MIDI Tester Schematic diagram
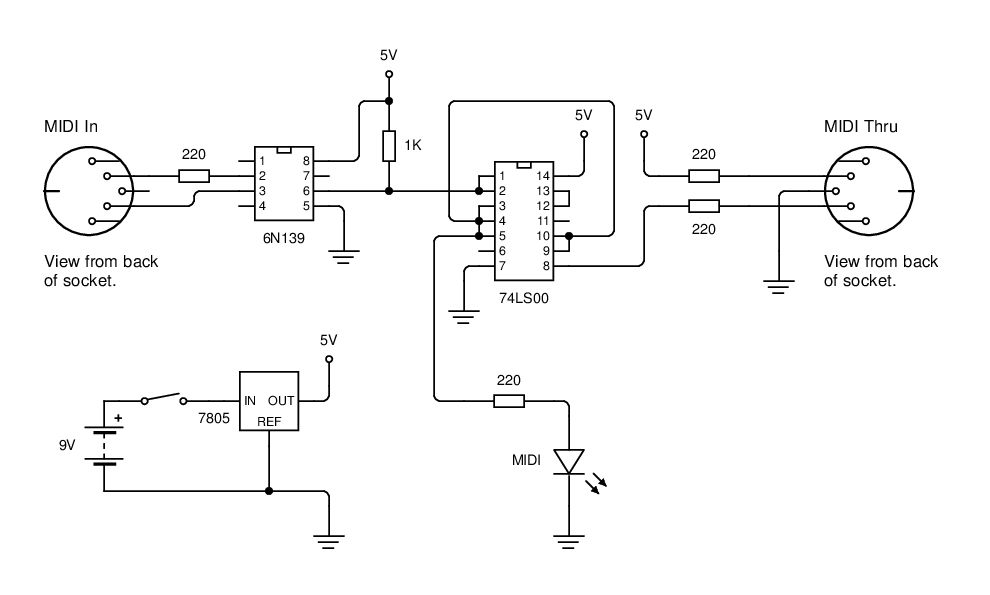
MIDI data is transmitted between instruments using a current loop, and an opto-isolator (6N139) is employed to convert this current loop into TTL pulses.
The circuit utilizes the 6N139 opto-isolator to separate the MIDI signal from the receiving device, ensuring that any electrical noise or ground loops do not affect the performance of the MIDI system. The opto-isolator consists of an LED and a phototransistor, which are optically coupled but electrically isolated from each other.
In this configuration, the MIDI signal is applied to the LED side of the 6N139. When the current loop is activated by the MIDI signal, the LED emits light, which is detected by the phototransistor on the output side. This results in a corresponding TTL pulse, which can be used by digital devices for further processing.
The circuit design should include appropriate resistors to limit the current through the LED to a safe level, typically around 10-20 mA, ensuring reliable operation of the opto-isolator. The output from the phototransistor can be connected to the input of a microcontroller or any other digital logic device that requires TTL level signals.
By implementing this approach, the integrity of the MIDI data transmission is maintained while providing electrical isolation, which is critical for preventing interference and protecting sensitive components in the MIDI system.As MIDI data is transmitted between instruments using a current loop, a opto-isolator (6N139) is used to convert this current loop into TTL pulses. Th.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the 6N139 opto-isolator to separate the MIDI signal from the receiving device, ensuring that any electrical noise or ground loops do not affect the performance of the MIDI system. The opto-isolator consists of an LED and a phototransistor, which are optically coupled but electrically isolated from each other.
In this configuration, the MIDI signal is applied to the LED side of the 6N139. When the current loop is activated by the MIDI signal, the LED emits light, which is detected by the phototransistor on the output side. This results in a corresponding TTL pulse, which can be used by digital devices for further processing.
The circuit design should include appropriate resistors to limit the current through the LED to a safe level, typically around 10-20 mA, ensuring reliable operation of the opto-isolator. The output from the phototransistor can be connected to the input of a microcontroller or any other digital logic device that requires TTL level signals.
By implementing this approach, the integrity of the MIDI data transmission is maintained while providing electrical isolation, which is critical for preventing interference and protecting sensitive components in the MIDI system.As MIDI data is transmitted between instruments using a current loop, a opto-isolator (6N139) is used to convert this current loop into TTL pulses. Th.. 🔗 External reference