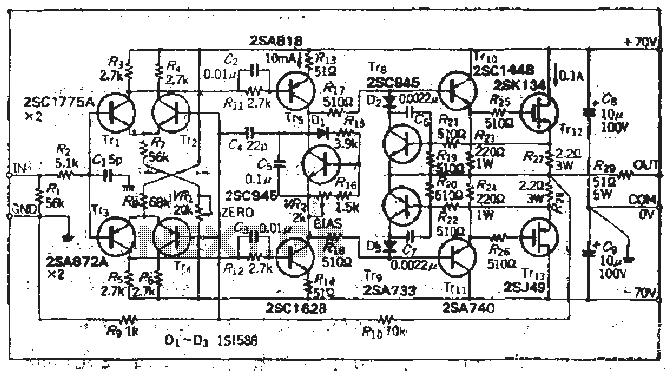
op amp Twin T circuit noisy
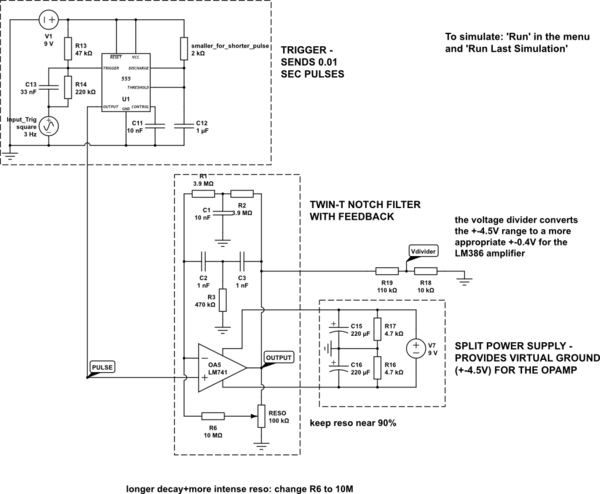
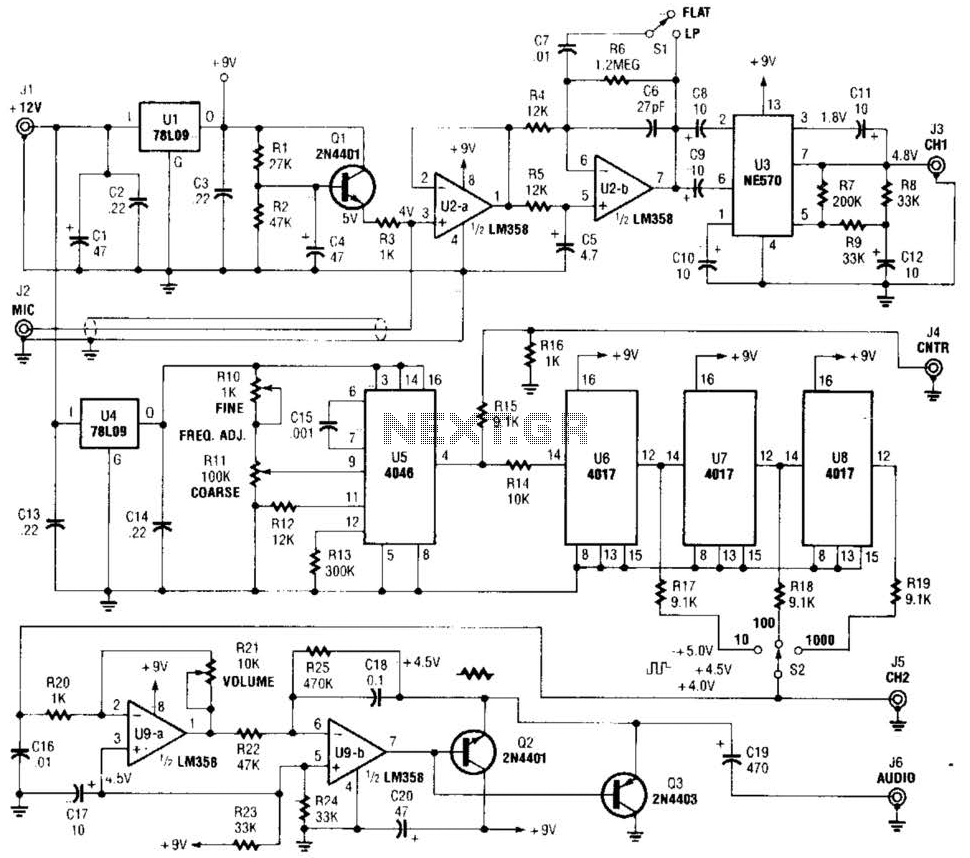
The circuit is constructed on a breadboard and produces the expected sound characteristics, specifically a damped sine wave reminiscent of large 808/909-style kicks. However, it exhibits a significant amount of noise. An attempt was made to mitigate this by adding a large electrolytic capacitor between V+ and GND, which improved the situation somewhat, but the noise persists. Additionally, the circuit generates a buzzing sound when touching the potentiometers or wires. The entire setup is powered by a split power supply from a switchable adapter, specifically for the operational amplifier, while the remainder of the circuit operates on 0-9V.
The described circuit is a sound synthesis device that utilizes operational amplifiers to generate audio signals, particularly for creating kick drum sounds similar to iconic drum machines. The damped sine wave output is characteristic of the sound design typically sought in electronic music production. The noise issues observed may stem from several potential sources, including inadequate power supply decoupling, grounding problems, or interference from external sources.
To address the noise, it is advisable to implement a more robust power supply filtering strategy. This can include adding additional bypass capacitors (both ceramic and electrolytic) close to the power pins of the operational amplifiers. A combination of smaller capacitors (e.g., 100nF ceramic) and larger electrolytic capacitors (e.g., 10µF to 100µF) can help filter high and low-frequency noise effectively.
Grounding practices also play a crucial role in minimizing noise. A star grounding configuration is recommended, where all ground connections converge at a single point, reducing ground loop issues. Ensuring that the signal ground and power ground are separated until they meet at the power supply can further reduce buzz and hum.
The buzzing sound when touching the potentiometers or wires suggests potential issues with shielding or grounding. Shielded cables should be used for any signal paths, particularly those that are susceptible to interference. Additionally, ensuring that the potentiometers are grounded properly and that their enclosures are connected to ground can help reduce this noise.
Lastly, if the circuit is susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), consider placing the breadboard inside a metal enclosure or using a Faraday cage to shield it from external electromagnetic fields. This can significantly enhance the overall performance and sound quality of the circuit, providing a cleaner output with reduced noise and interference.It`s built on a breadboard and it sounds exactly how it should sound (damped sine wave, big 808/909-kind of kicks). However it`s noisy. I`ve tried adding a big electrolytic cap between V+ and GND. It makes difference yet it`s still very noisy. Also, the circuit tends to `buzz` when I touch the pots or a wire. Any idea how to kill that The whole circuit is powered from a split power supply from a switchable adaptor (I mean the op amp, the rest of the circuit is powered from 0-9V).
🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a sound synthesis device that utilizes operational amplifiers to generate audio signals, particularly for creating kick drum sounds similar to iconic drum machines. The damped sine wave output is characteristic of the sound design typically sought in electronic music production. The noise issues observed may stem from several potential sources, including inadequate power supply decoupling, grounding problems, or interference from external sources.
To address the noise, it is advisable to implement a more robust power supply filtering strategy. This can include adding additional bypass capacitors (both ceramic and electrolytic) close to the power pins of the operational amplifiers. A combination of smaller capacitors (e.g., 100nF ceramic) and larger electrolytic capacitors (e.g., 10µF to 100µF) can help filter high and low-frequency noise effectively.
Grounding practices also play a crucial role in minimizing noise. A star grounding configuration is recommended, where all ground connections converge at a single point, reducing ground loop issues. Ensuring that the signal ground and power ground are separated until they meet at the power supply can further reduce buzz and hum.
The buzzing sound when touching the potentiometers or wires suggests potential issues with shielding or grounding. Shielded cables should be used for any signal paths, particularly those that are susceptible to interference. Additionally, ensuring that the potentiometers are grounded properly and that their enclosures are connected to ground can help reduce this noise.
Lastly, if the circuit is susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI), consider placing the breadboard inside a metal enclosure or using a Faraday cage to shield it from external electromagnetic fields. This can significantly enhance the overall performance and sound quality of the circuit, providing a cleaner output with reduced noise and interference.It`s built on a breadboard and it sounds exactly how it should sound (damped sine wave, big 808/909-kind of kicks). However it`s noisy. I`ve tried adding a big electrolytic cap between V+ and GND. It makes difference yet it`s still very noisy. Also, the circuit tends to `buzz` when I touch the pots or a wire. Any idea how to kill that The whole circuit is powered from a split power supply from a switchable adaptor (I mean the op amp, the rest of the circuit is powered from 0-9V).
🔗 External reference