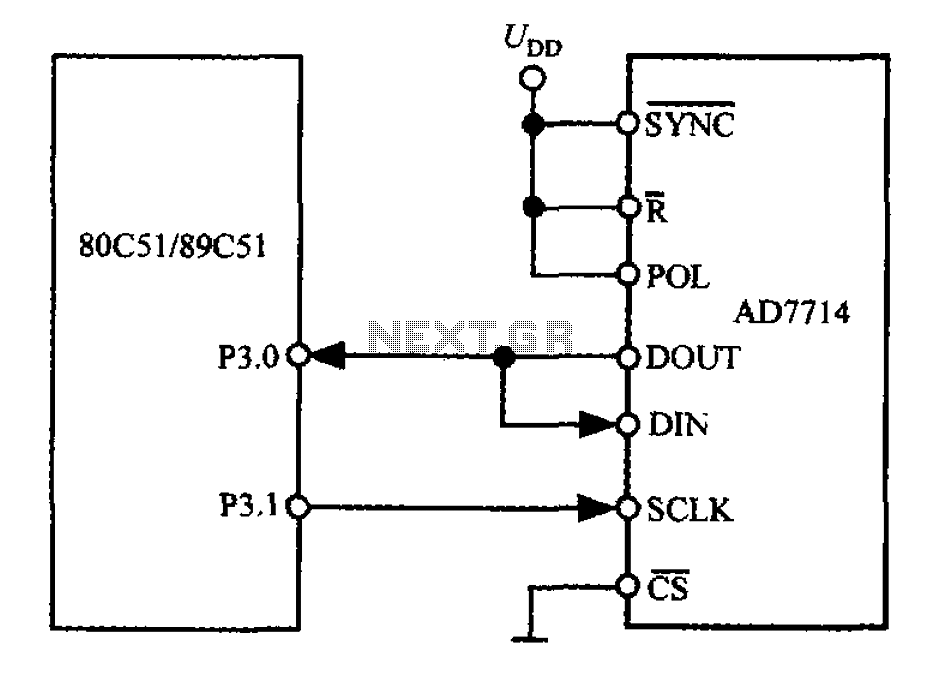
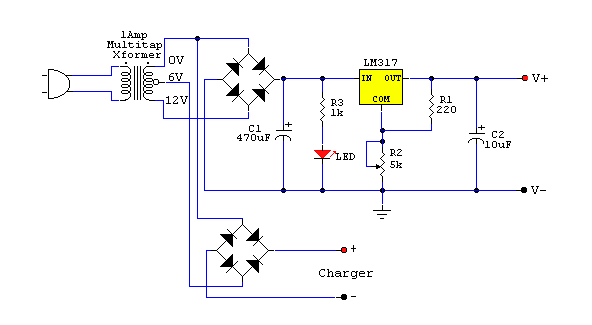
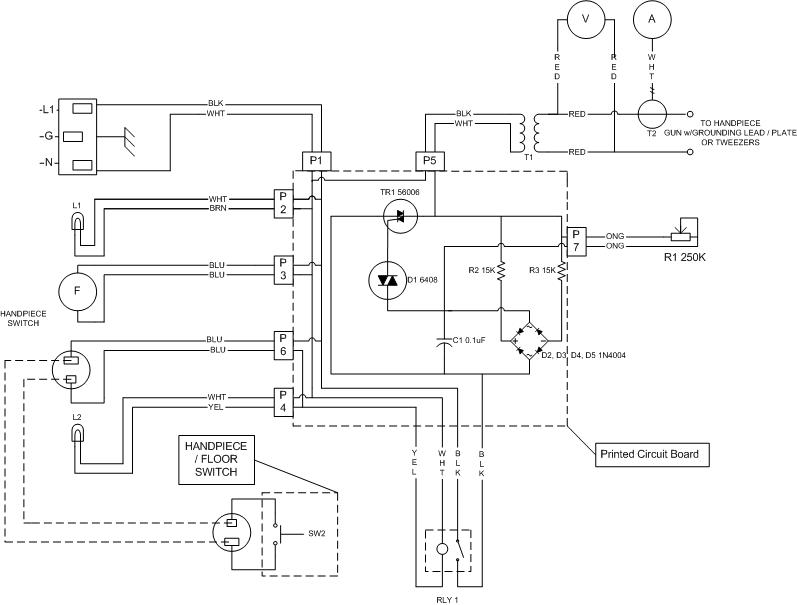
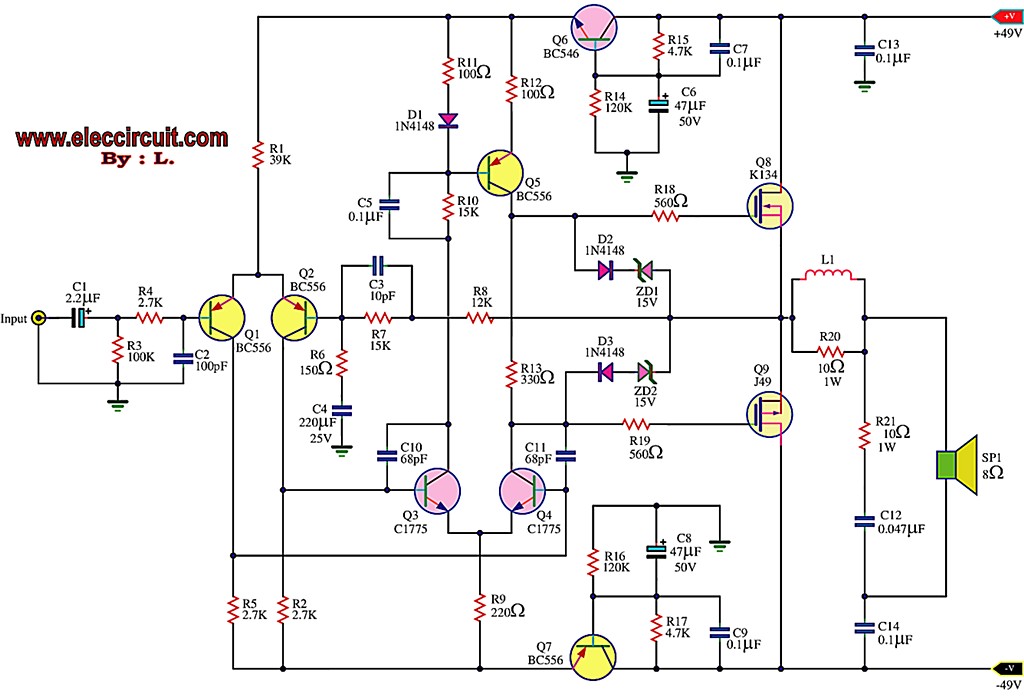
MONITOR POWER SAVER FOR COMPUTERS
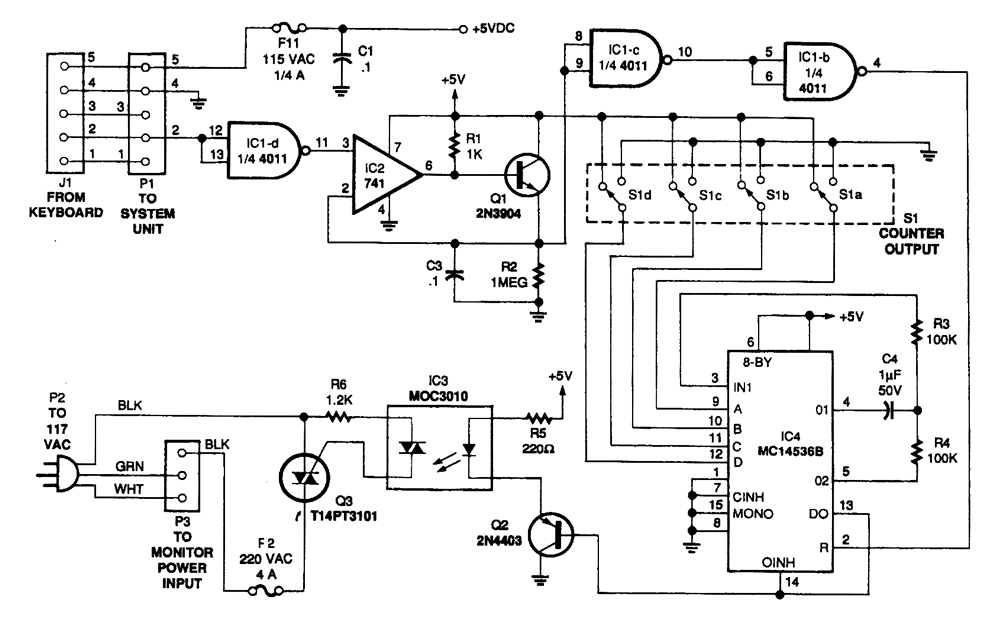
The circuit monitors PC keyboard activity through a five-pin DIN connector J1. When a key is pressed, the keyboard transmits a series of negative-going pulses on pin 2. In conjunction with Q1 and C3, the operational amplifier operates as an integrator, which elongates the continuously varying periods of the input pulses to a relatively constant duration.
The described circuit is designed to monitor keyboard activity through a five-pin DIN connector, specifically utilizing pin 2 to receive negative-going pulses generated by key presses. The integration of an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a transistor (Q1) and a capacitor (C3) is pivotal for processing these pulses.
When a key is pressed, the keyboard sends a rapid succession of negative pulses. The op-amp is configured to function as an integrator; this means that it takes the varying input signal and converts it into a smoother output signal. The integration process results in the output voltage reflecting the average value of the input pulses over time. This is particularly useful for applications where consistent signal timing is required, as it mitigates the effects of rapid fluctuations in the input signal.
The design likely incorporates feedback mechanisms to stabilize the integration process and ensure that the output remains within a desired range. The choice of components, such as the specific op-amp model, transistor type, and capacitor value, will influence the performance characteristics, including response time and stability of the output signal.
Overall, this circuit is essential for applications that require reliable detection of keyboard activity, transforming the rapid pulses generated by key presses into a more manageable and consistent output signal that can be used for further processing or analysis.The circuit monitors PC keyboard activity through five-pin DIN connector J1. When the user presses a key, the keyboard sends a series of negative-going pulses on pin 2. In conjunction with Q1 and C3, the op amp essentially functions as an integrator, which stretches the continually varying periods of the input pulses to a relatively constant period with a.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to monitor keyboard activity through a five-pin DIN connector, specifically utilizing pin 2 to receive negative-going pulses generated by key presses. The integration of an operational amplifier (op-amp) in conjunction with a transistor (Q1) and a capacitor (C3) is pivotal for processing these pulses.
When a key is pressed, the keyboard sends a rapid succession of negative pulses. The op-amp is configured to function as an integrator; this means that it takes the varying input signal and converts it into a smoother output signal. The integration process results in the output voltage reflecting the average value of the input pulses over time. This is particularly useful for applications where consistent signal timing is required, as it mitigates the effects of rapid fluctuations in the input signal.
The design likely incorporates feedback mechanisms to stabilize the integration process and ensure that the output remains within a desired range. The choice of components, such as the specific op-amp model, transistor type, and capacitor value, will influence the performance characteristics, including response time and stability of the output signal.
Overall, this circuit is essential for applications that require reliable detection of keyboard activity, transforming the rapid pulses generated by key presses into a more manageable and consistent output signal that can be used for further processing or analysis.The circuit monitors PC keyboard activity through five-pin DIN connector J1. When the user presses a key, the keyboard sends a series of negative-going pulses on pin 2. In conjunction with Q1 and C3, the op amp essentially functions as an integrator, which stretches the continually varying periods of the input pulses to a relatively constant period with a.. 🔗 External reference