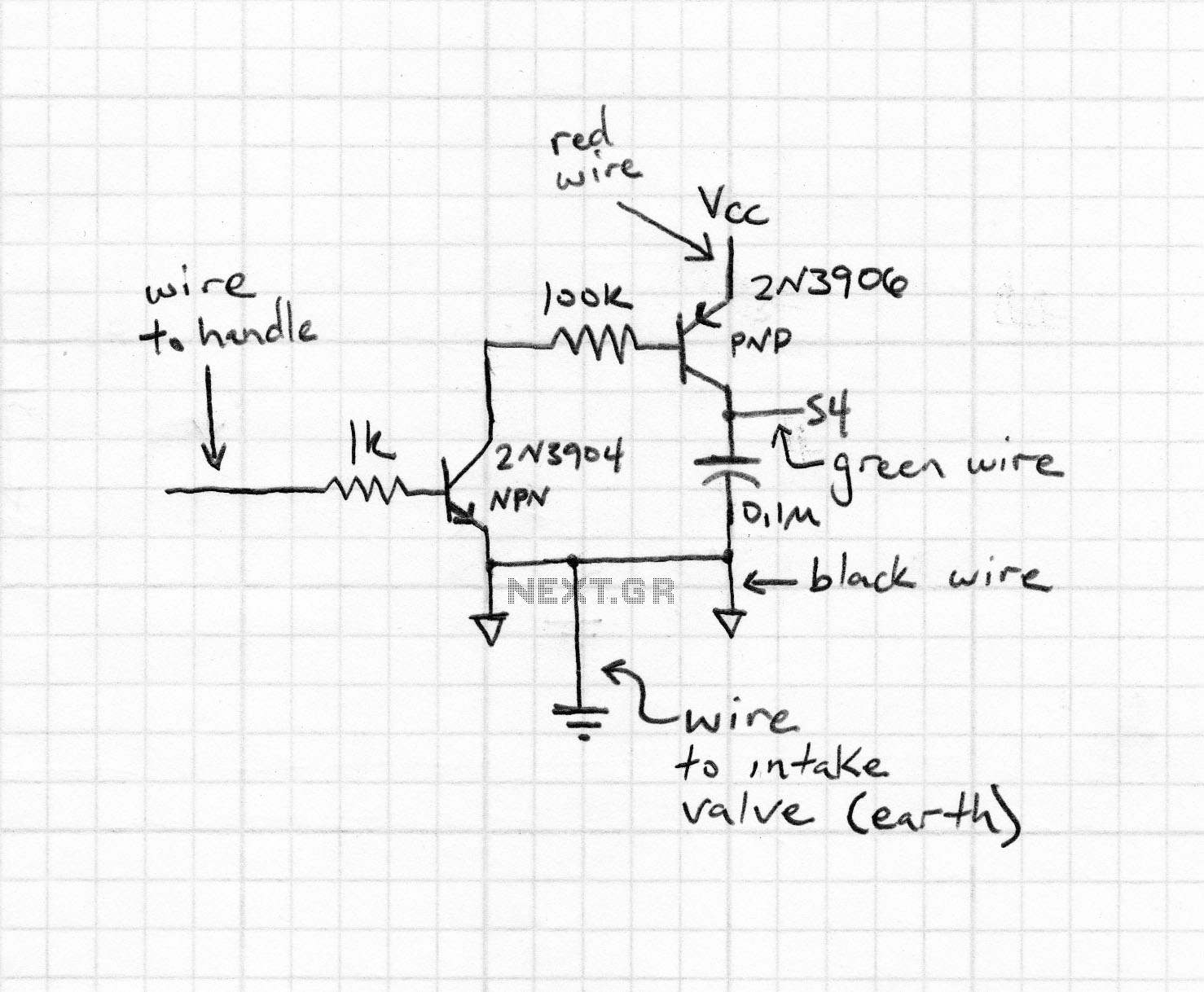
peak detector
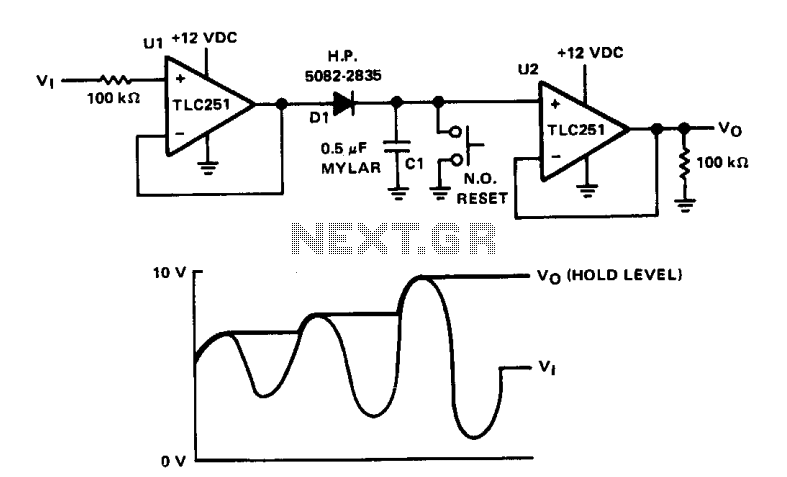
The circuit is designed to capture and hold the peak input voltage on capacitor C1, allowing the output voltage V0 to be read at the output of operational amplifier U2. Operational amplifiers U1 and U2 are configured as voltage followers. When a signal is applied to input Vj, capacitor C1 charges to the same voltage through diode D1. The positive peak voltage on C1 maintains the output voltage V0 at this level until the capacitor is reset (shorted). Higher positive peaks will increase this level, while lower peaks will be disregarded. C1 can be reset manually using a switch or electronically with a normally off FET. The capacitor selected for C1 should exhibit low leakage and low dielectric absorption, and diode D1 should also have low leakage. To detect peak values of negative polarity signals, diode D1 can be reversed.
The circuit operates by utilizing two operational amplifiers, U1 and U2, configured as voltage followers to ensure that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage without loading the circuit. The input voltage, applied at Vj, is directed to capacitor C1 through diode D1. The diode allows current to flow in one direction, ensuring that C1 charges to the peak voltage level of the input signal. This configuration is essential for maintaining the peak voltage on C1, which is crucial for applications requiring peak detection.
Capacitor C1 must be chosen carefully to minimize leakage current and dielectric absorption, which can affect the accuracy of the peak voltage held. Low leakage ensures that the capacitor does not discharge significantly over time, while low dielectric absorption prevents the capacitor from retaining unwanted charge, which could lead to erroneous readings.
The reset functionality is an important aspect of this circuit. It allows the stored peak voltage to be cleared either manually or electronically. A manual reset can be implemented using a switch that short-circuits C1, discharging it completely. Alternatively, an electronic reset can be achieved using a field-effect transistor (FET) that is normally off. When triggered, the FET will conduct, effectively discharging C1 and allowing for a new peak voltage to be captured.
To detect negative peak values, diode D1 can be reversed, allowing negative voltages to charge C1. This flexibility enhances the circuit's utility in applications where both positive and negative peak detection is necessary.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable means of capturing and holding peak voltages, with considerations for reset mechanisms and component selection critical to its performance.The purpose of the circuit is to hold the peak of the input voltage on capacitor Cl, and read the value, V0, at the output of U2. Op amps Ul and U2 are connected as voltage followers. When a signal is applied to Vj, Cl will charge to this same voltage through diode Dl. This positive peak voltage on Cl will maintain V0 at this level until the capacitor is reset (shorted).
Of course, higher positive peaks will raise this level while lower power peaks will be ignored. Cl can be reset manually with a switch, or electronically with an FET that is normally off. The capacitor specified for Cl should have low leakage and low dielectric absorption. Diode Dl should also have low leakage. Peak values of negative polarity signals may be detected by reversing Dl.
The circuit operates by utilizing two operational amplifiers, U1 and U2, configured as voltage followers to ensure that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage without loading the circuit. The input voltage, applied at Vj, is directed to capacitor C1 through diode D1. The diode allows current to flow in one direction, ensuring that C1 charges to the peak voltage level of the input signal. This configuration is essential for maintaining the peak voltage on C1, which is crucial for applications requiring peak detection.
Capacitor C1 must be chosen carefully to minimize leakage current and dielectric absorption, which can affect the accuracy of the peak voltage held. Low leakage ensures that the capacitor does not discharge significantly over time, while low dielectric absorption prevents the capacitor from retaining unwanted charge, which could lead to erroneous readings.
The reset functionality is an important aspect of this circuit. It allows the stored peak voltage to be cleared either manually or electronically. A manual reset can be implemented using a switch that short-circuits C1, discharging it completely. Alternatively, an electronic reset can be achieved using a field-effect transistor (FET) that is normally off. When triggered, the FET will conduct, effectively discharging C1 and allowing for a new peak voltage to be captured.
To detect negative peak values, diode D1 can be reversed, allowing negative voltages to charge C1. This flexibility enhances the circuit's utility in applications where both positive and negative peak detection is necessary.
Overall, this circuit provides a reliable means of capturing and holding peak voltages, with considerations for reset mechanisms and component selection critical to its performance.The purpose of the circuit is to hold the peak of the input voltage on capacitor Cl, and read the value, V0, at the output of U2. Op amps Ul and U2 are connected as voltage followers. When a signal is applied to Vj, Cl will charge to this same voltage through diode Dl. This positive peak voltage on Cl will maintain V0 at this level until the capacitor is reset (shorted).
Of course, higher positive peaks will raise this level while lower power peaks will be ignored. Cl can be reset manually with a switch, or electronically with an FET that is normally off. The capacitor specified for Cl should have low leakage and low dielectric absorption. Diode Dl should also have low leakage. Peak values of negative polarity signals may be detected by reversing Dl.