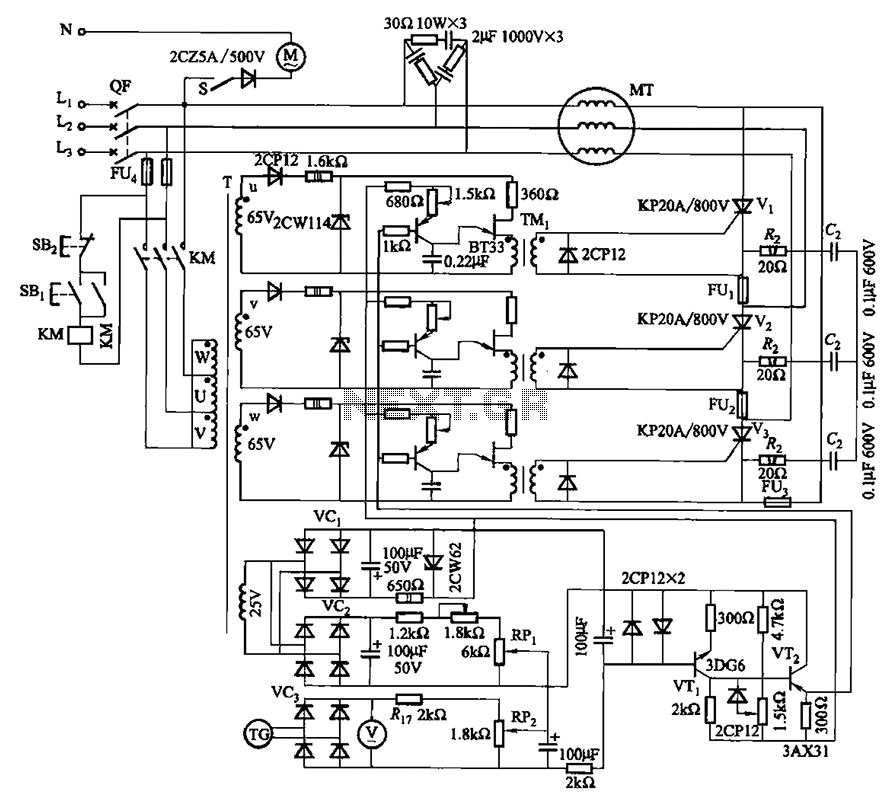
mini drill speed regulator
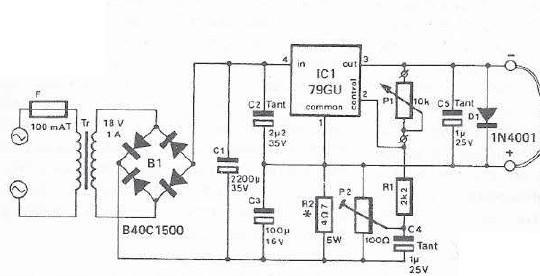
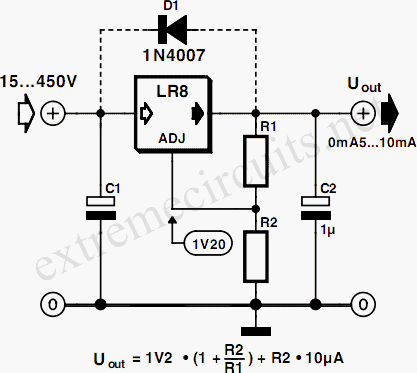
An integrated voltage regulator connected in reverse to a mini drill allows for speed adjustment within specific limits, maintaining a constant speed regardless of load. The electronic speed control is achieved through a voltage regulator, which can power motors requiring a supply voltage between 2.5 V and 12 V, with a maximum current draw of 1 A. The output voltage is determined by the ratio of resistances R1 and R2, given by the formula Uout = (R1 + R2) Uc/R2, where Uc is -2.23 V for the 79GU voltage regulator. The P2 potentiometer adjusts the degree of coupling, increasing the output voltage with rising output current, thus maintaining a constant preset speed. The maximum voltage measured when the P2 is fully turned up should be approximately 20% lower than the motor's maximum allowable voltage. If this is not the case, the value of R1 should be adjusted accordingly. The voltage regulator includes thermal protection but must be mounted on a suitably sized heatsink.
The described circuit utilizes an integrated voltage regulator to control the speed of a mini drill motor effectively. The configuration allows for a variable output voltage that can be tailored to the specific requirements of different motors within the defined voltage range. The critical components include the voltage regulator (79GU), resistors R1 and R2, and the potentiometer P2.
In this setup, R1 and R2 form a voltage divider that sets the output voltage. The formula Uout = (R1 + R2) Uc/R2 indicates how the output voltage is influenced by the resistance values. Adjusting R1 or R2 will change the output voltage accordingly. The potentiometer P2 acts as a variable resistor, allowing for fine-tuning of the coupling degree, which directly affects the output voltage and consequently the motor speed.
Thermal management is essential in this circuit. The voltage regulator is equipped with thermal protection to prevent overheating, which is critical when operating at higher currents. Proper sizing of the heatsink is necessary to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
Overall, this circuit provides a versatile solution for controlling the speed of mini drill motors, accommodating various operational demands while ensuring consistent performance and safety through thermal management.With an integrated voltage regulator connected reverse to a mini drill can be adjusted speed within certain limits so that it remain constant, independently of load. In the scheme presented below the electronic speed control is made by a voltage regulator, allowing use of motor which require a supply voltage from 2.
5 V to 12 V at a maximum current absorbed by an 1A. Output voltage is determined by the ratio of resistances R1 and R2. Uout = (R1 + R2) Uc/R2. Uc is equal to -2. 23 V for 79GU voltage regulator. With the P2 potentiometer can be adjusted the degree of coupling (coupling the output voltage increases with increasing output current). Thus remains constant preset speed. Maximum voltage measured when the P2 is turned up must be about 20% lower than the maximum allowable voltage of the motor (if is not, the value of R1 should be reduced or enlarged accordingly).
Voltage regulator is designed with thermal protection, but it must be mounted on a properly dimensioned radiator. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes an integrated voltage regulator to control the speed of a mini drill motor effectively. The configuration allows for a variable output voltage that can be tailored to the specific requirements of different motors within the defined voltage range. The critical components include the voltage regulator (79GU), resistors R1 and R2, and the potentiometer P2.
In this setup, R1 and R2 form a voltage divider that sets the output voltage. The formula Uout = (R1 + R2) Uc/R2 indicates how the output voltage is influenced by the resistance values. Adjusting R1 or R2 will change the output voltage accordingly. The potentiometer P2 acts as a variable resistor, allowing for fine-tuning of the coupling degree, which directly affects the output voltage and consequently the motor speed.
Thermal management is essential in this circuit. The voltage regulator is equipped with thermal protection to prevent overheating, which is critical when operating at higher currents. Proper sizing of the heatsink is necessary to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
Overall, this circuit provides a versatile solution for controlling the speed of mini drill motors, accommodating various operational demands while ensuring consistent performance and safety through thermal management.With an integrated voltage regulator connected reverse to a mini drill can be adjusted speed within certain limits so that it remain constant, independently of load. In the scheme presented below the electronic speed control is made by a voltage regulator, allowing use of motor which require a supply voltage from 2.
5 V to 12 V at a maximum current absorbed by an 1A. Output voltage is determined by the ratio of resistances R1 and R2. Uout = (R1 + R2) Uc/R2. Uc is equal to -2. 23 V for 79GU voltage regulator. With the P2 potentiometer can be adjusted the degree of coupling (coupling the output voltage increases with increasing output current). Thus remains constant preset speed. Maximum voltage measured when the P2 is turned up must be about 20% lower than the maximum allowable voltage of the motor (if is not, the value of R1 should be reduced or enlarged accordingly).
Voltage regulator is designed with thermal protection, but it must be mounted on a properly dimensioned radiator. 🔗 External reference