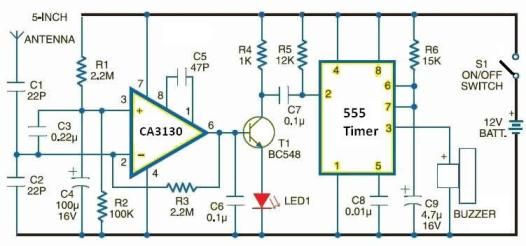
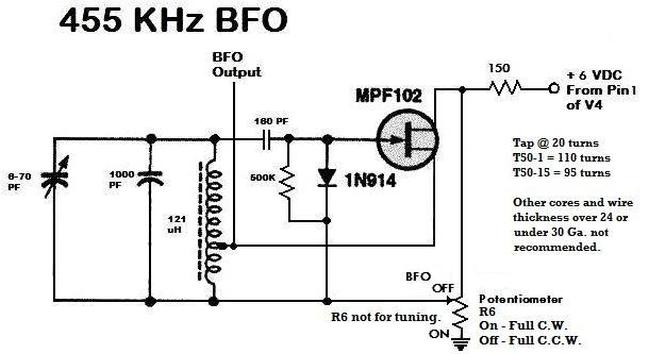
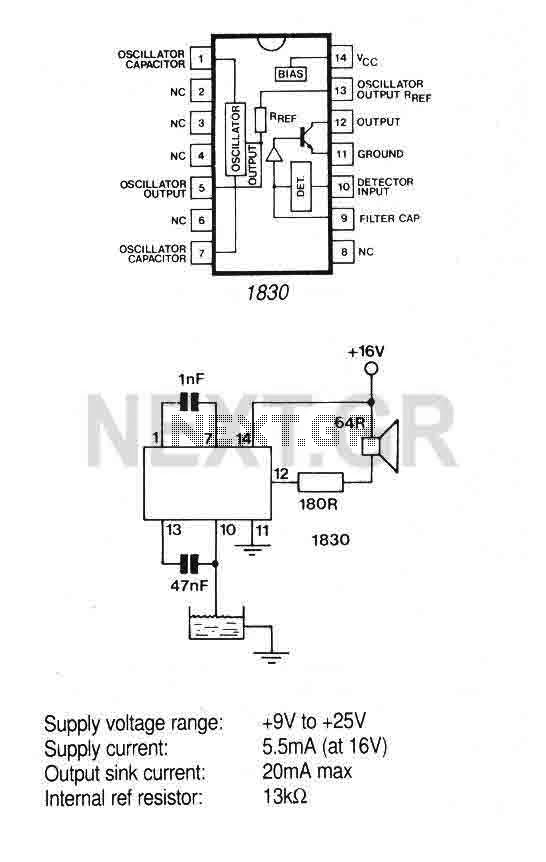
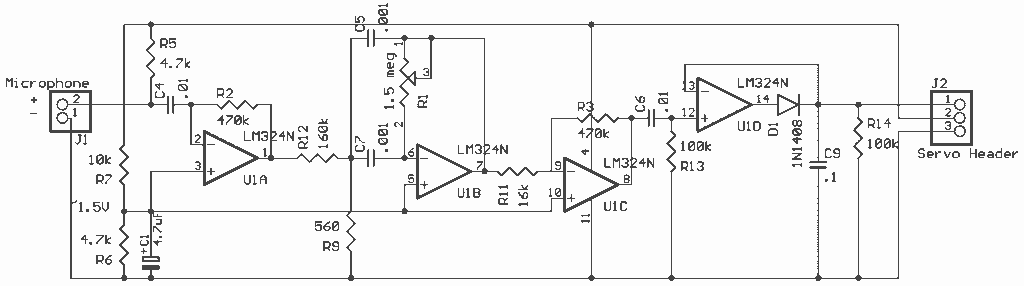
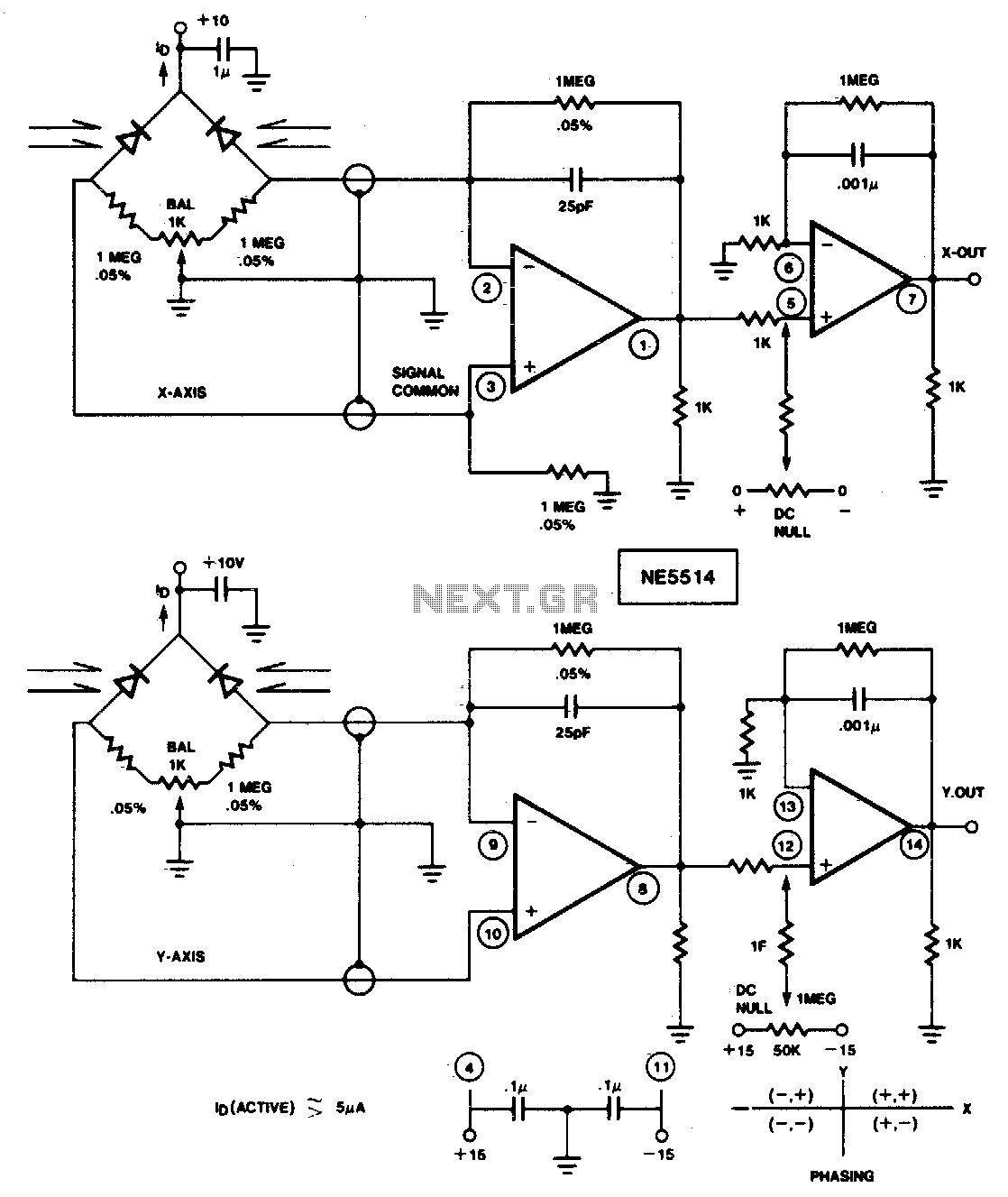
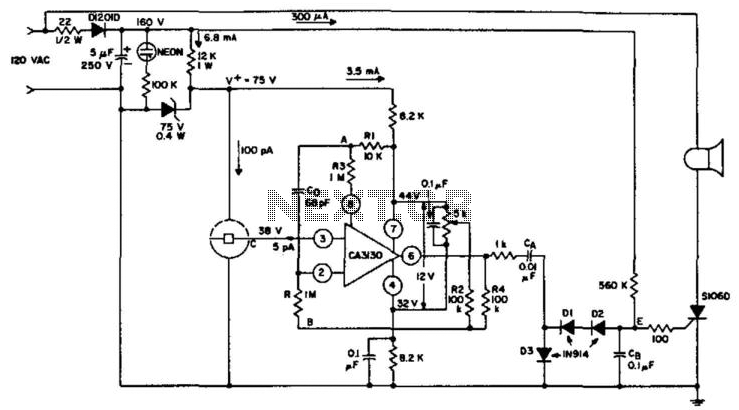
Optical Pyrometer Detect The Spectrum Composition
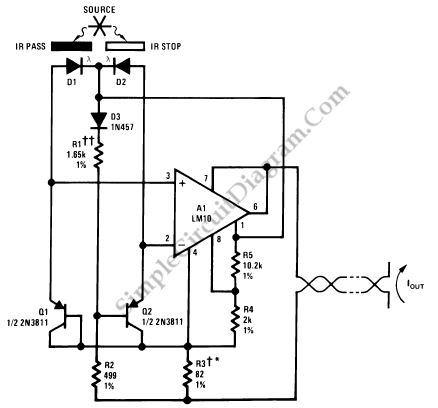
This pyrometer is used to measure the temperature of an incandescent body. The principle behind this measurement is that the hotter the body, the spectrum of the emitted radiation will shift.
A pyrometer is a non-contact temperature measurement device that operates based on the principle of thermal radiation. It is particularly useful for measuring the temperatures of objects that are too hot to touch or are located in hazardous environments. The operation of a pyrometer is based on Planck's law of blackbody radiation, which states that the intensity of radiation emitted by a body at a certain temperature is dependent on the wavelength of the radiation.
In practical applications, a pyrometer detects the infrared radiation emitted by an incandescent body. As the temperature of the body increases, it emits radiation at shorter wavelengths, which corresponds to a higher temperature. The pyrometer typically consists of an optical system, a detector, and a signal processing unit. The optical system collects the emitted radiation and focuses it onto a detector, which converts the infrared radiation into an electrical signal.
The signal processing unit then analyzes this electrical signal to determine the temperature of the incandescent body. Calibration of the pyrometer is essential to ensure accuracy, as different materials emit radiation differently. Various types of pyrometers exist, including optical, infrared, and ratio pyrometers, each suited for specific temperature ranges and applications.
In industrial settings, pyrometers are commonly used in processes such as metal forging, glass manufacturing, and ceramics production, where precise temperature control is critical for product quality. The ability to measure temperature without direct contact allows for greater safety and efficiency in these high-temperature environments.This pyrometer is used to measure an incandescent body. The principle for this measurement is that the hotter the body, the spectrum of the radiation will.. 🔗 External reference
A pyrometer is a non-contact temperature measurement device that operates based on the principle of thermal radiation. It is particularly useful for measuring the temperatures of objects that are too hot to touch or are located in hazardous environments. The operation of a pyrometer is based on Planck's law of blackbody radiation, which states that the intensity of radiation emitted by a body at a certain temperature is dependent on the wavelength of the radiation.
In practical applications, a pyrometer detects the infrared radiation emitted by an incandescent body. As the temperature of the body increases, it emits radiation at shorter wavelengths, which corresponds to a higher temperature. The pyrometer typically consists of an optical system, a detector, and a signal processing unit. The optical system collects the emitted radiation and focuses it onto a detector, which converts the infrared radiation into an electrical signal.
The signal processing unit then analyzes this electrical signal to determine the temperature of the incandescent body. Calibration of the pyrometer is essential to ensure accuracy, as different materials emit radiation differently. Various types of pyrometers exist, including optical, infrared, and ratio pyrometers, each suited for specific temperature ranges and applications.
In industrial settings, pyrometers are commonly used in processes such as metal forging, glass manufacturing, and ceramics production, where precise temperature control is critical for product quality. The ability to measure temperature without direct contact allows for greater safety and efficiency in these high-temperature environments.This pyrometer is used to measure an incandescent body. The principle for this measurement is that the hotter the body, the spectrum of the radiation will.. 🔗 External reference