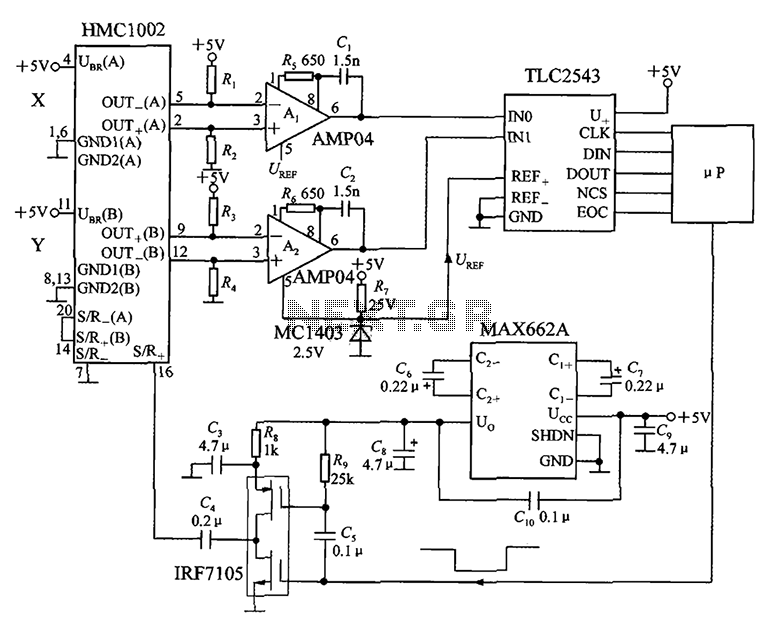
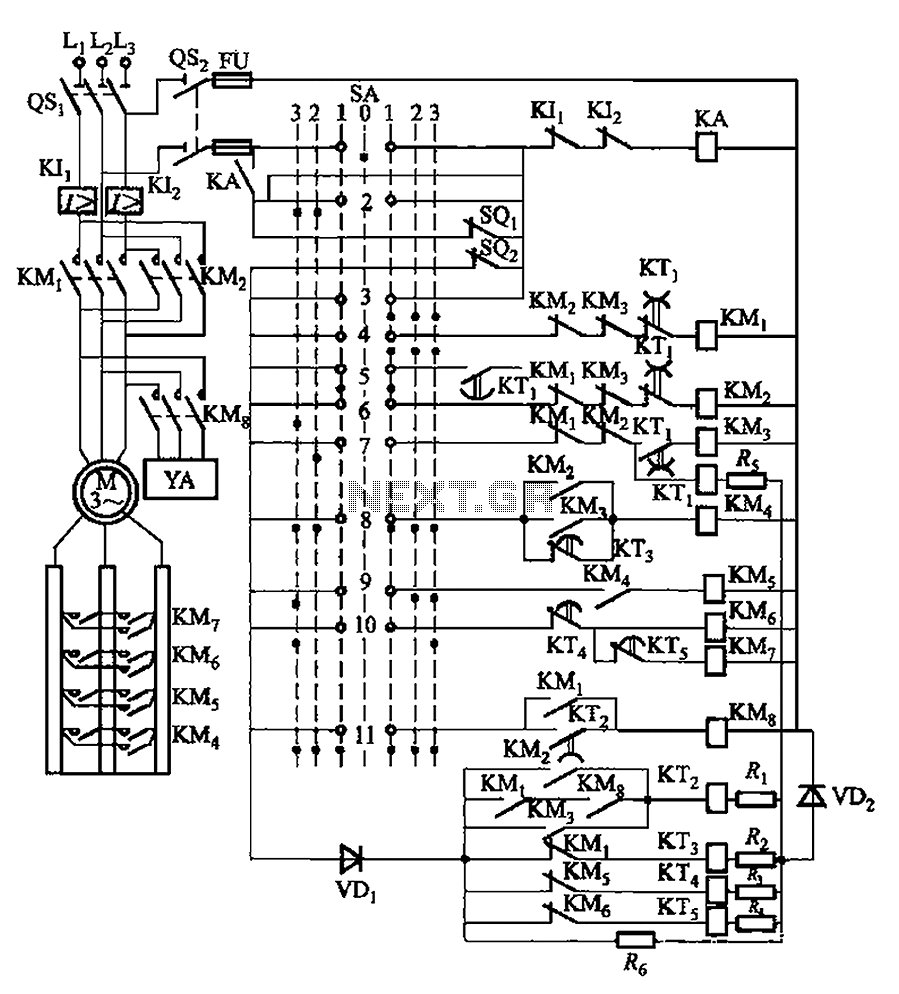
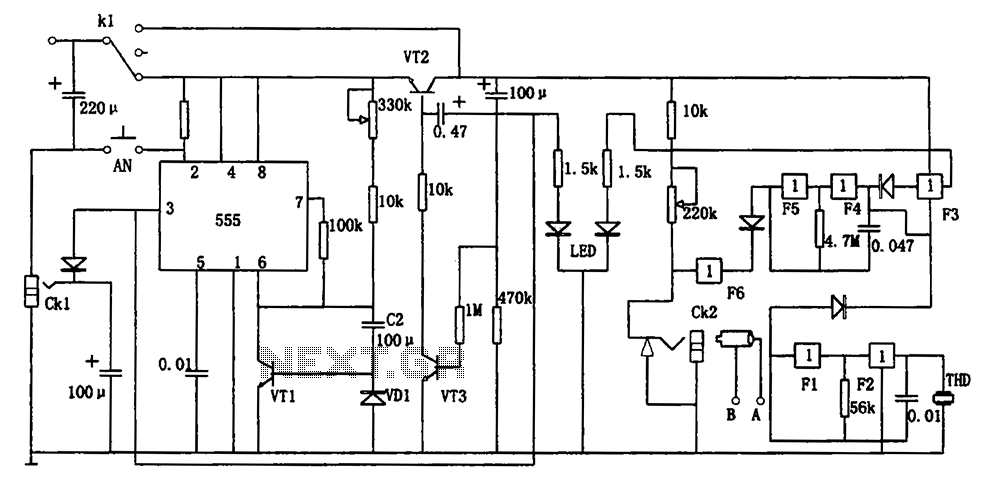
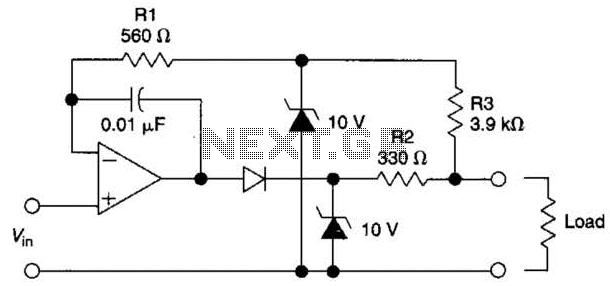
One synchronous motor thyristor excitation circuit
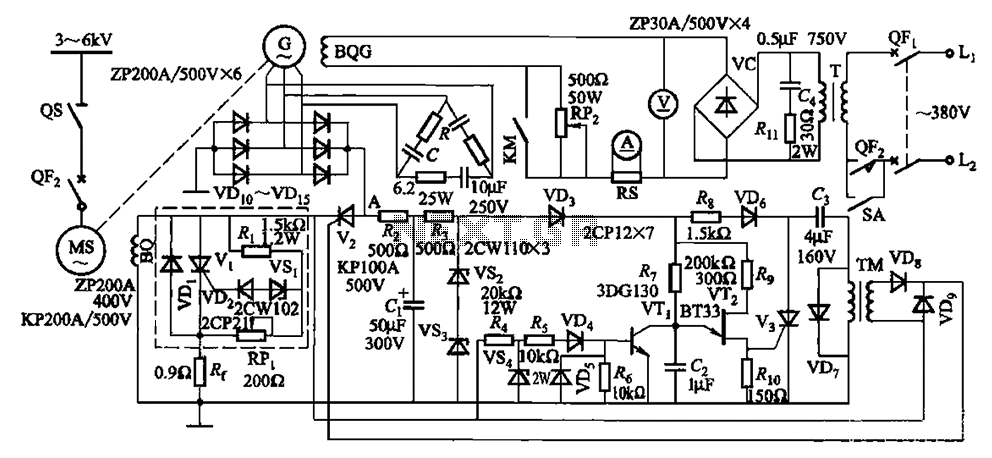
The circuit depicted in Figure 16-105 illustrates a synchronous motor. The components include BQ, which represents its field winding, and G, which denotes the AC excitation for the motor. The notation BQG indicates the field winding, with an empty box symbolizing part of the de-excitation process.
The synchronous motor circuit operates by utilizing alternating current (AC) to energize the field winding (BQ) while maintaining synchronization with the supply frequency. The AC excitation (G) is crucial as it generates the magnetic field required for the motor's operation. The interaction between the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's magnetic field allows the motor to maintain a constant speed, which is determined by the frequency of the AC supply.
The de-excitation process, represented by the empty box in the circuit, is essential for controlling the motor's operation during various load conditions. When the motor is required to reduce speed or stop, the de-excitation mechanism reduces the current flowing through the field winding, allowing for a smoother transition and preventing sudden changes that could damage the motor or connected equipment.
In summary, the schematic provides a clear representation of the synchronous motor's operational principles, highlighting the importance of the field winding and AC excitation in maintaining consistent performance and the role of de-excitation in managing motor behavior under different operational scenarios. Circuit shown in Figure 16-105. Figure, MS synchronous motor. BQ its field winding; G AC excitation hair motors, BQG its field winding {empty box as part of the de-excitation.
The synchronous motor circuit operates by utilizing alternating current (AC) to energize the field winding (BQ) while maintaining synchronization with the supply frequency. The AC excitation (G) is crucial as it generates the magnetic field required for the motor's operation. The interaction between the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's magnetic field allows the motor to maintain a constant speed, which is determined by the frequency of the AC supply.
The de-excitation process, represented by the empty box in the circuit, is essential for controlling the motor's operation during various load conditions. When the motor is required to reduce speed or stop, the de-excitation mechanism reduces the current flowing through the field winding, allowing for a smoother transition and preventing sudden changes that could damage the motor or connected equipment.
In summary, the schematic provides a clear representation of the synchronous motor's operational principles, highlighting the importance of the field winding and AC excitation in maintaining consistent performance and the role of de-excitation in managing motor behavior under different operational scenarios. Circuit shown in Figure 16-105. Figure, MS synchronous motor. BQ its field winding; G AC excitation hair motors, BQG its field winding {empty box as part of the de-excitation.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713