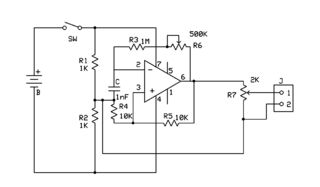
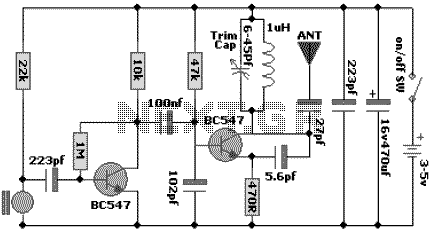
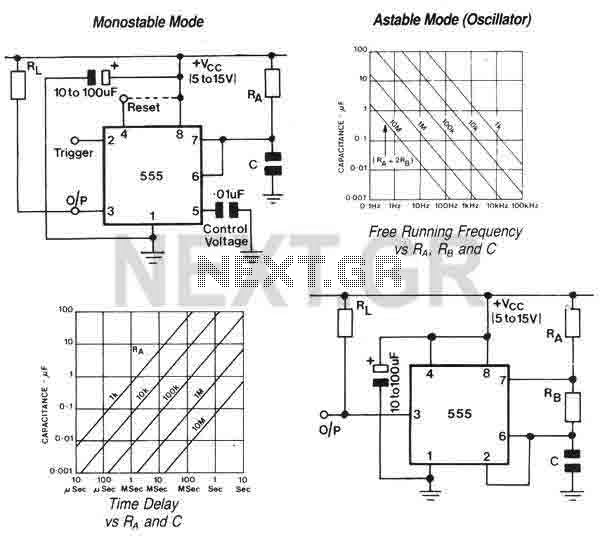
Opamp Wien-bridge oscillator
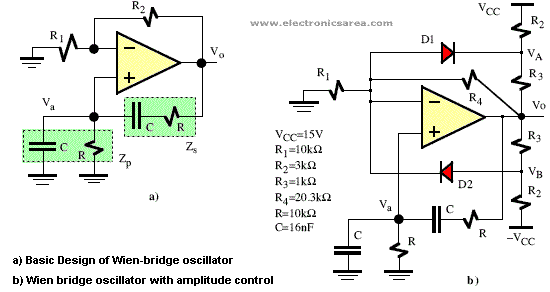
The Wien-bridge oscillator consists of an operational amplifier (OA) in a non-inverting configuration with a gain of 1 + R2/R1 and an RC feedback network.
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It employs a specific arrangement of resistors and capacitors to establish the frequency of oscillation. The core of the circuit is an operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting mode, which provides the necessary amplification for the oscillations to sustain.
In the basic configuration, the Wien-bridge oscillator includes two resistors (R1 and R2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a bridge circuit. The resistors and capacitors are selected such that they set the frequency of oscillation according to the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R \sqrt{C1 \cdot C2}} \]
where R is the resistance value chosen for R1 and R2. The gain of the operational amplifier is determined by the ratio of R2 to R1, which must be greater than three for stable oscillation. This gain condition ensures that the feedback network provides the right amount of positive feedback to sustain oscillations.
To maintain stable oscillations and prevent saturation of the operational amplifier, a light bulb or thermistor is often used as a variable resistor in the feedback loop. This component adjusts the gain dynamically, allowing the oscillator to stabilize at the desired amplitude.
The output of the Wien-bridge oscillator is a sine wave, which can be utilized in various applications, including signal generators, audio applications, and testing equipment. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice in both educational and professional settings for generating high-quality sine waves.The Wien-bridge oscillator, consists of an Operational Amplifier (OA) in a non-inverting configuration with gain 1 + R2/R1 and a RC feedback network.. 🔗 External reference
The Wien-bridge oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves. It employs a specific arrangement of resistors and capacitors to establish the frequency of oscillation. The core of the circuit is an operational amplifier configured in a non-inverting mode, which provides the necessary amplification for the oscillations to sustain.
In the basic configuration, the Wien-bridge oscillator includes two resistors (R1 and R2) and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a bridge circuit. The resistors and capacitors are selected such that they set the frequency of oscillation according to the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{2\pi R \sqrt{C1 \cdot C2}} \]
where R is the resistance value chosen for R1 and R2. The gain of the operational amplifier is determined by the ratio of R2 to R1, which must be greater than three for stable oscillation. This gain condition ensures that the feedback network provides the right amount of positive feedback to sustain oscillations.
To maintain stable oscillations and prevent saturation of the operational amplifier, a light bulb or thermistor is often used as a variable resistor in the feedback loop. This component adjusts the gain dynamically, allowing the oscillator to stabilize at the desired amplitude.
The output of the Wien-bridge oscillator is a sine wave, which can be utilized in various applications, including signal generators, audio applications, and testing equipment. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice in both educational and professional settings for generating high-quality sine waves.The Wien-bridge oscillator, consists of an Operational Amplifier (OA) in a non-inverting configuration with gain 1 + R2/R1 and a RC feedback network.. 🔗 External reference