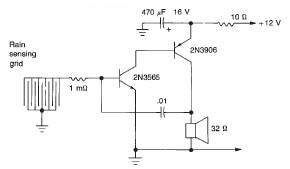
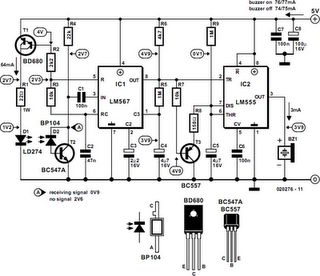
Fluid Level Detector (LM1830N)
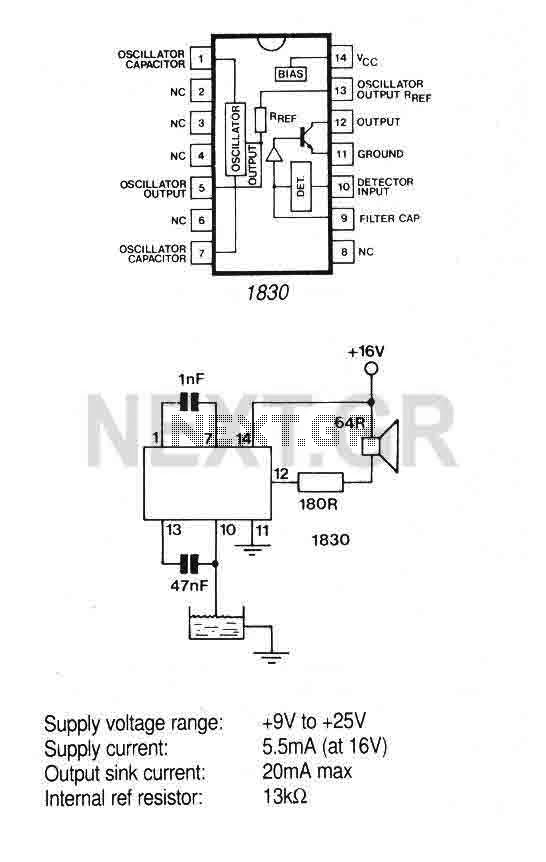
The IC is ideal for detecting the presence, absence or level of water or other conducting liquids. A detector determines the presence or absence of fluid by comparing the resistance of the fluid with the IC's internal reference resistance. An AC signal is used to prevent plating of the probe. When the probe resistance increases the loudspeaker will emit a 500Hz tone. Alternatively an LED could be connected.
The integrated circuit (IC) described functions as a fluid detection system, specifically designed to identify the presence, absence, or level of conductive liquids such as water. The core operation of the IC relies on a resistance measurement technique, where it continuously compares the resistance of the detected fluid against a predefined internal reference resistance. This comparative analysis allows the IC to ascertain whether the fluid is present or not based on changes in resistance.
To ensure reliable operation and to mitigate issues such as electrolysis or probe plating, the IC employs an alternating current (AC) signal for the detection mechanism. The AC signal helps to maintain the integrity of the probe over prolonged usage, which is critical in applications where the probe is immersed in liquid for extended periods.
When the resistance of the fluid increases—indicating a decrease in conductivity, which may occur when the fluid level falls or when the probe is exposed to non-conductive substances—the IC triggers an output signal. This output can be configured to drive a loudspeaker, which produces a 500Hz tone, providing an audible alert to the user regarding the fluid status.
Additionally, the circuit can be adapted to include a light-emitting diode (LED) as an alternative output indicator. In this configuration, the LED would illuminate in response to changes in fluid resistance, providing a visual cue alongside or instead of the audible signal. This dual-output capability enhances the versatility of the fluid detection system, allowing it to be used in various applications, including water level monitoring in tanks, leak detection systems, and other scenarios where liquid presence is critical.
The overall design can be implemented using a straightforward circuit layout that includes the IC, the detection probe, a power supply, and output devices such as a loudspeaker or LED. Proper component selection and circuit design will ensure optimal performance and reliability in detecting conductive liquids.The IC is ideal for detecting the presence, absence or level of water or other conducting liquids. A detector determines the presence or absence of fluid by comparing the resistance of the fluid with the IC's internal reference resistance. An AC signal is used to prevent plating of the probe. When the probe resistance increases the loudspeaker will emit a 500Hz tone. Alternatively an LED could be connected. 🔗 External reference
The integrated circuit (IC) described functions as a fluid detection system, specifically designed to identify the presence, absence, or level of conductive liquids such as water. The core operation of the IC relies on a resistance measurement technique, where it continuously compares the resistance of the detected fluid against a predefined internal reference resistance. This comparative analysis allows the IC to ascertain whether the fluid is present or not based on changes in resistance.
To ensure reliable operation and to mitigate issues such as electrolysis or probe plating, the IC employs an alternating current (AC) signal for the detection mechanism. The AC signal helps to maintain the integrity of the probe over prolonged usage, which is critical in applications where the probe is immersed in liquid for extended periods.
When the resistance of the fluid increases—indicating a decrease in conductivity, which may occur when the fluid level falls or when the probe is exposed to non-conductive substances—the IC triggers an output signal. This output can be configured to drive a loudspeaker, which produces a 500Hz tone, providing an audible alert to the user regarding the fluid status.
Additionally, the circuit can be adapted to include a light-emitting diode (LED) as an alternative output indicator. In this configuration, the LED would illuminate in response to changes in fluid resistance, providing a visual cue alongside or instead of the audible signal. This dual-output capability enhances the versatility of the fluid detection system, allowing it to be used in various applications, including water level monitoring in tanks, leak detection systems, and other scenarios where liquid presence is critical.
The overall design can be implemented using a straightforward circuit layout that includes the IC, the detection probe, a power supply, and output devices such as a loudspeaker or LED. Proper component selection and circuit design will ensure optimal performance and reliability in detecting conductive liquids.The IC is ideal for detecting the presence, absence or level of water or other conducting liquids. A detector determines the presence or absence of fluid by comparing the resistance of the fluid with the IC's internal reference resistance. An AC signal is used to prevent plating of the probe. When the probe resistance increases the loudspeaker will emit a 500Hz tone. Alternatively an LED could be connected. 🔗 External reference