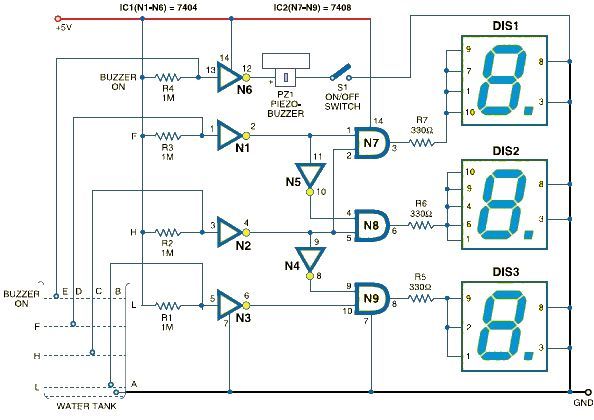
Thyristor interface circuit operational amplifier
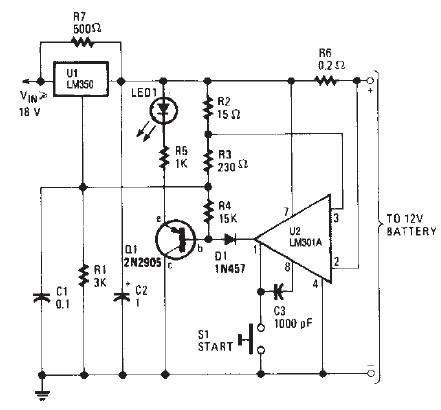
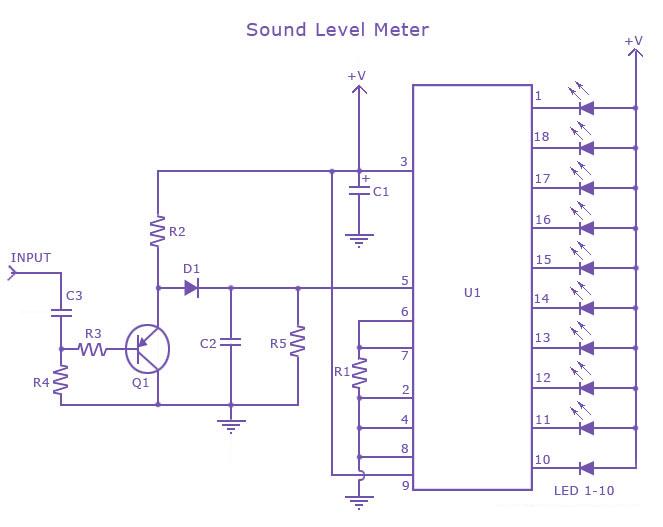
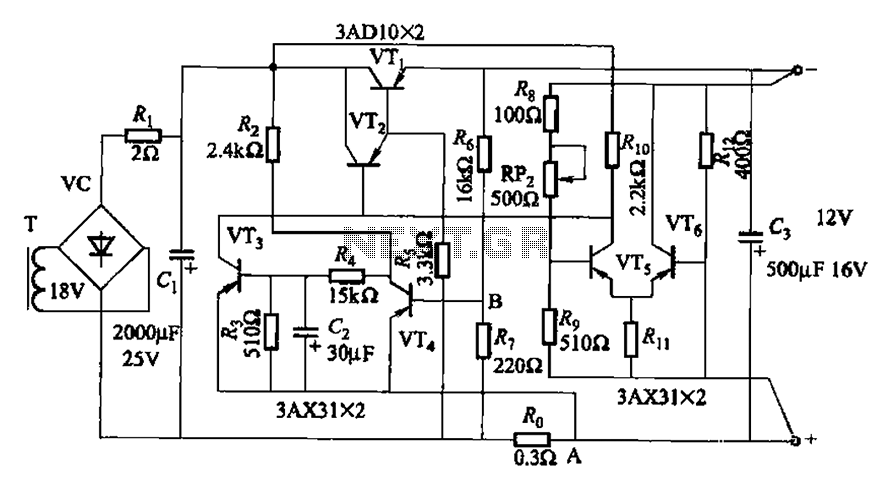
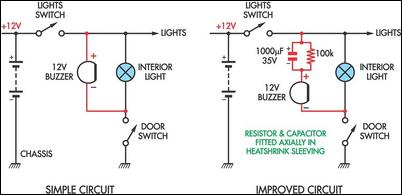
A transistor optocoupler interface circuit, as described in section 15.1.6, has been implemented. This circuit serves as a transistor interface with other circuits.
The transistor optocoupler interface circuit utilizes a light-emitting diode (LED) and a phototransistor to achieve electrical isolation between different parts of a system while allowing signal transmission. The LED emits light when current flows through it, and this light is detected by the phototransistor, which then allows current to flow in its circuit, effectively transferring the signal.
In this implementation, the circuit typically consists of an input stage that includes a resistor connected to the LED, which limits the current to a safe level. The LED is connected in series with the input signal source, ensuring that when the input signal is high, the LED turns on, emitting light. The phototransistor is positioned in proximity to the LED, with its collector and emitter configured to control the output circuit.
The output side may include additional components such as pull-up resistors to ensure proper voltage levels when the phototransistor is in the off state. This arrangement helps maintain the integrity of the signal and prevents noise from affecting the output.
The transistor interface circuit is particularly useful in applications where electrical isolation is necessary, such as in power electronics, microcontroller interfacing, and communication systems. It provides a reliable means of interfacing between different voltage levels and protecting sensitive components from high voltages or spikes that may occur in the system.
Careful selection of the LED and phototransistor parameters, including their forward current, reverse voltage, and switching speed, is crucial to ensure optimal performance of the optocoupler circuit in its intended application.Transistor optocouplers interface circuit as described in 15.1.6 has been. Transistor interface circuit with other circuit
The transistor optocoupler interface circuit utilizes a light-emitting diode (LED) and a phototransistor to achieve electrical isolation between different parts of a system while allowing signal transmission. The LED emits light when current flows through it, and this light is detected by the phototransistor, which then allows current to flow in its circuit, effectively transferring the signal.
In this implementation, the circuit typically consists of an input stage that includes a resistor connected to the LED, which limits the current to a safe level. The LED is connected in series with the input signal source, ensuring that when the input signal is high, the LED turns on, emitting light. The phototransistor is positioned in proximity to the LED, with its collector and emitter configured to control the output circuit.
The output side may include additional components such as pull-up resistors to ensure proper voltage levels when the phototransistor is in the off state. This arrangement helps maintain the integrity of the signal and prevents noise from affecting the output.
The transistor interface circuit is particularly useful in applications where electrical isolation is necessary, such as in power electronics, microcontroller interfacing, and communication systems. It provides a reliable means of interfacing between different voltage levels and protecting sensitive components from high voltages or spikes that may occur in the system.
Careful selection of the LED and phototransistor parameters, including their forward current, reverse voltage, and switching speed, is crucial to ensure optimal performance of the optocoupler circuit in its intended application.Transistor optocouplers interface circuit as described in 15.1.6 has been. Transistor interface circuit with other circuit