Mobile Phone Travel Charger
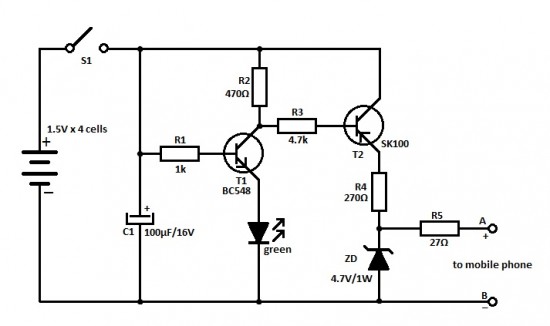
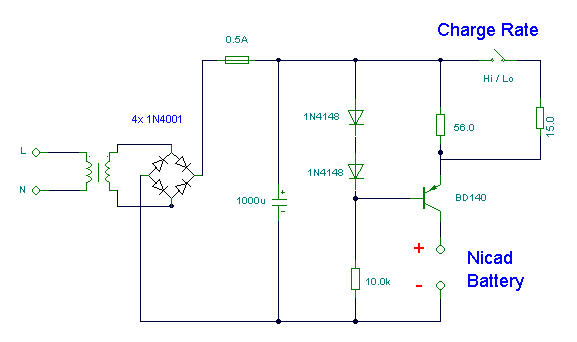
This is an ideal mobile charger that utilizes 1.5-volt pen cells to charge mobile phones while traveling. It can replenish a cell phone battery three or four times.
The mobile charger circuit is designed to be compact and portable, making it suitable for travel. It primarily consists of a battery holder for 1.5-volt pen cells, a voltage regulator, and a charging connector compatible with mobile phones. The circuit can accommodate multiple pen cells connected in series to achieve the necessary voltage output, typically 5 volts, which is required for charging most mobile devices.
The charger begins with the insertion of the pen cells into the holder, ensuring correct polarity to avoid damage to the circuit. The combined output voltage from the cells is then fed into a voltage regulator, such as the LM7805, which stabilizes the output to a consistent 5 volts. This regulator is essential for protecting the mobile phone from voltage fluctuations that could potentially harm its battery.
Additionally, a charging connector, such as a Micro USB or USB-C, is integrated into the design, allowing for easy connection to various mobile phone models. To enhance safety and efficiency, a diode may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which could discharge the pen cells when the charger is not in use.
The performance of this charger allows for multiple recharges of a mobile phone battery, making it a reliable option for users on the go. The simplicity of the circuit also facilitates easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. Overall, this mobile charger provides a practical solution for maintaining device power during travel.Here is an ideal mobile charger using 1.5 volt pen cells to charge mobile phone while traveling. It can replenish cell phone battery three or four times in.. 🔗 External reference
The mobile charger circuit is designed to be compact and portable, making it suitable for travel. It primarily consists of a battery holder for 1.5-volt pen cells, a voltage regulator, and a charging connector compatible with mobile phones. The circuit can accommodate multiple pen cells connected in series to achieve the necessary voltage output, typically 5 volts, which is required for charging most mobile devices.
The charger begins with the insertion of the pen cells into the holder, ensuring correct polarity to avoid damage to the circuit. The combined output voltage from the cells is then fed into a voltage regulator, such as the LM7805, which stabilizes the output to a consistent 5 volts. This regulator is essential for protecting the mobile phone from voltage fluctuations that could potentially harm its battery.
Additionally, a charging connector, such as a Micro USB or USB-C, is integrated into the design, allowing for easy connection to various mobile phone models. To enhance safety and efficiency, a diode may be included in the circuit to prevent reverse current flow, which could discharge the pen cells when the charger is not in use.
The performance of this charger allows for multiple recharges of a mobile phone battery, making it a reliable option for users on the go. The simplicity of the circuit also facilitates easy assembly and troubleshooting, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike. Overall, this mobile charger provides a practical solution for maintaining device power during travel.Here is an ideal mobile charger using 1.5 volt pen cells to charge mobile phone while traveling. It can replenish cell phone battery three or four times in.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
.png)