Module thermometer temperature meter for digital multimeter using the ic lm35
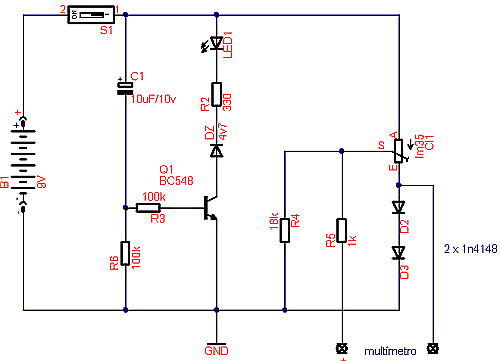
Temperature sensor converter designed for use with a digital multimeter, capable of measuring temperatures from -40 °C to 110 °C. It features a state indicator and requires no calibration, utilizing the LM35 integrated circuit. The freezing point of water is 0 °C, while the boiling point at sea level is 100 °C. These reference points allow for rapid temperature scaling. The term "degrees Celsius" is used instead of "centigrade," which refers to a scale of 100. The circuit requires a 9V battery and negative voltage supply, as specified in the LM35 datasheet, using diodes D2 and D3. Resistor R5 ensures the sensor's output voltage is negative relative to the multimeter's ground for measuring temperatures below 0 °C. Resistor R4 decouples the probe output from the high impedance output of the multimeter. The transistor Q1 controls the power supply and checks the battery status. When switch S1 is pressed, an LED lights up to indicate that the battery voltage is above 7V, which is necessary for proper circuit operation. The LM35 should be encased in a metal tube approximately 5 to 10 cm long, connected to the main circuit via a maximum 1-meter trifler cable. The tube must be sealed at both ends to facilitate liquid measurements. The battery should be housed in a small plastic box, and the circuit board must be insulated from the battery to prevent short circuits and damage from corrosive battery contents. Before measuring temperature, the battery should be tested by pressing S1; if all is well, the unit can be connected to the multimeter to take measurements. Depending on the multimeter settings, the voltage output will range from -4 to 1.1V in the 10V DC scale or from -400 to 1100mV in the 2000mV scale, corresponding to temperatures from -40 to 110 °C. In the first case, the decimal point is ignored, while in the latter, it is placed after the third digit.
The temperature sensor converter circuit employs the LM35 integrated circuit, which is a precision temperature sensor that outputs a voltage linearly proportional to the centigrade temperature. The circuit operates effectively within the specified temperature range, utilizing two critical reference points: the freezing point and boiling point of water, which facilitate accurate temperature scaling.
The design incorporates a 9V battery, providing the necessary power for the circuit's operation. The use of diodes D2 and D3 is essential for establishing a negative voltage supply, which is crucial for measuring temperatures below 0 °C. Resistor R5 plays a vital role in ensuring that the output voltage from the LM35 remains negative concerning the multimeter's ground, enabling accurate readings in the sub-zero temperature range.
Resistor R4 is used to decouple the output of the temperature probe from the high impedance input of the multimeter, ensuring that the readings are not affected by loading effects. The transistor Q1 acts as a power control device, monitoring the battery voltage. When switch S1 is engaged, the LED indicator provides a visual confirmation that the battery voltage exceeds the operational threshold of 7V, ensuring reliability in measurements.
The LM35 sensor is encased in a metal tube, which serves to protect the sensor while allowing it to accurately measure the temperature of liquids. The tube's length, between 5 to 10 cm, is optimal for achieving rapid thermal response, and the cable connecting the sensor to the main circuit is limited to a maximum length of 1 meter to minimize signal degradation.
To ensure safety and functionality, the battery is housed in a small plastic enclosure, with the circuit board insulated to prevent any short circuits or potential damage caused by battery leakage. Before initiating temperature measurements, users are advised to verify the battery status by pressing S1. Once confirmed operational, the unit can be connected to a multimeter, which will display the corresponding voltage output based on the measured temperature.
The multimeter's settings will dictate the displayed voltage range, which correlates directly to the temperature being measured. Understanding the relationship between the voltage output and temperature will enable users to interpret the readings accurately, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the temperature measurement system.Converser of temperature tension. To be used with a digital multimeter with reach from -40 °C to 110 °C. With checker of the state of it laughed and a without any adjustment, thanks to LM35! The ice is founded the 0 °C and the point of ebullition of the water, at sea level it is of 100 °C. Using those two point of reference is gauged the temperatu re scale quickly. When I speak to °C it is degrees Celsius and not centigrade as we can see in some literatures. Centigrade it is a scale of 100. While temperature is going besides 100. Then the correct is to speak degrees Celsius! Good it arrives of blG blG Today thanks to the circuit integrated specialized of National Semiconductor, denominated LM35, we didn`t need of nor a calibration to obtain the correct temperature. For the circuit we needed a battery of 9v and of a tension of negative feeding. Obtained according to the datasheet of LM35 by the Diodes D2 and D3. The resistor R5 allows the tension of exit of the sensor to be negative in relation to mass of the multimeter so that she can measure resistances below 0 °C.
The resistor R4 desaclop the exit of the probe in relation to exit of high impedance of the multimeter. The circuit based on the transistor Q1 serves as device of control of the feeding tension and of proof of the state of the battery.
When closing the key S1, The led will light informing that the tension of the battery is above 7V, that is necessary for the correct operation of the circuit. LM35 should be set up in a metallic tube from about 5 to 10 CM, linked to the main circuit through a cable trifler of at the most 1 m of length.
The tube should be closed tightly on the two sides to allow the measure of liquids. it/you appeases main and the battery should be placed in a box of plastic small. The plate should be isolated of the battery to avoid short circuit and damages caused by the corrosive content of the battery. Before doing a temperature measure it tests the pile pressing S1, everything ok is enough to connect the unit to the multimeter to accomplish the measures.
In agreement with the temperature the multimeter in the scale of Volt DC 10V will indicate a tension from -4 to 1, 1V or in the scale from 2000mV -400 to 1100mV, that depends on the multimeter, that tension corresponds the temperature from -40 to 110 °C. In the first case the decimal point will be despised and in the another it increases a decimal point after the third digit.
With time it becomes used to. 🔗 External reference
The temperature sensor converter circuit employs the LM35 integrated circuit, which is a precision temperature sensor that outputs a voltage linearly proportional to the centigrade temperature. The circuit operates effectively within the specified temperature range, utilizing two critical reference points: the freezing point and boiling point of water, which facilitate accurate temperature scaling.
The design incorporates a 9V battery, providing the necessary power for the circuit's operation. The use of diodes D2 and D3 is essential for establishing a negative voltage supply, which is crucial for measuring temperatures below 0 °C. Resistor R5 plays a vital role in ensuring that the output voltage from the LM35 remains negative concerning the multimeter's ground, enabling accurate readings in the sub-zero temperature range.
Resistor R4 is used to decouple the output of the temperature probe from the high impedance input of the multimeter, ensuring that the readings are not affected by loading effects. The transistor Q1 acts as a power control device, monitoring the battery voltage. When switch S1 is engaged, the LED indicator provides a visual confirmation that the battery voltage exceeds the operational threshold of 7V, ensuring reliability in measurements.
The LM35 sensor is encased in a metal tube, which serves to protect the sensor while allowing it to accurately measure the temperature of liquids. The tube's length, between 5 to 10 cm, is optimal for achieving rapid thermal response, and the cable connecting the sensor to the main circuit is limited to a maximum length of 1 meter to minimize signal degradation.
To ensure safety and functionality, the battery is housed in a small plastic enclosure, with the circuit board insulated to prevent any short circuits or potential damage caused by battery leakage. Before initiating temperature measurements, users are advised to verify the battery status by pressing S1. Once confirmed operational, the unit can be connected to a multimeter, which will display the corresponding voltage output based on the measured temperature.
The multimeter's settings will dictate the displayed voltage range, which correlates directly to the temperature being measured. Understanding the relationship between the voltage output and temperature will enable users to interpret the readings accurately, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the temperature measurement system.Converser of temperature tension. To be used with a digital multimeter with reach from -40 °C to 110 °C. With checker of the state of it laughed and a without any adjustment, thanks to LM35! The ice is founded the 0 °C and the point of ebullition of the water, at sea level it is of 100 °C. Using those two point of reference is gauged the temperatu re scale quickly. When I speak to °C it is degrees Celsius and not centigrade as we can see in some literatures. Centigrade it is a scale of 100. While temperature is going besides 100. Then the correct is to speak degrees Celsius! Good it arrives of blG blG Today thanks to the circuit integrated specialized of National Semiconductor, denominated LM35, we didn`t need of nor a calibration to obtain the correct temperature. For the circuit we needed a battery of 9v and of a tension of negative feeding. Obtained according to the datasheet of LM35 by the Diodes D2 and D3. The resistor R5 allows the tension of exit of the sensor to be negative in relation to mass of the multimeter so that she can measure resistances below 0 °C.
The resistor R4 desaclop the exit of the probe in relation to exit of high impedance of the multimeter. The circuit based on the transistor Q1 serves as device of control of the feeding tension and of proof of the state of the battery.
When closing the key S1, The led will light informing that the tension of the battery is above 7V, that is necessary for the correct operation of the circuit. LM35 should be set up in a metallic tube from about 5 to 10 CM, linked to the main circuit through a cable trifler of at the most 1 m of length.
The tube should be closed tightly on the two sides to allow the measure of liquids. it/you appeases main and the battery should be placed in a box of plastic small. The plate should be isolated of the battery to avoid short circuit and damages caused by the corrosive content of the battery. Before doing a temperature measure it tests the pile pressing S1, everything ok is enough to connect the unit to the multimeter to accomplish the measures.
In agreement with the temperature the multimeter in the scale of Volt DC 10V will indicate a tension from -4 to 1, 1V or in the scale from 2000mV -400 to 1100mV, that depends on the multimeter, that tension corresponds the temperature from -40 to 110 °C. In the first case the decimal point will be despised and in the another it increases a decimal point after the third digit.
With time it becomes used to. 🔗 External reference