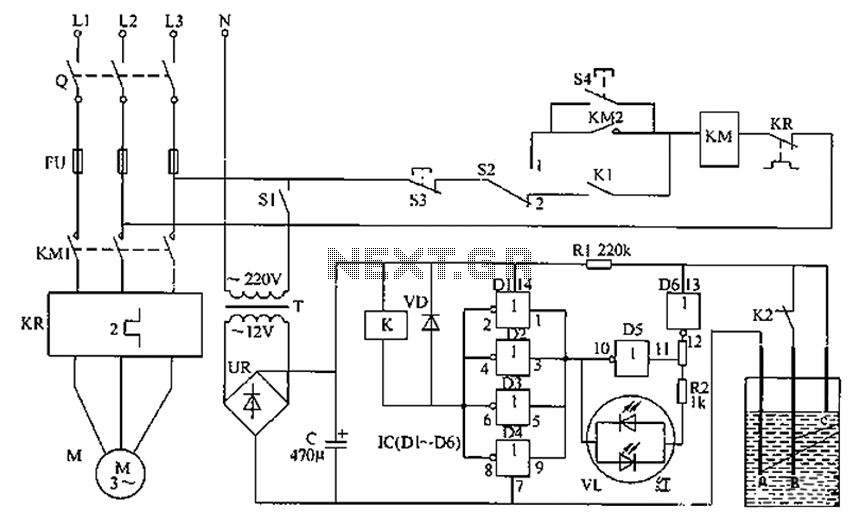
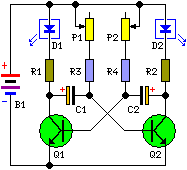
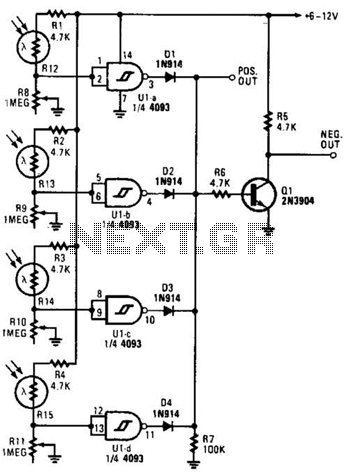
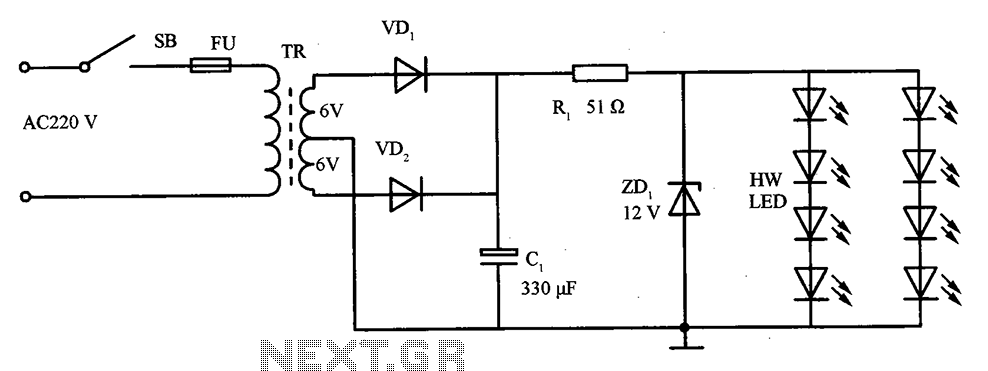
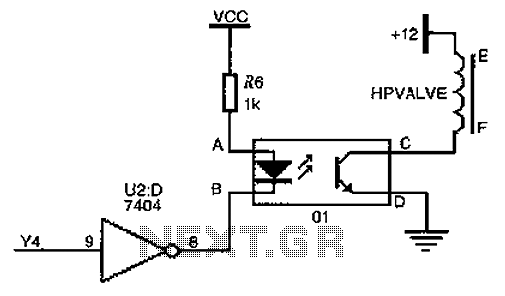
Noise generator circuit
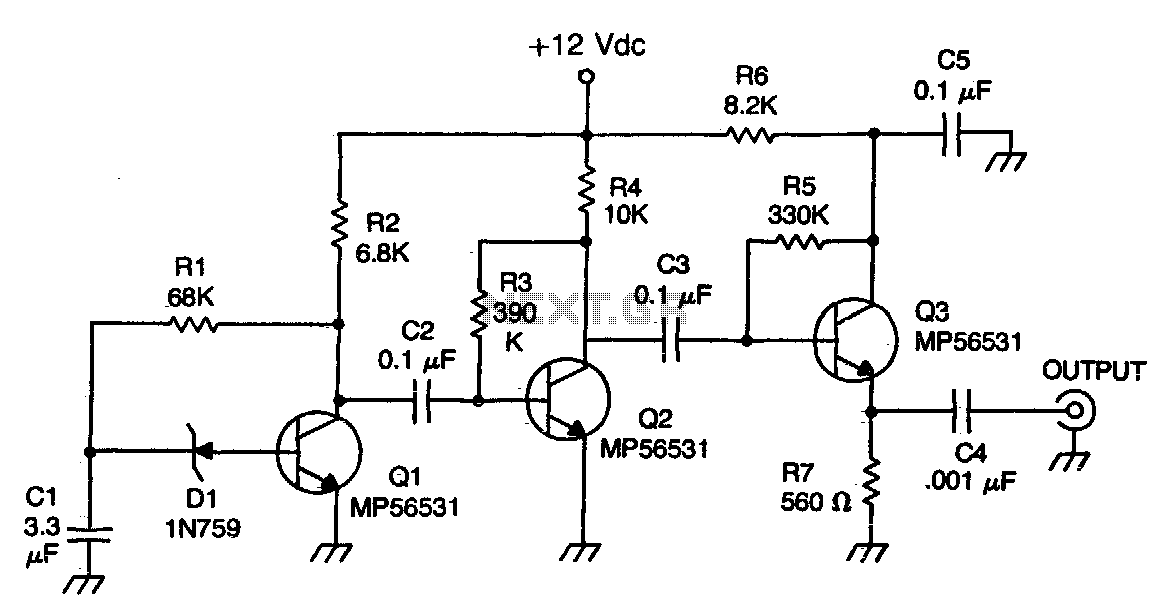
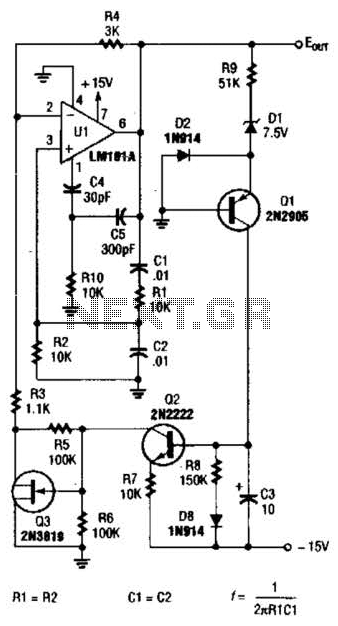
The Zener diode functions as an avalanche rectifier in reverse bias mode, connected to the input circuit of a wideband RF amplifier. The noise is amplified and subsequently applied to the cascade wideband amplifier, utilizing transistors Q2 and Q3.
The circuit incorporates a Zener diode configured to operate in reverse bias, allowing it to maintain a stable voltage across its terminals. This characteristic is critical in RF applications, where maintaining signal integrity is essential. The Zener diode effectively clamps voltage spikes and provides voltage regulation, ensuring that the input signal to the wideband RF amplifier remains within acceptable limits.
In this specific configuration, the Zener diode is positioned at the input of the wideband RF amplifier to mitigate any unwanted noise that may interfere with the amplification process. The subsequent stages of the amplifier are comprised of transistors Q2 and Q3, which are configured in a cascade arrangement. This configuration allows for enhanced gain and improved bandwidth, making it suitable for a wide range of RF applications.
The noise picked up by the input circuit is amplified by the first stage, which is critical for improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The amplified signal is then fed into the next stage, where Q2 and Q3 further boost the signal strength. This cascading effect is vital for achieving the desired amplification levels, ensuring that the output signal is robust enough for further processing or transmission.
Overall, the integration of the Zener diode within the input circuit of the wideband RF amplifier plays a crucial role in maintaining signal integrity and enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier system.The zener diode is an avalanche rectifier in the reverse bias mode connected toiihe input circuit ofa wideband rf amplifier The noise is amplified and applied to the cascade wideband amplifier, transistors Q2 and Q3. 🔗 External reference
The circuit incorporates a Zener diode configured to operate in reverse bias, allowing it to maintain a stable voltage across its terminals. This characteristic is critical in RF applications, where maintaining signal integrity is essential. The Zener diode effectively clamps voltage spikes and provides voltage regulation, ensuring that the input signal to the wideband RF amplifier remains within acceptable limits.
In this specific configuration, the Zener diode is positioned at the input of the wideband RF amplifier to mitigate any unwanted noise that may interfere with the amplification process. The subsequent stages of the amplifier are comprised of transistors Q2 and Q3, which are configured in a cascade arrangement. This configuration allows for enhanced gain and improved bandwidth, making it suitable for a wide range of RF applications.
The noise picked up by the input circuit is amplified by the first stage, which is critical for improving the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The amplified signal is then fed into the next stage, where Q2 and Q3 further boost the signal strength. This cascading effect is vital for achieving the desired amplification levels, ensuring that the output signal is robust enough for further processing or transmission.
Overall, the integration of the Zener diode within the input circuit of the wideband RF amplifier plays a crucial role in maintaining signal integrity and enhancing the overall performance of the amplifier system.The zener diode is an avalanche rectifier in the reverse bias mode connected toiihe input circuit ofa wideband rf amplifier The noise is amplified and applied to the cascade wideband amplifier, transistors Q2 and Q3. 🔗 External reference