Oscillator with frequency doubled output
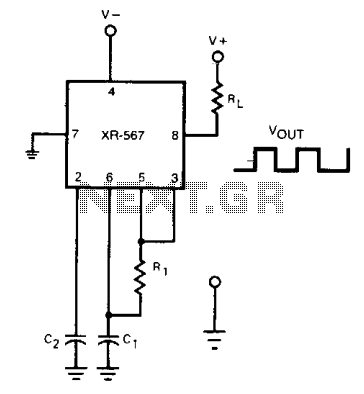
The frequency of the current-controlled oscillator can be doubled by feeding a portion of the square-wave output from pin 5 back to the input at pin 3. This configuration allows the quadrature detector to operate as a frequency doubler, resulting in an output of 2 f0 at pin 8.
The current-controlled oscillator (CCO) operates by generating an output frequency that is dependent on an external control current. In this specific configuration, the feedback mechanism is crucial for frequency doubling. By connecting a portion of the output from pin 5 back to pin 3, the oscillator can effectively double its output frequency. This feedback creates a condition where the oscillator's output frequency becomes twice the original frequency, denoted as 2 f0.
The quadrature detector plays an essential role in this process. It is designed to detect phase differences and can thus be utilized as a frequency doubler in this application. The output from the quadrature detector at pin 8 reflects the doubled frequency, enabling various applications that require higher frequency signals.
In practical implementations, careful consideration should be given to the values of the components involved in the feedback loop, as they will influence the stability and performance of the oscillator. Additionally, the characteristics of the square-wave output must be analyzed to ensure that the feedback does not introduce unwanted harmonics or distortions that could affect the integrity of the doubled frequency output. Proper tuning and calibration of the circuit may be necessary to achieve optimal performance.The current-controlled oscillator frequency can be doubled by applying a portion of the square-wave output at pin 5 back to the input at pin 3, as shown. In this manner, the quadrature detector functions as a frequency doubier and produces an output of 2 f0 at pin 8. 🔗 External reference
The current-controlled oscillator (CCO) operates by generating an output frequency that is dependent on an external control current. In this specific configuration, the feedback mechanism is crucial for frequency doubling. By connecting a portion of the output from pin 5 back to pin 3, the oscillator can effectively double its output frequency. This feedback creates a condition where the oscillator's output frequency becomes twice the original frequency, denoted as 2 f0.
The quadrature detector plays an essential role in this process. It is designed to detect phase differences and can thus be utilized as a frequency doubler in this application. The output from the quadrature detector at pin 8 reflects the doubled frequency, enabling various applications that require higher frequency signals.
In practical implementations, careful consideration should be given to the values of the components involved in the feedback loop, as they will influence the stability and performance of the oscillator. Additionally, the characteristics of the square-wave output must be analyzed to ensure that the feedback does not introduce unwanted harmonics or distortions that could affect the integrity of the doubled frequency output. Proper tuning and calibration of the circuit may be necessary to achieve optimal performance.The current-controlled oscillator frequency can be doubled by applying a portion of the square-wave output at pin 5 back to the input at pin 3, as shown. In this manner, the quadrature detector functions as a frequency doubier and produces an output of 2 f0 at pin 8. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713