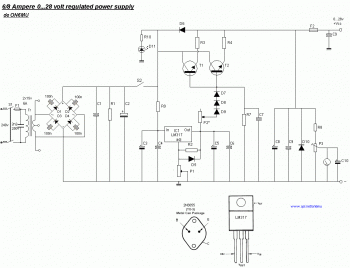
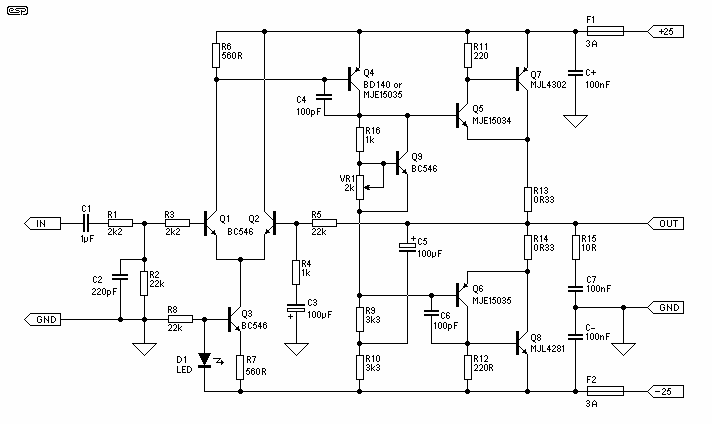
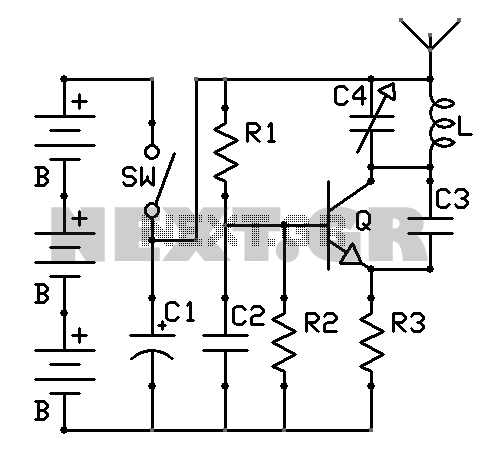
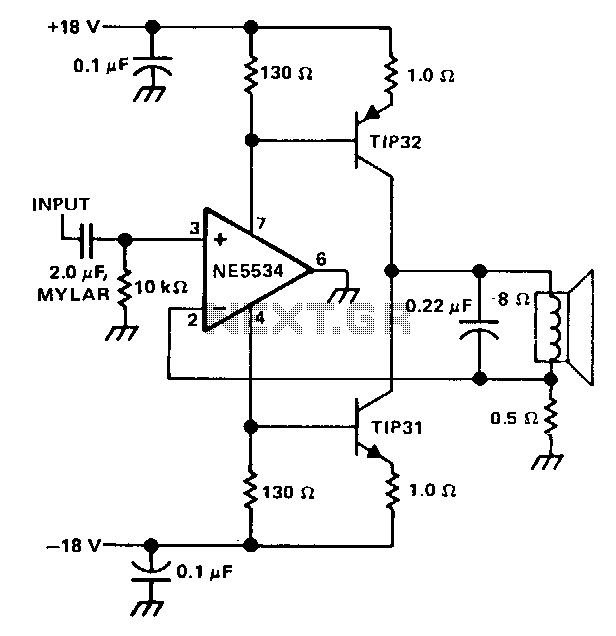
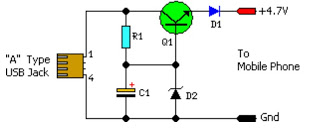
New Power Topology Propels Quarter-Brick Bus Converter to Benchmark Power Density
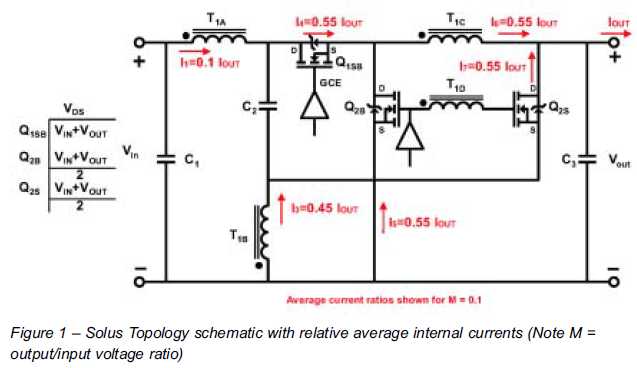
The ability to reduce power losses is crucial. This document describes a new ultra-high-performance topology that is expected to serve as the foundation for next-generation DC-DC power supplies in high-demand applications.
The proposed ultra-high-performance topology aims to significantly enhance the efficiency of DC-DC power conversion systems. By minimizing power losses, this topology seeks to address the growing demands for energy efficiency in various electronic devices and applications, particularly in high-performance computing, telecommunications, and electric vehicle charging systems.
This topology may incorporate advanced techniques such as synchronous rectification, soft switching, and resonant conversion methods. Synchronous rectification utilizes MOSFETs instead of traditional diodes to reduce conduction losses, thereby improving overall efficiency. Soft switching techniques, including zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and zero-current switching (ZCS), allow for the reduction of switching losses during the transition of the power devices, further enhancing performance.
The implementation of this topology is expected to involve a combination of high-frequency operation and optimized magnetic components, which can lead to smaller, lighter designs while maintaining or improving power output. The use of high-performance control algorithms will also play a critical role in adapting to varying load conditions and ensuring stable operation across a wide range of input and output voltages.
In conclusion, this innovative topology is positioned to set a new standard in the design of DC-DC power supplies, providing a robust solution for reducing power losses and improving efficiency in next-generation electronic systems.The ability to reduce power losses is most important Describing here a new ultra-high-performance topology expected to be the foundation for next-generation dc-dc power supplies in high.. 🔗 External reference
The proposed ultra-high-performance topology aims to significantly enhance the efficiency of DC-DC power conversion systems. By minimizing power losses, this topology seeks to address the growing demands for energy efficiency in various electronic devices and applications, particularly in high-performance computing, telecommunications, and electric vehicle charging systems.
This topology may incorporate advanced techniques such as synchronous rectification, soft switching, and resonant conversion methods. Synchronous rectification utilizes MOSFETs instead of traditional diodes to reduce conduction losses, thereby improving overall efficiency. Soft switching techniques, including zero-voltage switching (ZVS) and zero-current switching (ZCS), allow for the reduction of switching losses during the transition of the power devices, further enhancing performance.
The implementation of this topology is expected to involve a combination of high-frequency operation and optimized magnetic components, which can lead to smaller, lighter designs while maintaining or improving power output. The use of high-performance control algorithms will also play a critical role in adapting to varying load conditions and ensuring stable operation across a wide range of input and output voltages.
In conclusion, this innovative topology is positioned to set a new standard in the design of DC-DC power supplies, providing a robust solution for reducing power losses and improving efficiency in next-generation electronic systems.The ability to reduce power losses is most important Describing here a new ultra-high-performance topology expected to be the foundation for next-generation dc-dc power supplies in high.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713