On After Delay with Mosfet
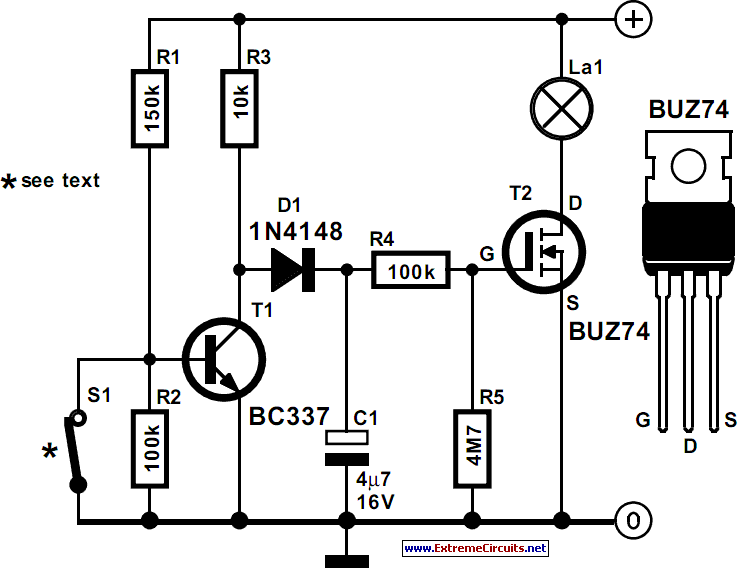
This is an On After Delay Circuit. It utilizes a MOSFET in the circuit for easier delay implementation compared to using a transistor. The operation of the circuit begins when switch S1 is pressed.
The On After Delay Circuit is designed to activate an output after a predetermined delay following the closure of switch S1. The use of a MOSFET provides advantages such as higher efficiency and faster switching capabilities compared to traditional transistors.
The circuit typically consists of a MOSFET, a resistor, a capacitor, and a switch. When S1 is pressed, current flows through the resistor, charging the capacitor. The time it takes for the capacitor to charge to a specific voltage level determines the delay period. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold voltage of the MOSFET, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow to the load.
The resistor-capacitor (RC) time constant is critical in determining the delay duration. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = R × C, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired delay can be achieved.
It is essential to ensure that the MOSFET selected can handle the load current and voltage requirements. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures should be considered to prevent overheating during operation. The circuit can be used in various applications, such as timed lighting, motor control, or any scenario where a delayed activation is required.
Overall, the On After Delay Circuit is a versatile and efficient solution for implementing time delays in electronic systems.That be On After Delay Circuit. I uses mosfet in the circuit for delay easy more than the transistor. By have the work of the circuit be when press , S1 ,.. 🔗 External reference
The On After Delay Circuit is designed to activate an output after a predetermined delay following the closure of switch S1. The use of a MOSFET provides advantages such as higher efficiency and faster switching capabilities compared to traditional transistors.
The circuit typically consists of a MOSFET, a resistor, a capacitor, and a switch. When S1 is pressed, current flows through the resistor, charging the capacitor. The time it takes for the capacitor to charge to a specific voltage level determines the delay period. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold voltage of the MOSFET, the MOSFET turns on, allowing current to flow to the load.
The resistor-capacitor (RC) time constant is critical in determining the delay duration. The time constant (τ) can be calculated using the formula τ = R × C, where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. By selecting appropriate values for R and C, the desired delay can be achieved.
It is essential to ensure that the MOSFET selected can handle the load current and voltage requirements. Additionally, proper heat dissipation measures should be considered to prevent overheating during operation. The circuit can be used in various applications, such as timed lighting, motor control, or any scenario where a delayed activation is required.
Overall, the On After Delay Circuit is a versatile and efficient solution for implementing time delays in electronic systems.That be On After Delay Circuit. I uses mosfet in the circuit for delay easy more than the transistor. By have the work of the circuit be when press , S1 ,.. 🔗 External reference