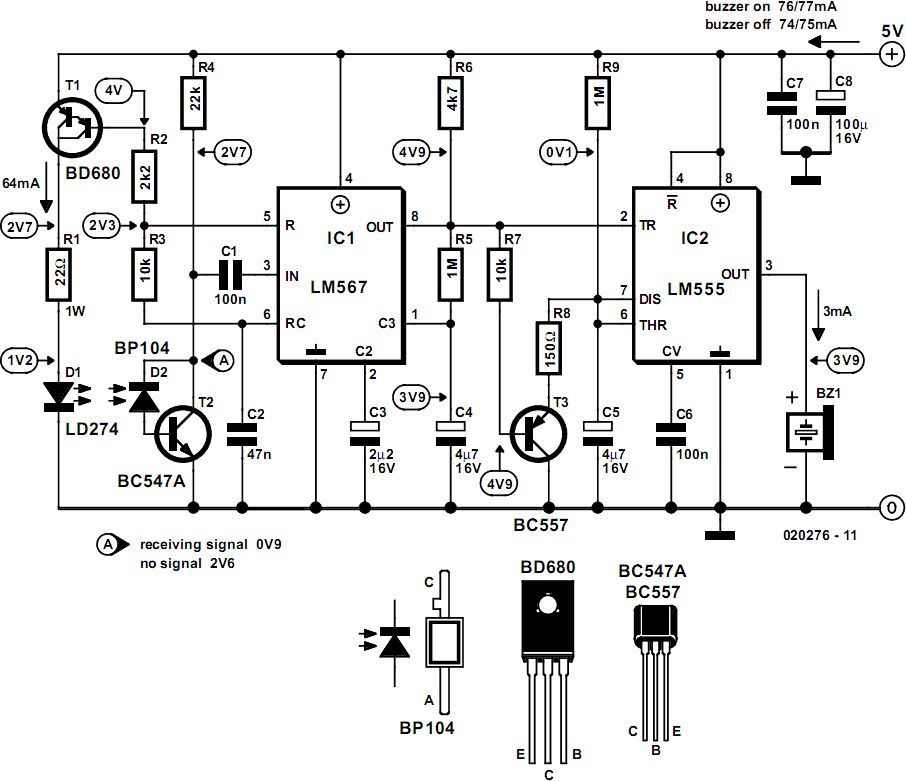
Metal Detector DIY
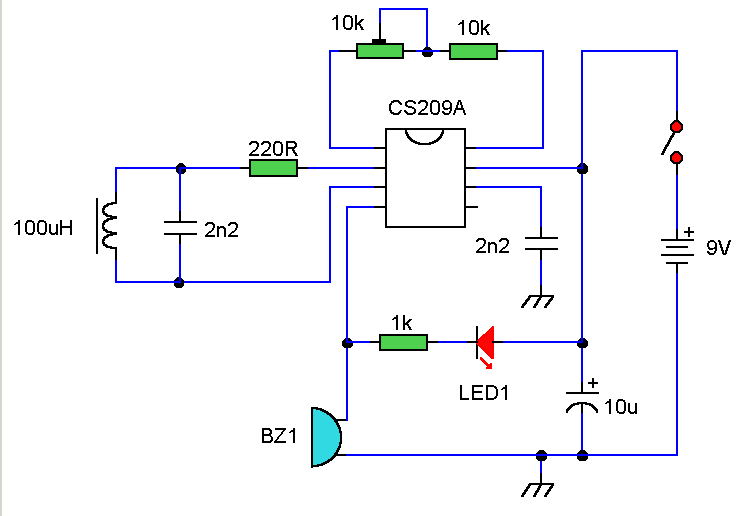
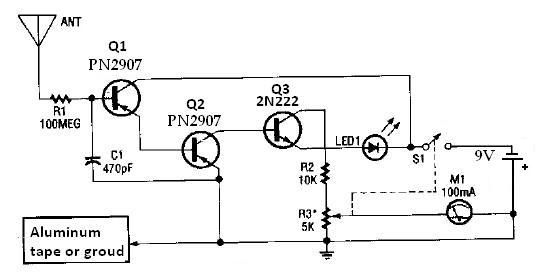
The core component of this DIY metal detector circuit is the CS209A. The metal detector is constructed using a single 100 µH coil. The CS209A features an oscillator that creates an LC circuit; the inductance of the coil alters when it is in proximity to metal objects. LED 1 illuminates and the buzzer activates when there is a change in the coil's inductance. The assembly process is straightforward, involving the adjustment of VR1 (initially positioned away from any metal objects) until LED 1 lights up and the buzzer sounds, followed by fine-tuning VR1 until both the LED and buzzer deactivate.
The CS209A metal detector circuit operates on the principle of inductance variation in response to nearby metallic objects. The oscillator within the CS209A generates an alternating current that flows through the 100 µH coil, forming an LC circuit. This circuit is sensitive to changes in inductance caused by the presence of metal, which alters the oscillation frequency.
When metal is detected, the change in inductance triggers the LED and buzzer. The LED serves as a visual indicator, while the buzzer provides an audible alert, enhancing the user experience. The variable resistor, VR1, plays a critical role in calibrating the circuit. Initially, VR1 is adjusted to a position where the circuit is inactive (away from any metal). As the user brings the coil closer to metal objects, the inductance change causes the LED to illuminate and the buzzer to sound, indicating detection.
Fine-tuning VR1 allows for sensitivity adjustments, ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to metal detection without false positives from environmental noise or other non-metallic influences. This feature is particularly important in practical applications, where the ability to discern between different types of interference can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the metal detector.
Overall, the design of this DIY metal detector circuit is efficient and user-friendly, making it suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and operation, while the functionality provided by the CS209A ensures reliable performance in detecting metallic objects.The heart of this DIY metal detector circuit is CS209A. The metal detector is build with one 100 µH coil. CS209A has one oscillator which forms a LC circuit, the inductance of the coil will change when it is near metal objects. LED 1 will light and the buzzer turns on when the coil is changing inductance. The setup is easy, VR1 is adjusted (away f rom any metal objects) so that LED 1 will light and the buzzer sounds on, and then VR1 will be trimmed until led and buzzer are off. 🔗 External reference
The CS209A metal detector circuit operates on the principle of inductance variation in response to nearby metallic objects. The oscillator within the CS209A generates an alternating current that flows through the 100 µH coil, forming an LC circuit. This circuit is sensitive to changes in inductance caused by the presence of metal, which alters the oscillation frequency.
When metal is detected, the change in inductance triggers the LED and buzzer. The LED serves as a visual indicator, while the buzzer provides an audible alert, enhancing the user experience. The variable resistor, VR1, plays a critical role in calibrating the circuit. Initially, VR1 is adjusted to a position where the circuit is inactive (away from any metal). As the user brings the coil closer to metal objects, the inductance change causes the LED to illuminate and the buzzer to sound, indicating detection.
Fine-tuning VR1 allows for sensitivity adjustments, ensuring that the circuit remains responsive to metal detection without false positives from environmental noise or other non-metallic influences. This feature is particularly important in practical applications, where the ability to discern between different types of interference can significantly enhance the effectiveness of the metal detector.
Overall, the design of this DIY metal detector circuit is efficient and user-friendly, making it suitable for hobbyists and professionals alike. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy assembly and operation, while the functionality provided by the CS209A ensures reliable performance in detecting metallic objects.The heart of this DIY metal detector circuit is CS209A. The metal detector is build with one 100 µH coil. CS209A has one oscillator which forms a LC circuit, the inductance of the coil will change when it is near metal objects. LED 1 will light and the buzzer turns on when the coil is changing inductance. The setup is easy, VR1 is adjusted (away f rom any metal objects) so that LED 1 will light and the buzzer sounds on, and then VR1 will be trimmed until led and buzzer are off. 🔗 External reference