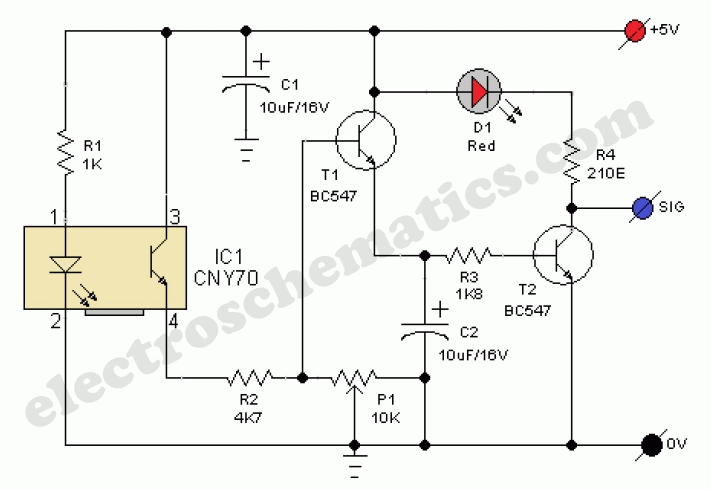
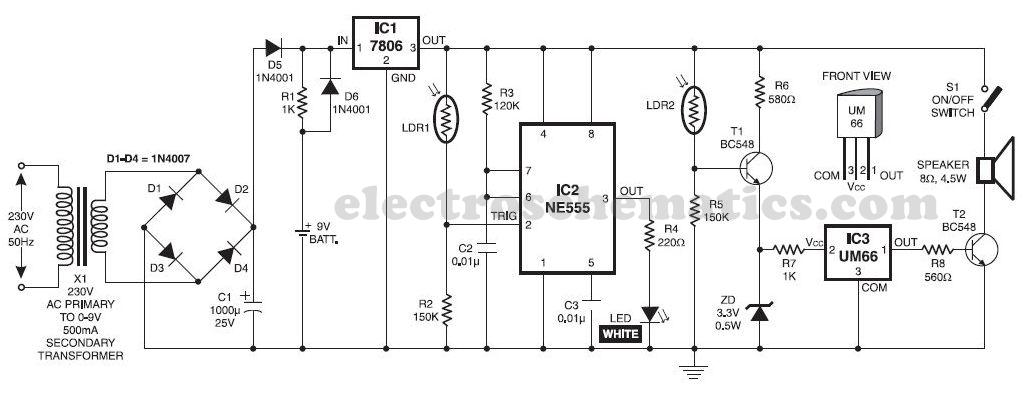
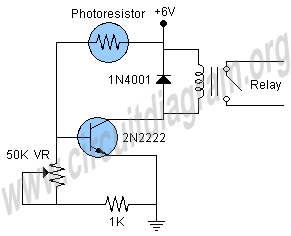
Open doors and windows automatic laser beam control circuit
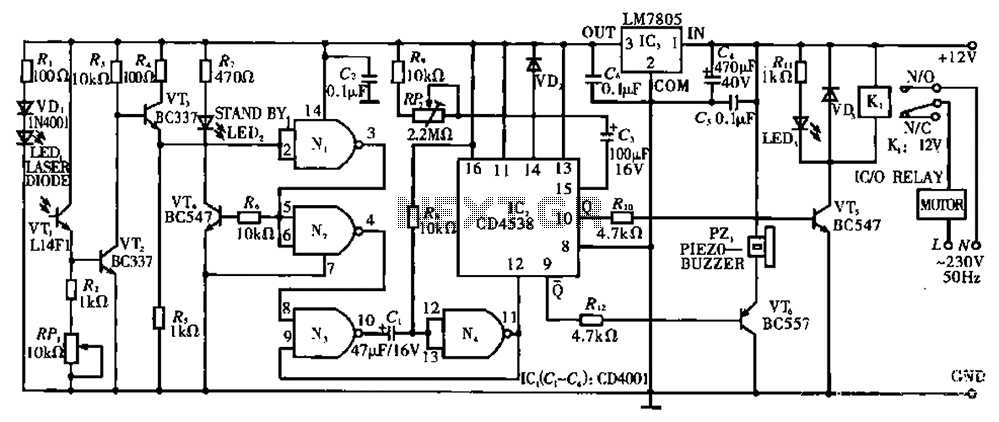
Circuit T operates on the principle of utilizing a laser diode LED as a light emitter. This circuit incorporates a laser diode that serves similar functions as a light-emitting diode. It features a resistor (R) and a diode (VD) that protect the laser diode from excessive current. Additionally, a multi-loop trimming potentiometer (RP) is included to adjust the sensitivity of the laser. Under normal conditions, when the laser beam strikes a phototransistor (VT), it causes conduction in VT, leading to a zero base potential at VT3 (zero bias). Consequently, the emitter potential of VT3 is also zero. This zero potential is applied to the first gate of an integrated circuit (CD4001), resulting in a high output. Furthermore, the high resistance of transistor VT4 allows it to conduct, illuminating a green LED. At this point, the circuit remains in a standby state, awaiting further action.
The described circuit T employs a laser diode LED as a primary light source, functioning effectively as both a laser and a light-emitting diode. The inclusion of a resistor (R) and a protection diode (VD) is crucial for safeguarding the laser diode from current surges, which could otherwise damage the component. The multi-loop trimming potentiometer (RP) serves as an adjustable element, allowing users to fine-tune the sensitivity of the laser detection system according to specific requirements or environmental conditions.
In operation, when the laser beam is directed towards the phototransistor (VT), it triggers conduction in the device. This conduction results in a zero base potential at VT3, indicating that the phototransistor is effectively responding to the laser light. The emitter of VT3 also reaches a zero potential, which is then fed into the first gate of the CD4001 integrated circuit. The logic gate interprets this zero potential as a high output signal.
The high output from the CD4001 is pivotal for the subsequent operation of the circuit. It facilitates the conduction of transistor VT4, which is connected in such a way that it can amplify the output signal. The conduction of VT4 leads to the activation of a green LED, providing a visual indication of the system's readiness or standby state. This feature enhances user interaction by signaling that the circuit is operational and awaiting further input.
Overall, Circuit T exemplifies a well-designed electronic system that integrates a laser diode, phototransistor, and logic gate to create a responsive light detection mechanism. The careful selection of components and the inclusion of protective measures ensure reliability and functionality in various applications. Circuit T as principle: In this circuit, a laser diode LED, as a light hair emitter, in addition to other properties may also be used similar light emitter laser diode substitu tion pipe. Resistor R. And diode VD, as the laser diode current protection circuit, multi- loop trimming potentiometer RP, for adjusting the sensitivity of the laser. Under normal circumstances, when a laser beam is irradiated to a phototransistor VT. When on, VTz conduction, VT3 base potential is zero (VL zero bias), VT3 deadline, its emitter potential is zero.
The zero potential applied to the IC. (CD4001) first gate N, the input of the results of N. The output is high. But also through the high resistance of the transistor VT4 added to the base so that VT4 conduction, so that the green LED, lights up. In this case the circuit is in a standby state waiting.
The described circuit T employs a laser diode LED as a primary light source, functioning effectively as both a laser and a light-emitting diode. The inclusion of a resistor (R) and a protection diode (VD) is crucial for safeguarding the laser diode from current surges, which could otherwise damage the component. The multi-loop trimming potentiometer (RP) serves as an adjustable element, allowing users to fine-tune the sensitivity of the laser detection system according to specific requirements or environmental conditions.
In operation, when the laser beam is directed towards the phototransistor (VT), it triggers conduction in the device. This conduction results in a zero base potential at VT3, indicating that the phototransistor is effectively responding to the laser light. The emitter of VT3 also reaches a zero potential, which is then fed into the first gate of the CD4001 integrated circuit. The logic gate interprets this zero potential as a high output signal.
The high output from the CD4001 is pivotal for the subsequent operation of the circuit. It facilitates the conduction of transistor VT4, which is connected in such a way that it can amplify the output signal. The conduction of VT4 leads to the activation of a green LED, providing a visual indication of the system's readiness or standby state. This feature enhances user interaction by signaling that the circuit is operational and awaiting further input.
Overall, Circuit T exemplifies a well-designed electronic system that integrates a laser diode, phototransistor, and logic gate to create a responsive light detection mechanism. The careful selection of components and the inclusion of protective measures ensure reliability and functionality in various applications. Circuit T as principle: In this circuit, a laser diode LED, as a light hair emitter, in addition to other properties may also be used similar light emitter laser diode substitu tion pipe. Resistor R. And diode VD, as the laser diode current protection circuit, multi- loop trimming potentiometer RP, for adjusting the sensitivity of the laser. Under normal circumstances, when a laser beam is irradiated to a phototransistor VT. When on, VTz conduction, VT3 base potential is zero (VL zero bias), VT3 deadline, its emitter potential is zero.
The zero potential applied to the IC. (CD4001) first gate N, the input of the results of N. The output is high. But also through the high resistance of the transistor VT4 added to the base so that VT4 conduction, so that the green LED, lights up. In this case the circuit is in a standby state waiting.