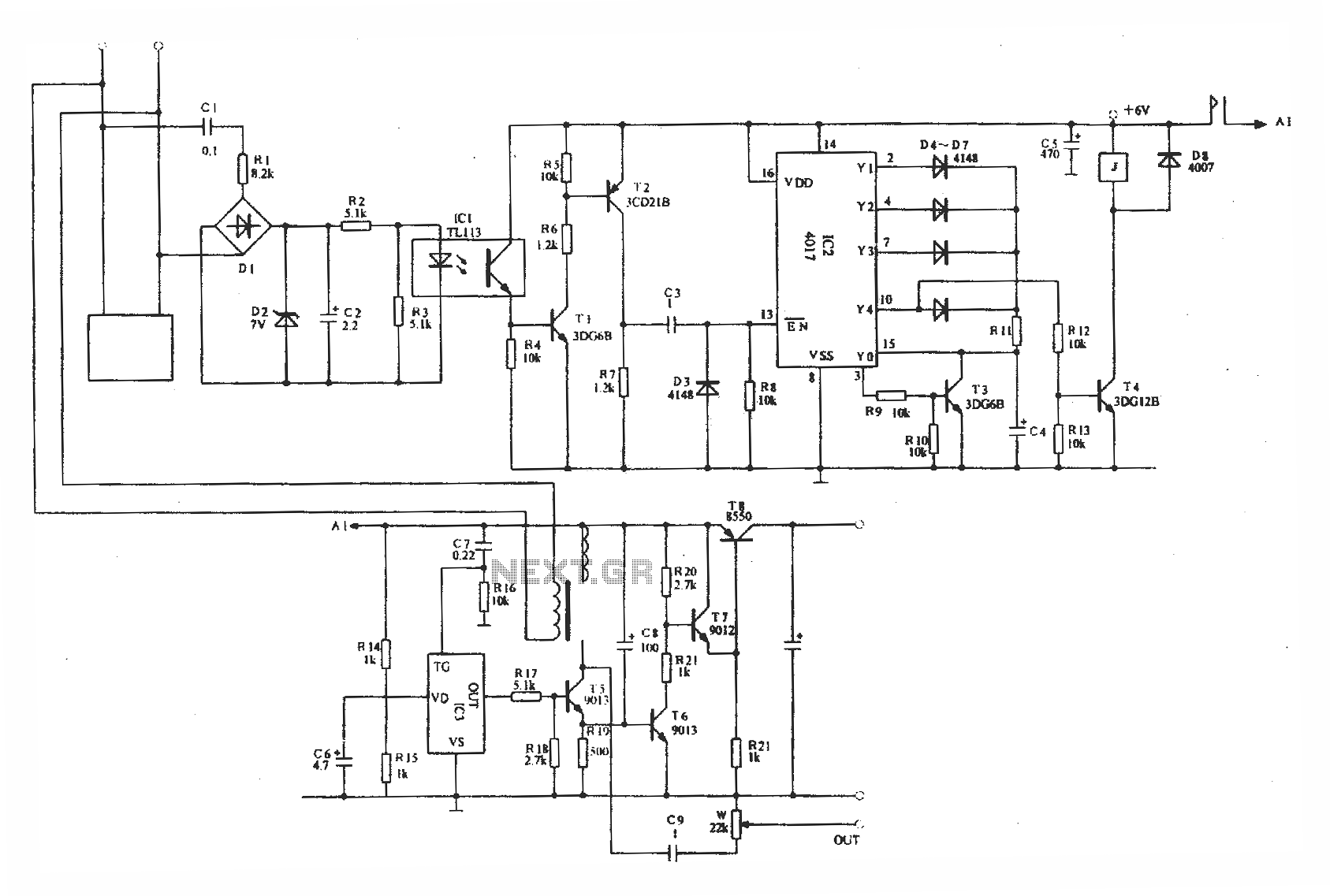
making isolation transformer
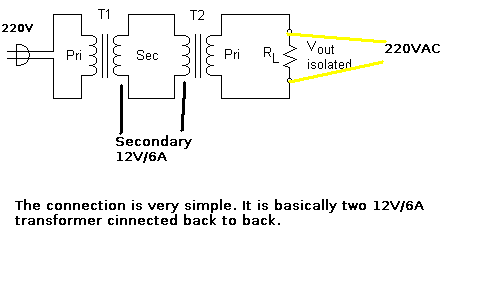
An isolation transformer is a transformer used to transfer electrical power from a source of alternating current (AC) to equipment while isolating the powered device from the power source.
An isolation transformer serves several critical functions in electrical systems. Primarily, it provides galvanic isolation between the input and output, which enhances safety by preventing direct electrical contact between the power source and the connected equipment. This isolation helps to protect sensitive devices from voltage spikes, surges, and other disturbances present in the power supply.
The construction of an isolation transformer typically involves two sets of windings: the primary winding, which connects to the AC power source, and the secondary winding, which supplies power to the load. These windings are magnetically coupled through a core, often made of laminated silicon steel, which minimizes energy losses due to eddy currents. The absence of a direct electrical connection between the input and output helps reduce the risk of electric shock and allows for the safe operation of equipment in environments where grounding may be unreliable.
Isolation transformers are commonly used in various applications, including medical equipment, laboratory instruments, and audio systems, where noise reduction and equipment protection are paramount. They can also be utilized to step up or step down voltage levels, depending on the winding ratios, thus providing versatility in power distribution.
In summary, an isolation transformer is an essential component in electrical systems, ensuring safety, protecting sensitive devices, and enhancing overall system performance through effective isolation and voltage management.An isolation transformer is a transformer used to transfer electrical power from a source of (AC) power to some equipment while isolating the powered device from the power source,.. 🔗 External reference
An isolation transformer serves several critical functions in electrical systems. Primarily, it provides galvanic isolation between the input and output, which enhances safety by preventing direct electrical contact between the power source and the connected equipment. This isolation helps to protect sensitive devices from voltage spikes, surges, and other disturbances present in the power supply.
The construction of an isolation transformer typically involves two sets of windings: the primary winding, which connects to the AC power source, and the secondary winding, which supplies power to the load. These windings are magnetically coupled through a core, often made of laminated silicon steel, which minimizes energy losses due to eddy currents. The absence of a direct electrical connection between the input and output helps reduce the risk of electric shock and allows for the safe operation of equipment in environments where grounding may be unreliable.
Isolation transformers are commonly used in various applications, including medical equipment, laboratory instruments, and audio systems, where noise reduction and equipment protection are paramount. They can also be utilized to step up or step down voltage levels, depending on the winding ratios, thus providing versatility in power distribution.
In summary, an isolation transformer is an essential component in electrical systems, ensuring safety, protecting sensitive devices, and enhancing overall system performance through effective isolation and voltage management.An isolation transformer is a transformer used to transfer electrical power from a source of (AC) power to some equipment while isolating the powered device from the power source,.. 🔗 External reference