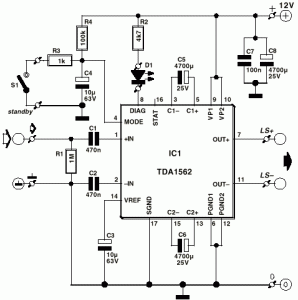
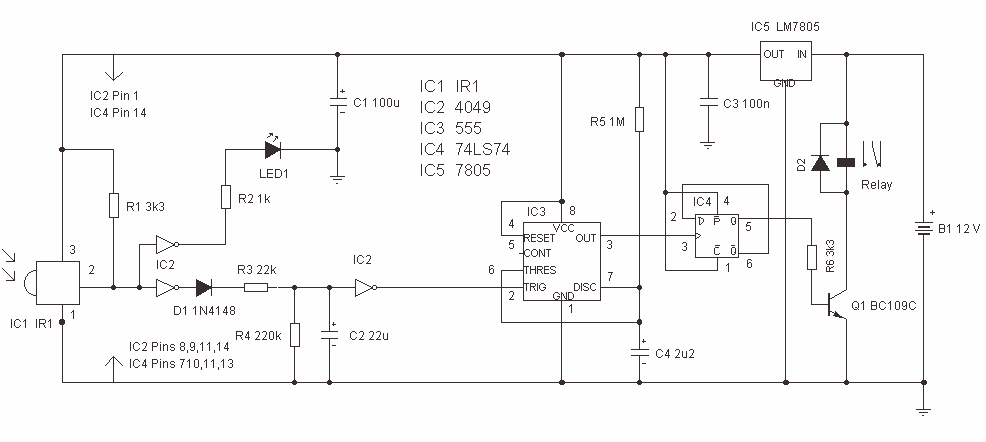
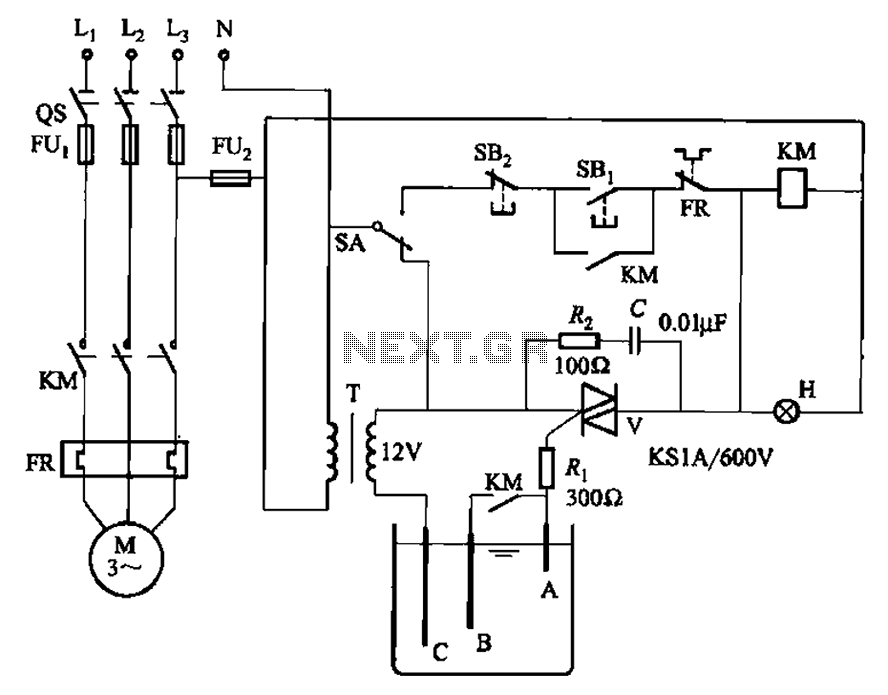
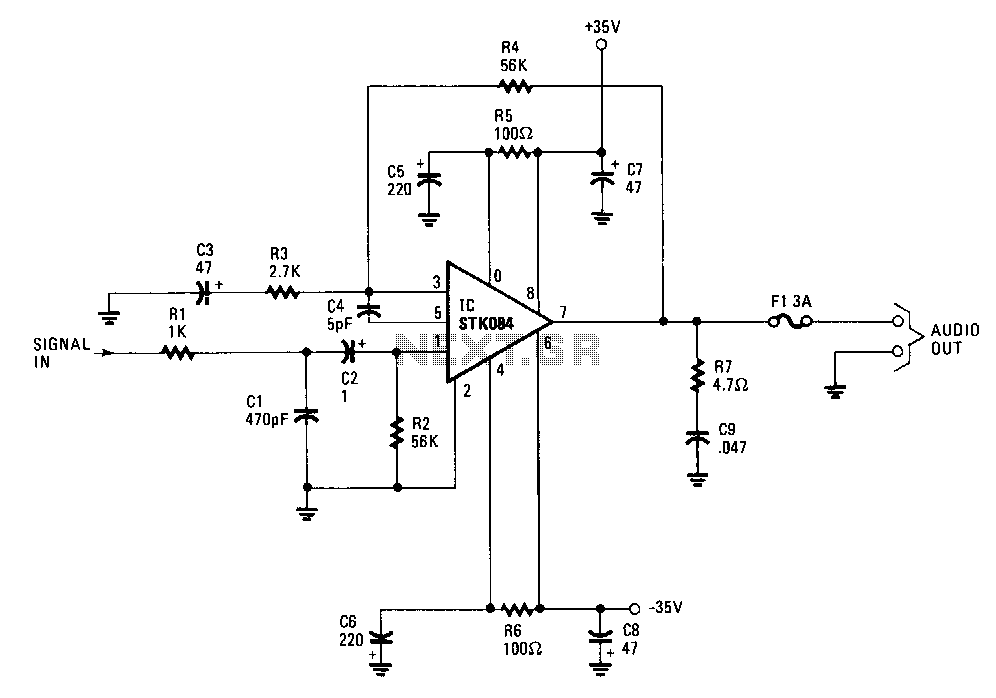
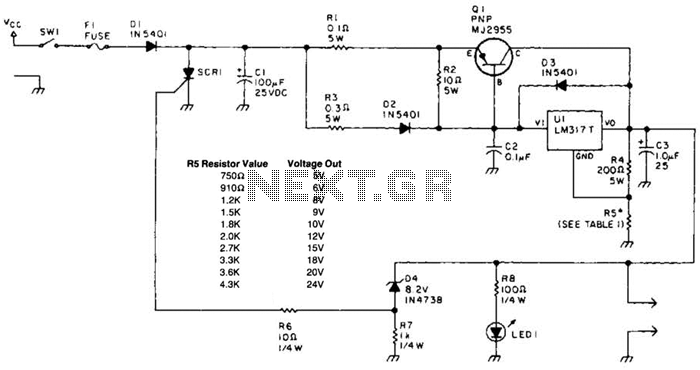
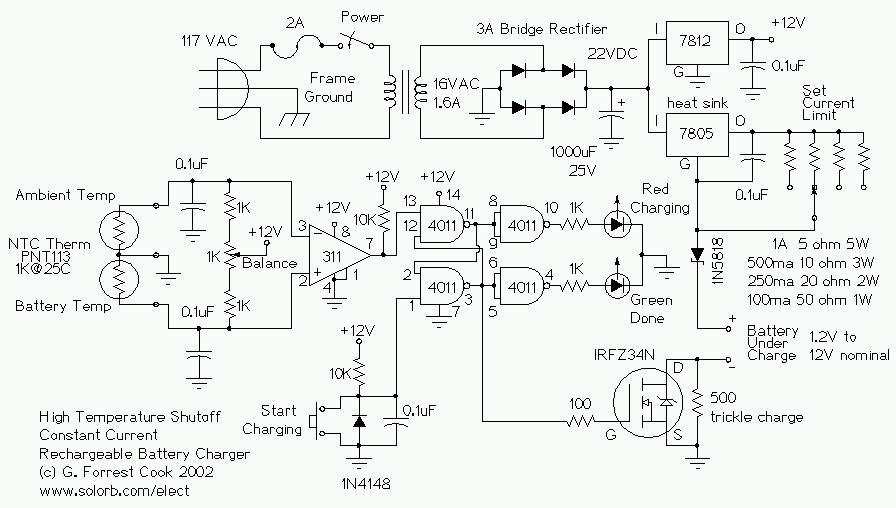
Motor-Speed Control Employs Class-D Power Amplifier
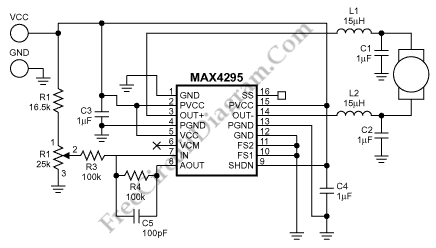
A dual benefit for battery-powered portable devices is provided by Class D audio amplifiers. They produce much less power dissipation than their linear counterparts.
Class D audio amplifiers, also known as switching amplifiers, are designed to achieve high efficiency and low power consumption, making them ideal for battery-operated devices. Unlike traditional linear amplifiers that dissipate significant amounts of power as heat, Class D amplifiers utilize pulse-width modulation (PWM) or other switching techniques to minimize energy loss. This characteristic allows them to deliver high output power with minimal thermal management requirements, which is crucial for portable applications where battery life is a primary concern.
The operational principle of a Class D amplifier involves converting the input audio signal into a series of pulses that switch the output devices (typically MOSFETs) on and off. This switching action occurs at a frequency much higher than the audio signal, allowing for efficient amplification of the signal without generating excessive heat. The output stage of a Class D amplifier is usually followed by a low-pass filter, which smooths out the pulse train back into a continuous audio waveform.
In addition to their efficiency, Class D amplifiers often feature compact designs, which are beneficial for space-constrained applications. The reduced size and weight of these amplifiers can lead to lighter and more portable devices. Furthermore, advancements in integrated circuit technology have enabled the development of highly integrated Class D amplifiers that combine multiple functions into a single chip, further enhancing their appeal for modern electronic devices.
Overall, the implementation of Class D audio amplifiers in battery-powered portable devices not only extends battery life but also contributes to improved sound quality and reduced thermal output, making them a preferred choice in contemporary audio applications.A dual benefit for battery-powered portable devices is provided by Class D audio amplifier. The produce much less power dissipation than do their linear cousins. 🔗 External reference
Class D audio amplifiers, also known as switching amplifiers, are designed to achieve high efficiency and low power consumption, making them ideal for battery-operated devices. Unlike traditional linear amplifiers that dissipate significant amounts of power as heat, Class D amplifiers utilize pulse-width modulation (PWM) or other switching techniques to minimize energy loss. This characteristic allows them to deliver high output power with minimal thermal management requirements, which is crucial for portable applications where battery life is a primary concern.
The operational principle of a Class D amplifier involves converting the input audio signal into a series of pulses that switch the output devices (typically MOSFETs) on and off. This switching action occurs at a frequency much higher than the audio signal, allowing for efficient amplification of the signal without generating excessive heat. The output stage of a Class D amplifier is usually followed by a low-pass filter, which smooths out the pulse train back into a continuous audio waveform.
In addition to their efficiency, Class D amplifiers often feature compact designs, which are beneficial for space-constrained applications. The reduced size and weight of these amplifiers can lead to lighter and more portable devices. Furthermore, advancements in integrated circuit technology have enabled the development of highly integrated Class D amplifiers that combine multiple functions into a single chip, further enhancing their appeal for modern electronic devices.
Overall, the implementation of Class D audio amplifiers in battery-powered portable devices not only extends battery life but also contributes to improved sound quality and reduced thermal output, making them a preferred choice in contemporary audio applications.A dual benefit for battery-powered portable devices is provided by Class D audio amplifier. The produce much less power dissipation than do their linear cousins. 🔗 External reference