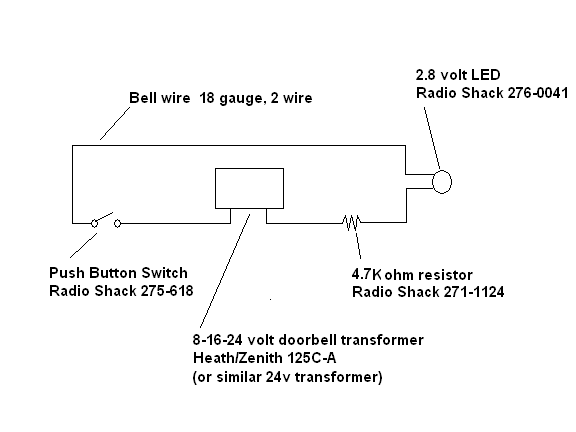
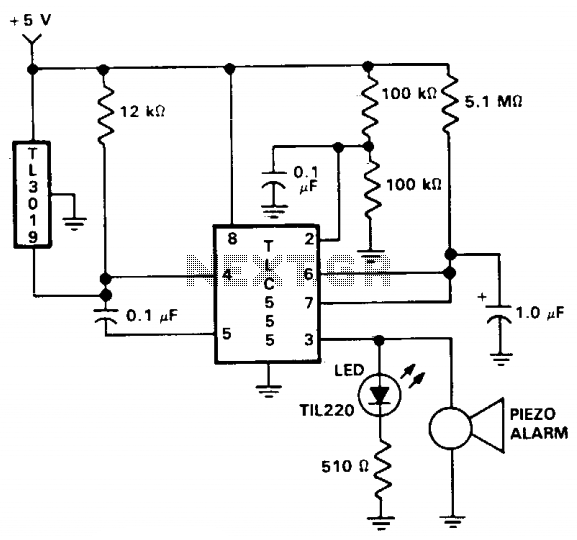
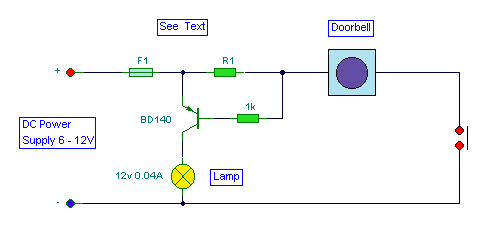
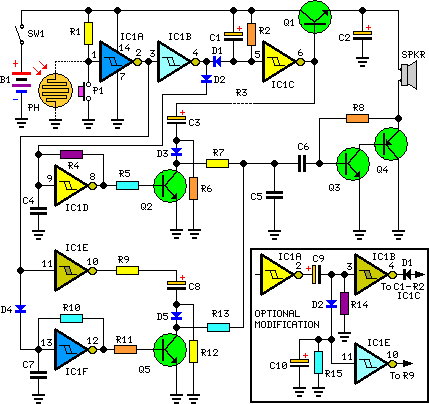
Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell
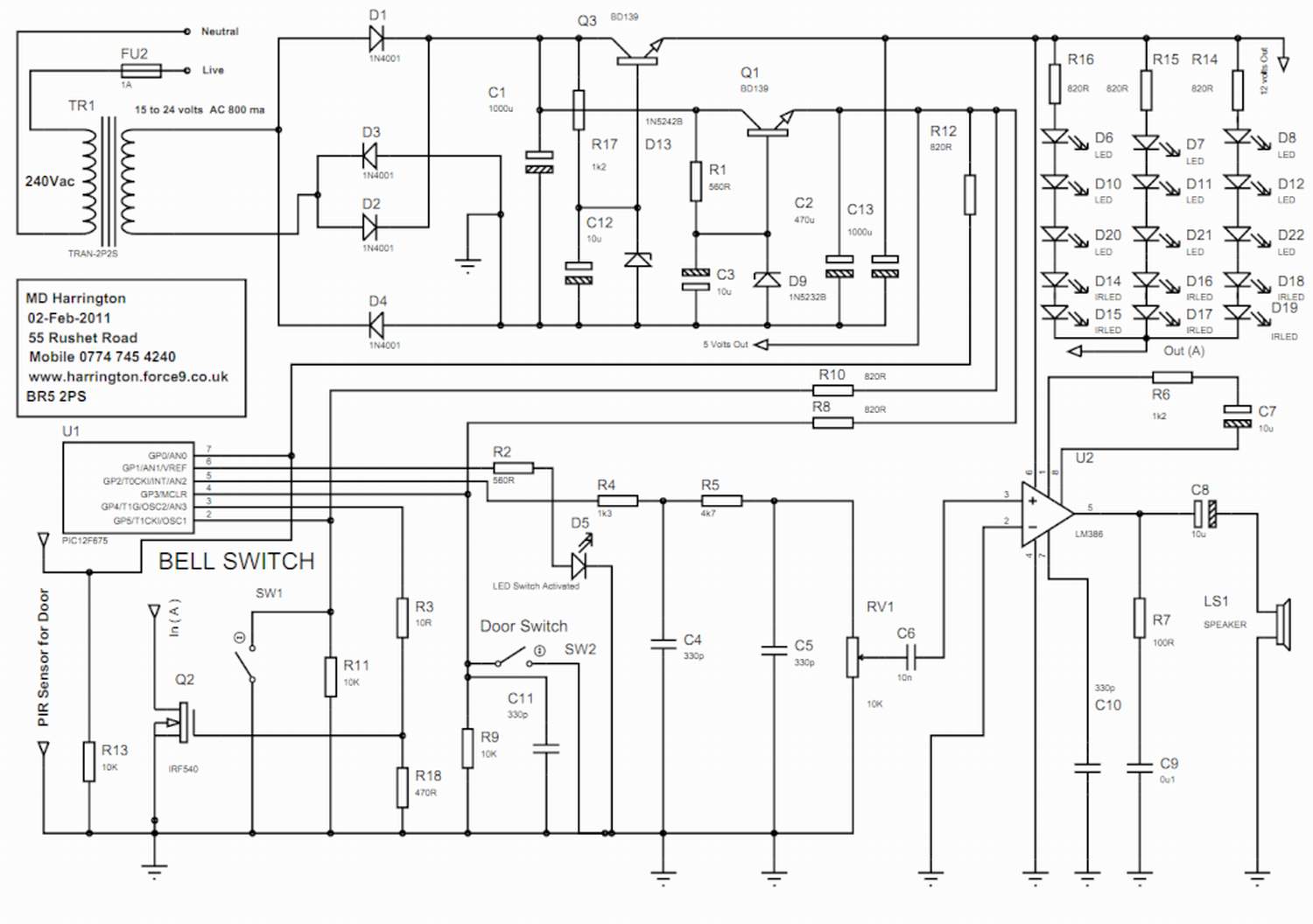
The Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell circuit includes a power supply, which is constructed using components such as TR1, Q3, D13, Q1, and D9.
The Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell circuit is designed to provide multiple functionalities in a single device, integrating a power supply and various operational components. The power supply section is crucial for ensuring that the entire circuit operates reliably and efficiently.
TR1 refers to a transformer that steps down the voltage from the mains supply to a lower level suitable for the doorbell circuit. This transformer is typically chosen based on the required output voltage and current ratings to ensure it can handle the load without overheating.
Q3 is likely a transistor that functions as a switch or amplifier within the circuit. Its role may involve controlling the flow of current to other components, such as the chime or LED indicators, depending on the doorbell's state (e.g., pressed or idle).
D13 and D9 are diodes that serve to rectify the AC voltage output from the transformer into a DC voltage, ensuring that the circuit receives a stable and usable power supply. The choice of diodes is critical, as they must be rated for the appropriate current and voltage levels to prevent failure.
Q1 could be another transistor or a part of a relay circuit that activates the doorbell chime or other features when the button is pressed. This component may also include additional elements, such as resistors or capacitors, to filter noise and stabilize the operation.
In summary, the Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell circuit is a carefully designed system that integrates a power supply and control components to deliver a reliable doorbell solution with multiple functionalities. Each component plays a specific role in the overall operation, contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of the device.Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell. The circuit comprises the power supply which is formed by TR1, Q3 , D13 , Q1 , D9.. 🔗 External reference
The Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell circuit is designed to provide multiple functionalities in a single device, integrating a power supply and various operational components. The power supply section is crucial for ensuring that the entire circuit operates reliably and efficiently.
TR1 refers to a transformer that steps down the voltage from the mains supply to a lower level suitable for the doorbell circuit. This transformer is typically chosen based on the required output voltage and current ratings to ensure it can handle the load without overheating.
Q3 is likely a transistor that functions as a switch or amplifier within the circuit. Its role may involve controlling the flow of current to other components, such as the chime or LED indicators, depending on the doorbell's state (e.g., pressed or idle).
D13 and D9 are diodes that serve to rectify the AC voltage output from the transformer into a DC voltage, ensuring that the circuit receives a stable and usable power supply. The choice of diodes is critical, as they must be rated for the appropriate current and voltage levels to prevent failure.
Q1 could be another transistor or a part of a relay circuit that activates the doorbell chime or other features when the button is pressed. This component may also include additional elements, such as resistors or capacitors, to filter noise and stabilize the operation.
In summary, the Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell circuit is a carefully designed system that integrates a power supply and control components to deliver a reliable doorbell solution with multiple functionalities. Each component plays a specific role in the overall operation, contributing to the efficiency and effectiveness of the device.Mark Harrington 3 in 1 Door Bell. The circuit comprises the power supply which is formed by TR1, Q3 , D13 , Q1 , D9.. 🔗 External reference