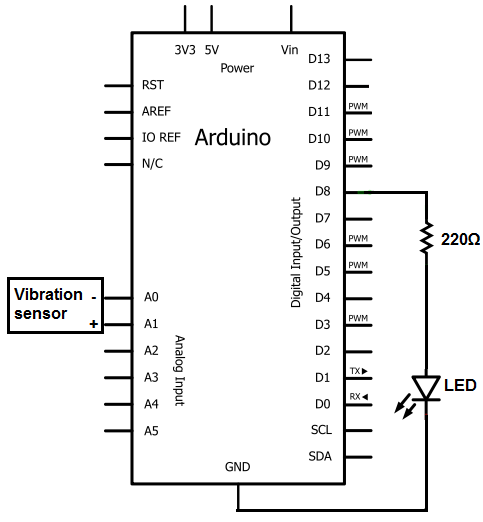
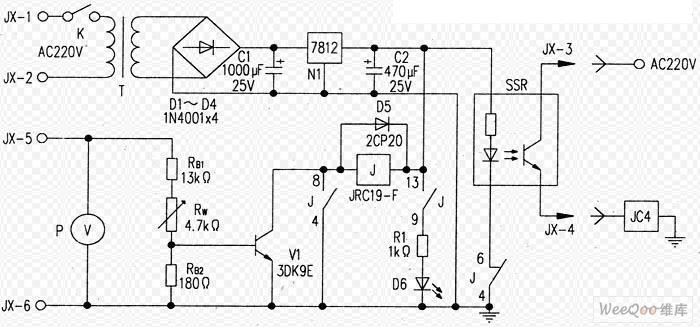
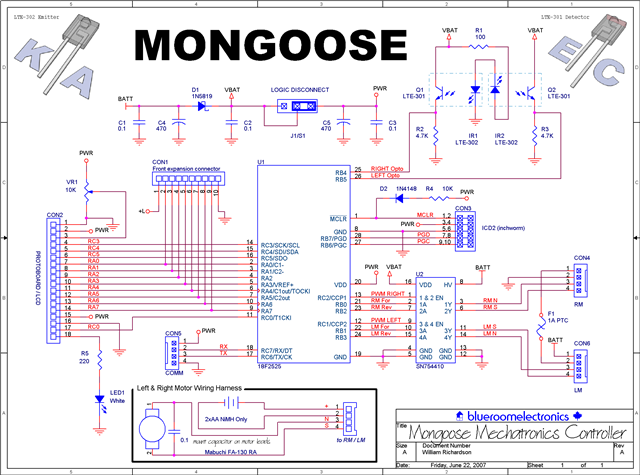
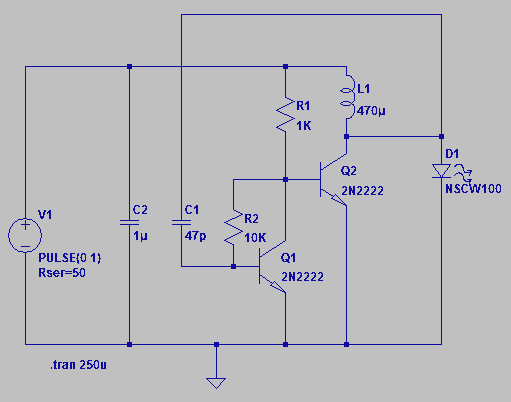
Optional Flip inverter circuit
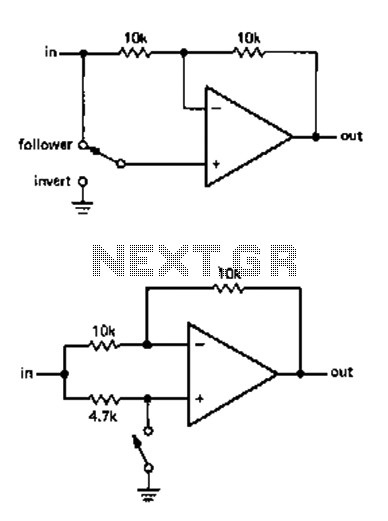
The circuit allows for the reversal or flipping of switch amplification without inversion. The voltage gain is dependent on the position of the switch, which can be either +1 or -1. There are two versions of the circuit, A and B, with a preference for version B due to its stability. In one version, flipping the switch may cause the non-inverting input to temporarily float, leading to unpredictable voltage induction through the wiring, which can result in audible disturbances such as clicks or murmurs. This phase inverter circuit provides polarity control, which is particularly useful for multi-channel audio power amplifiers. This functionality allows for the correction of speaker wiring or installation errors by using a switch instead of reconnecting cables.
The described circuit functions as a phase inverter, facilitating the reversal of audio signals while maintaining control over the amplification characteristics. The operation of this circuit hinges on a switch that determines the output polarity, thereby influencing the voltage gain. The two versions of the circuit, A and B, present distinct approaches to achieving this function. Version B is favored for its reduced susceptibility to noise and instability, particularly in scenarios where the non-inverting input may not have a defined voltage level.
In version A, the potential issue arises when the switch is engaged, causing the non-inverting input to float temporarily. This floating condition can induce unpredictable voltages through the switch's wiring, leading to audible artifacts that may compromise the audio quality. Such disturbances manifest as hard clicks or murmurs, which are undesirable in professional audio applications.
The phase inverter circuit is crucial in audio power amplification systems, especially in multi-channel setups where maintaining the correct polarity of signals is essential for optimal performance. By implementing this circuit, users can easily rectify wiring errors or misconfigurations in speaker connections. Instead of physically reconnecting cables, the user can simply toggle the switch, providing a practical and efficient solution to phase issues in audio systems. This design consideration enhances the usability and flexibility of audio equipment, ensuring reliable operation in various configurations.Use the circuit shown we can reverse or flip the switch amplification without inversion. Voltage gain depending on the position of the switch. This may be +1 or -1. Changing circuit has two versions, A and B. I personally prefer B type, because there is no non-inverting input voltage level is uncertain at the moment. In one version, when the switch is flipped, with the non-inverting input is temporary floating, which may lead to unpredictable voltage indu1ced through the wiring of the switch, so that the hard click or murmur. This phase inverter circuit provides a polarity control is useful, for example, many channel audio power amplifier supplied (or queen Only) This function flips stage situation with a speaker wiring or installation error, because it is easier push a switch, instead of re-connecting cable.
The described circuit functions as a phase inverter, facilitating the reversal of audio signals while maintaining control over the amplification characteristics. The operation of this circuit hinges on a switch that determines the output polarity, thereby influencing the voltage gain. The two versions of the circuit, A and B, present distinct approaches to achieving this function. Version B is favored for its reduced susceptibility to noise and instability, particularly in scenarios where the non-inverting input may not have a defined voltage level.
In version A, the potential issue arises when the switch is engaged, causing the non-inverting input to float temporarily. This floating condition can induce unpredictable voltages through the switch's wiring, leading to audible artifacts that may compromise the audio quality. Such disturbances manifest as hard clicks or murmurs, which are undesirable in professional audio applications.
The phase inverter circuit is crucial in audio power amplification systems, especially in multi-channel setups where maintaining the correct polarity of signals is essential for optimal performance. By implementing this circuit, users can easily rectify wiring errors or misconfigurations in speaker connections. Instead of physically reconnecting cables, the user can simply toggle the switch, providing a practical and efficient solution to phase issues in audio systems. This design consideration enhances the usability and flexibility of audio equipment, ensuring reliable operation in various configurations.Use the circuit shown we can reverse or flip the switch amplification without inversion. Voltage gain depending on the position of the switch. This may be +1 or -1. Changing circuit has two versions, A and B. I personally prefer B type, because there is no non-inverting input voltage level is uncertain at the moment. In one version, when the switch is flipped, with the non-inverting input is temporary floating, which may lead to unpredictable voltage indu1ced through the wiring of the switch, so that the hard click or murmur. This phase inverter circuit provides a polarity control is useful, for example, many channel audio power amplifier supplied (or queen Only) This function flips stage situation with a speaker wiring or installation error, because it is easier push a switch, instead of re-connecting cable.