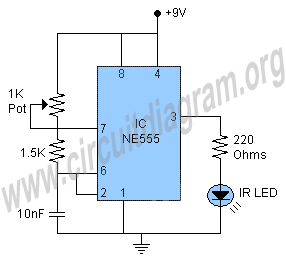
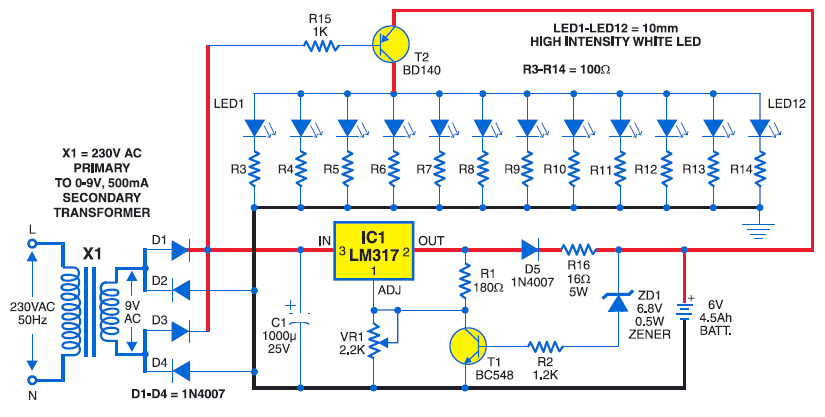
One zero trigger thyristor power adjustment circuit
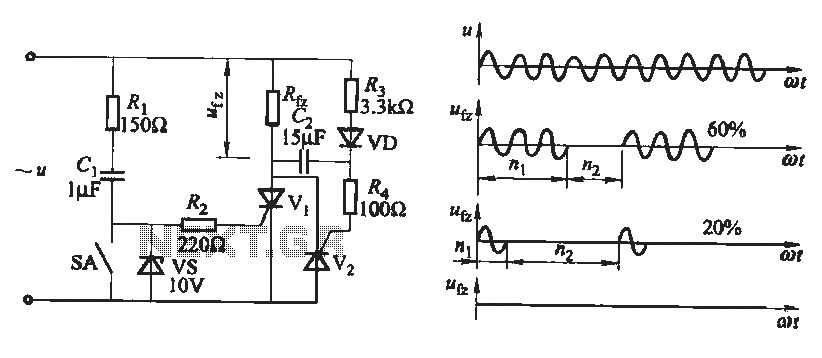
The output waveform of the thyristor zero trigger circuit is a sine wave, which does not generate electromagnetic interference like a phase-shift trigger circuit. This circuit serves as a basic thyristor power adjustment mechanism. In the circuit diagram, the regulator performs a clamping action and allows access to the charging capacitor Ci. The diode VD is responsible for preventing the reverse charge of the negative half cycle of the power supply capacitor Cz. The resistors Rz and R4 function as current limiting resistors to restrict the control current. The power outage timing is determined by the length of the time bar switch (or control contact) SA, which dictates the opening and closing times. The load power is controlled by the switch SA.
The thyristor zero trigger circuit is designed to provide a stable sine wave output while minimizing electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for applications requiring precise power control. The circuit employs a thyristor, which acts as a switch controlled by the gate current. The clamping action of the regulator is crucial for maintaining the voltage across the capacitor Ci, allowing it to charge efficiently while preventing overvoltage conditions.
The diode VD plays a critical role in ensuring that the capacitor Cz does not discharge negatively, which could lead to damaging reverse currents. By preventing reverse charge during the negative half cycle, the diode ensures the longevity and reliability of the circuit components. The current limiting resistors Rz and R4 are essential for protecting the thyristor and other components from excessive current, which could cause thermal runaway or failure.
The timing of power outages is a significant feature of this circuit, as it allows for controlled power delivery to the load. The time bar switch SA provides a means to adjust the duration of the power supply, effectively controlling the load power. This feature can be particularly useful in applications that require variable power levels or in systems where load conditions may change frequently.
In summary, the thyristor zero trigger circuit is an effective solution for achieving controlled sine wave output with minimal interference, utilizing key components such as regulators, diodes, and resistors to ensure stable operation and protection against adverse conditions. The design emphasizes reliability and adaptability, making it suitable for various electronic applications.Thyristor zero trigger circuit output waveform is a sine wave, it will not produce as phase-shift trigger circuit as electromagnetic interference. This is a zero trigger thyristor power adjustment of the basic circuit. The figure, the regulator vs plays clamping action and to provide access to the charging capacitor Ci; VD role is to prevent the negative half cycle of the power supply capacitor Cz reverse charge; resistance Rz and R4 are current limiting resistor to limit the control current. Figure, power outage time digging 1 and 2 depending on the time bar switch length (or control contact) SA opening and closing time.
That load power by the SA control.
The thyristor zero trigger circuit is designed to provide a stable sine wave output while minimizing electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for applications requiring precise power control. The circuit employs a thyristor, which acts as a switch controlled by the gate current. The clamping action of the regulator is crucial for maintaining the voltage across the capacitor Ci, allowing it to charge efficiently while preventing overvoltage conditions.
The diode VD plays a critical role in ensuring that the capacitor Cz does not discharge negatively, which could lead to damaging reverse currents. By preventing reverse charge during the negative half cycle, the diode ensures the longevity and reliability of the circuit components. The current limiting resistors Rz and R4 are essential for protecting the thyristor and other components from excessive current, which could cause thermal runaway or failure.
The timing of power outages is a significant feature of this circuit, as it allows for controlled power delivery to the load. The time bar switch SA provides a means to adjust the duration of the power supply, effectively controlling the load power. This feature can be particularly useful in applications that require variable power levels or in systems where load conditions may change frequently.
In summary, the thyristor zero trigger circuit is an effective solution for achieving controlled sine wave output with minimal interference, utilizing key components such as regulators, diodes, and resistors to ensure stable operation and protection against adverse conditions. The design emphasizes reliability and adaptability, making it suitable for various electronic applications.Thyristor zero trigger circuit output waveform is a sine wave, it will not produce as phase-shift trigger circuit as electromagnetic interference. This is a zero trigger thyristor power adjustment of the basic circuit. The figure, the regulator vs plays clamping action and to provide access to the charging capacitor Ci; VD role is to prevent the negative half cycle of the power supply capacitor Cz reverse charge; resistance Rz and R4 are current limiting resistor to limit the control current. Figure, power outage time digging 1 and 2 depending on the time bar switch length (or control contact) SA opening and closing time.
That load power by the SA control.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713