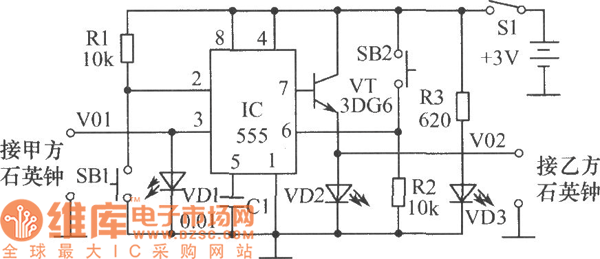
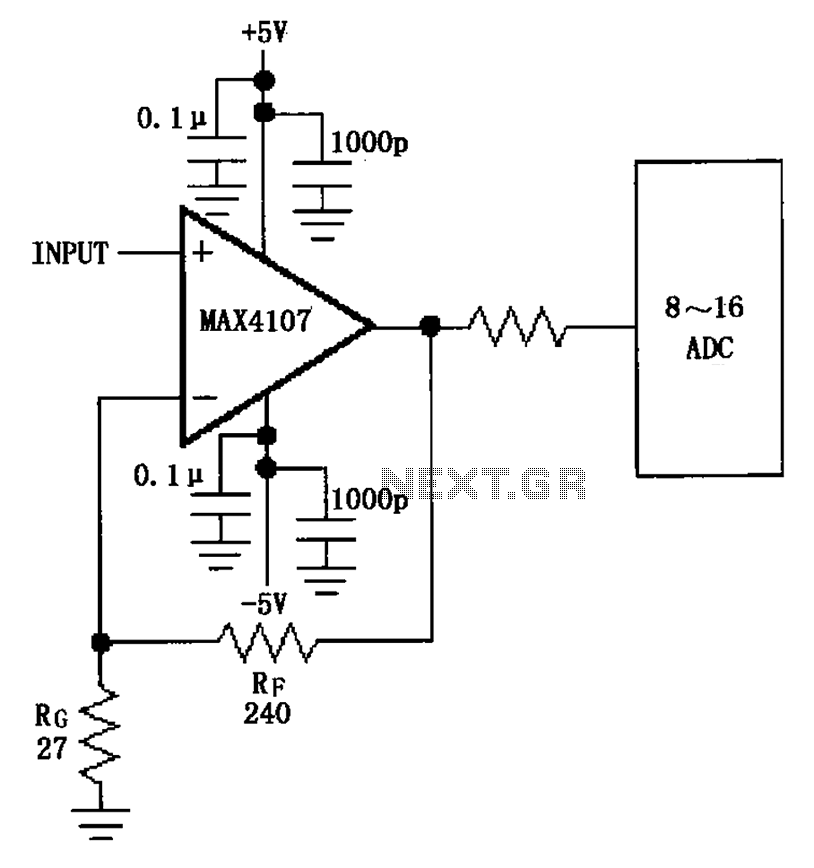
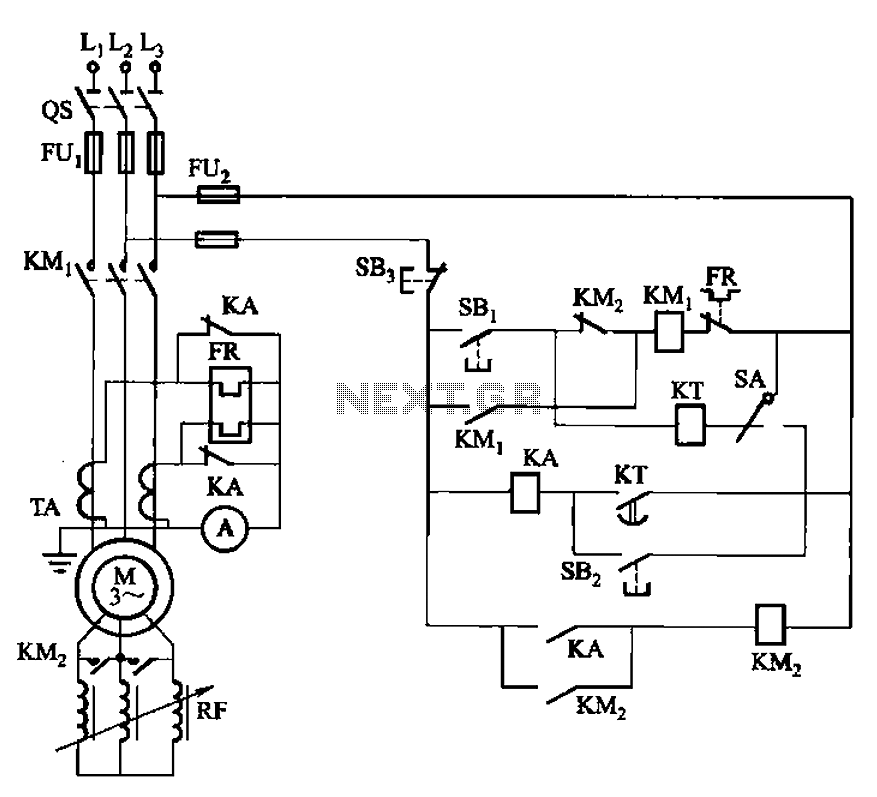
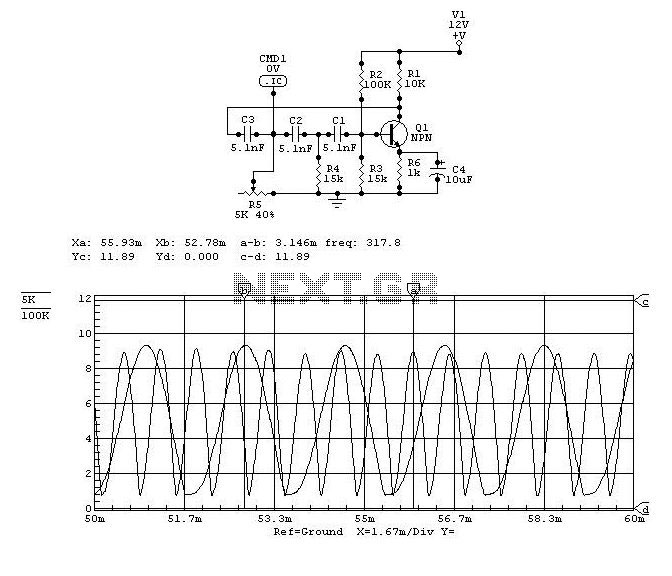
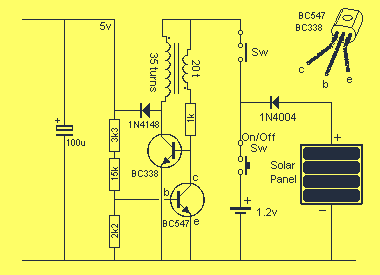
Optical safety switch circuit diagram
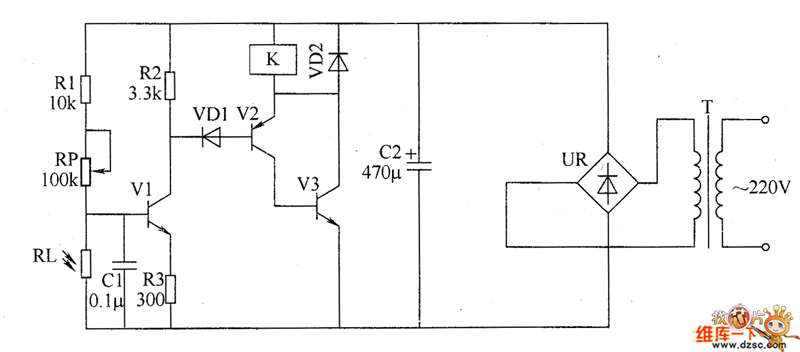
The optical safety switch circuit includes a power supply circuit, a light control circuit, and a control implementation circuit (switch circuit). The power circuit is made up of a power transformer (T), a bridge rectifier (UR), and a filter capacitor (C2). The light control circuit consists of a photosensitive resistor (RL), resistors (R1 to R3), a potentiometer (RP), a transistor (V1), and a capacitor (C1). The control implementation circuit is composed of diodes (VD1 and VD2), transistors (V2 and V3), and a relay (K). The AC 220V voltage is stepped down by transformer T, filtered by UR, and rectified by C2 to provide a 6V DC voltage for both the light control circuit and the control implementation circuit. Resistors R1 to R3 can be either 1/4W carbon or metal film types, while RP can be a variable potentiometer or a solid film variable resistor.
The optical safety switch circuit is designed to enhance safety in electronic systems by utilizing light-sensitive components to control the operation of a relay. The configuration begins with the power supply circuit, which plays a critical role in converting the high-voltage AC input (220V) into a usable low-voltage DC output (6V). The transformer (T) steps down the voltage, while the bridge rectifier (UR) converts the AC voltage into DC. The filter capacitor (C2) smooths the rectified output, ensuring a stable DC voltage supply.
In the light control circuit, the photosensitive resistor (RL) detects ambient light levels, adjusting the circuit's response based on light intensity. The resistors (R1 to R3) and the potentiometer (RP) form a voltage divider network that calibrates the sensitivity of the light detection. The transistor (V1) acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current based on the voltage received from the light control circuit. The capacitor (C1) may be used for stability and filtering purposes, further refining the control signal.
The control implementation circuit is responsible for executing the action based on the control signal. Diodes (VD1 and VD2) are used to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the relay (K) during operation. Transistors (V2 and V3) amplify the control signal to drive the relay, which can connect or disconnect a load based on the light conditions detected by the light control circuit.
Overall, this optical safety switch circuit is a robust solution for applications requiring automatic control based on light levels, enhancing operational safety and efficiency in various electronic devices.The optical safety switch circuit consists of the power supply circuit, light control circuit and control implementation circuit (switch circuit), the circuit is shown as the chart. Power circuit is composed of the power transformer T, bridge rectifier UR and filter capacitor C2. Light control circuit is composed of the photosensitive resistor RL, resistors R1 ~ R3, potentiometer RP, transistor V1 and capacitor C1. Control implementation circuit consists of the diodes VD1 and VD2, transistors V2 and V3 and the relay K. AC 220Y voltage bucked by T, filtered by UR and rectified by C2 can provide 6V DC voltage for light control circuit and control implementation circuit.
R1 ~ R3 use potentiometer l/4W carbon or metal film resistors. RP selects variable potentiometer or solid film variable resistor. 🔗 External reference
The optical safety switch circuit is designed to enhance safety in electronic systems by utilizing light-sensitive components to control the operation of a relay. The configuration begins with the power supply circuit, which plays a critical role in converting the high-voltage AC input (220V) into a usable low-voltage DC output (6V). The transformer (T) steps down the voltage, while the bridge rectifier (UR) converts the AC voltage into DC. The filter capacitor (C2) smooths the rectified output, ensuring a stable DC voltage supply.
In the light control circuit, the photosensitive resistor (RL) detects ambient light levels, adjusting the circuit's response based on light intensity. The resistors (R1 to R3) and the potentiometer (RP) form a voltage divider network that calibrates the sensitivity of the light detection. The transistor (V1) acts as a switch, controlling the flow of current based on the voltage received from the light control circuit. The capacitor (C1) may be used for stability and filtering purposes, further refining the control signal.
The control implementation circuit is responsible for executing the action based on the control signal. Diodes (VD1 and VD2) are used to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by the relay (K) during operation. Transistors (V2 and V3) amplify the control signal to drive the relay, which can connect or disconnect a load based on the light conditions detected by the light control circuit.
Overall, this optical safety switch circuit is a robust solution for applications requiring automatic control based on light levels, enhancing operational safety and efficiency in various electronic devices.The optical safety switch circuit consists of the power supply circuit, light control circuit and control implementation circuit (switch circuit), the circuit is shown as the chart. Power circuit is composed of the power transformer T, bridge rectifier UR and filter capacitor C2. Light control circuit is composed of the photosensitive resistor RL, resistors R1 ~ R3, potentiometer RP, transistor V1 and capacitor C1. Control implementation circuit consists of the diodes VD1 and VD2, transistors V2 and V3 and the relay K. AC 220Y voltage bucked by T, filtered by UR and rectified by C2 can provide 6V DC voltage for light control circuit and control implementation circuit.
R1 ~ R3 use potentiometer l/4W carbon or metal film resistors. RP selects variable potentiometer or solid film variable resistor. 🔗 External reference