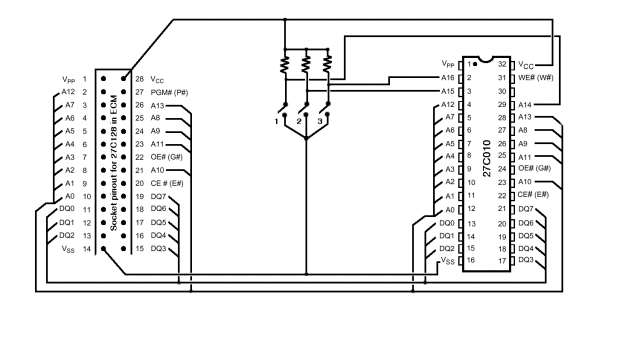
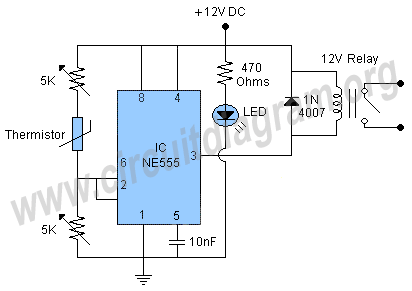
One circuit alarm phase
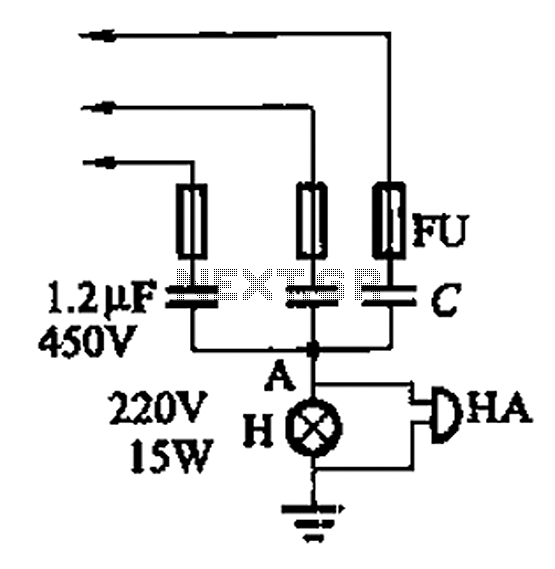
A 3-phase power system poses risks to electrical equipment, particularly asynchronous motors. To detect phase failure, an alarm circuit can be implemented. When the power supply is normal, the voltage at point A is approximately 0V, and no alarm is triggered. However, in the event of a phase loss (either one or two phases), the voltage at point A increases, activating the signal H and sounding the HA alarm.
The described circuit operates on the principle of monitoring the voltage levels in a 3-phase system to ensure the integrity of the power supply. The circuit includes a voltage sensing mechanism connected to point A, which is strategically placed to monitor the phase voltages. Under normal operating conditions, the voltage at this point remains at or near zero volts, indicating that all three phases are functioning correctly.
In the event of a phase failure, the voltage at point A will rise above the normal threshold. This change is detected by a comparator circuit which is designed to trigger when the voltage exceeds a predefined level. The output of the comparator activates an indicator light (signal H) and a bell (HA alarm), alerting personnel to the fault condition.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the readings, ensuring reliable operation. A reset mechanism could be integrated to allow for the manual silencing of the alarm once the issue has been addressed, preventing unnecessary disruptions.
Overall, this phase failure detection circuit is essential for protecting sensitive electrical equipment, particularly asynchronous motors, from damage due to power supply irregularities. Its design emphasizes responsiveness and reliability, making it a critical component in industrial electrical systems.3-phase power, would endanger the electrical equipment (especially asynchronous motor) security, in order to detect phase failure, it can be made with a broken alarm. Circuit s hown in Figure 13-110. When the power supply is normal, A point voltage about as ov, no alarm; when phase loss (one phase or two-phase), A point voltage increases, the signal H is lit, bells HA alarm.
The described circuit operates on the principle of monitoring the voltage levels in a 3-phase system to ensure the integrity of the power supply. The circuit includes a voltage sensing mechanism connected to point A, which is strategically placed to monitor the phase voltages. Under normal operating conditions, the voltage at this point remains at or near zero volts, indicating that all three phases are functioning correctly.
In the event of a phase failure, the voltage at point A will rise above the normal threshold. This change is detected by a comparator circuit which is designed to trigger when the voltage exceeds a predefined level. The output of the comparator activates an indicator light (signal H) and a bell (HA alarm), alerting personnel to the fault condition.
The circuit may also include additional components such as resistors and capacitors to filter noise and stabilize the readings, ensuring reliable operation. A reset mechanism could be integrated to allow for the manual silencing of the alarm once the issue has been addressed, preventing unnecessary disruptions.
Overall, this phase failure detection circuit is essential for protecting sensitive electrical equipment, particularly asynchronous motors, from damage due to power supply irregularities. Its design emphasizes responsiveness and reliability, making it a critical component in industrial electrical systems.3-phase power, would endanger the electrical equipment (especially asynchronous motor) security, in order to detect phase failure, it can be made with a broken alarm. Circuit s hown in Figure 13-110. When the power supply is normal, A point voltage about as ov, no alarm; when phase loss (one phase or two-phase), A point voltage increases, the signal H is lit, bells HA alarm.