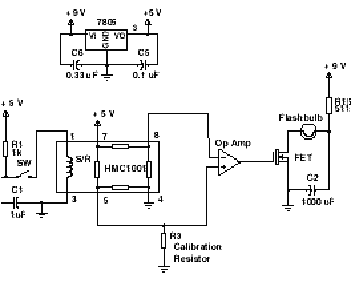
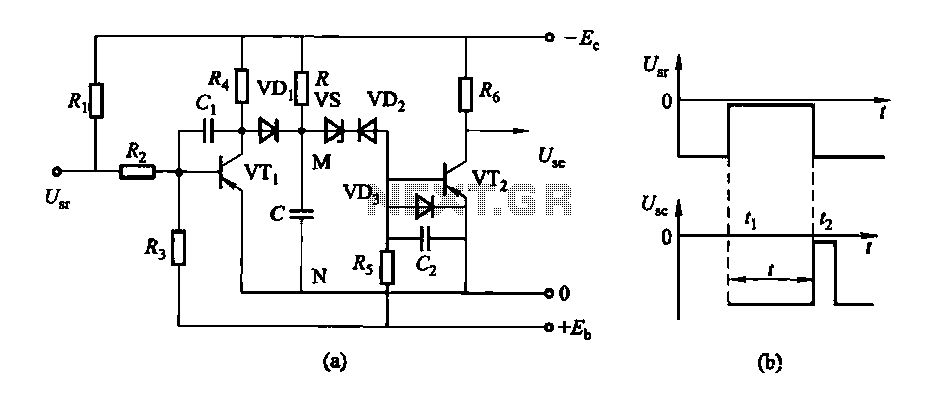
Permanent Magnet Motor Control with SCR
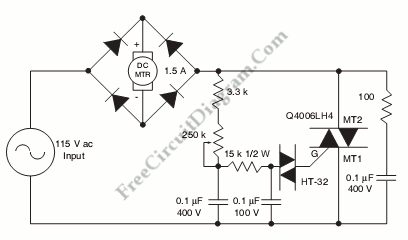
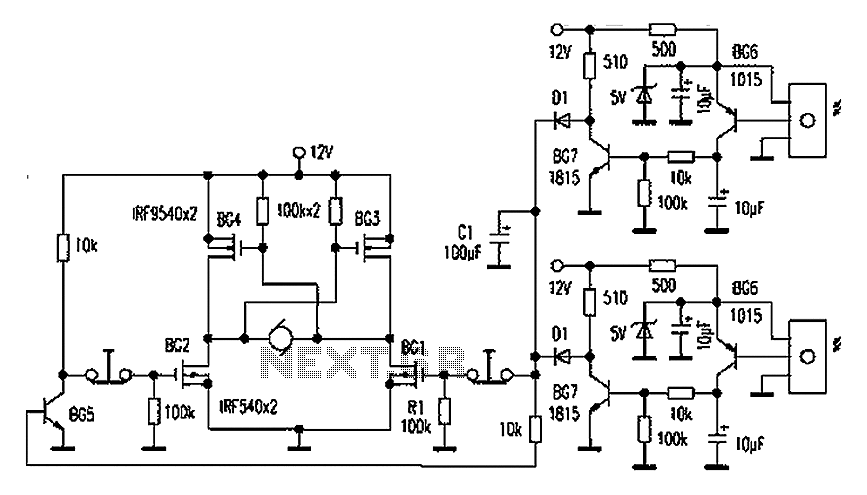
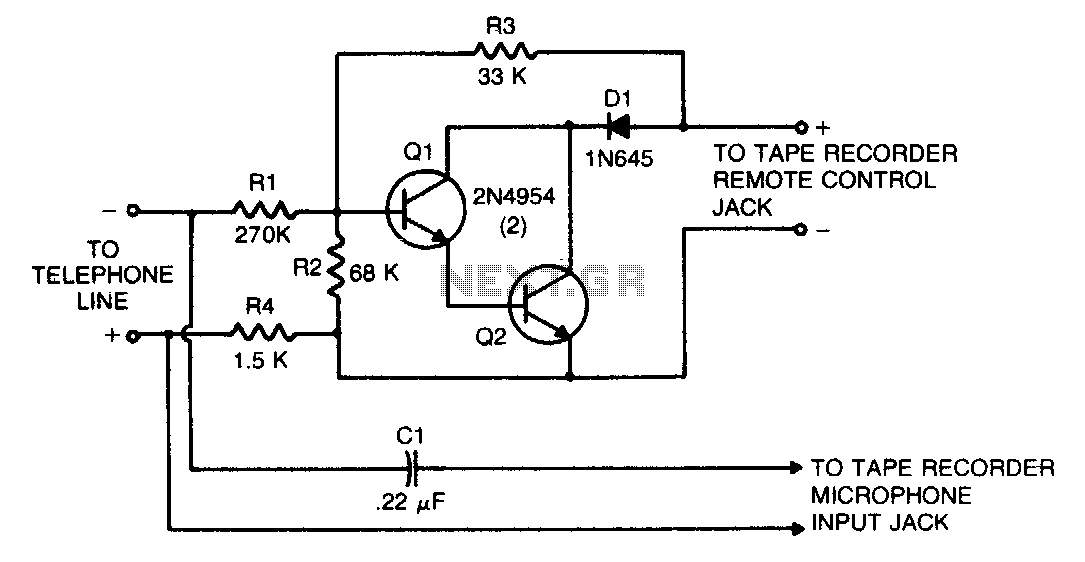
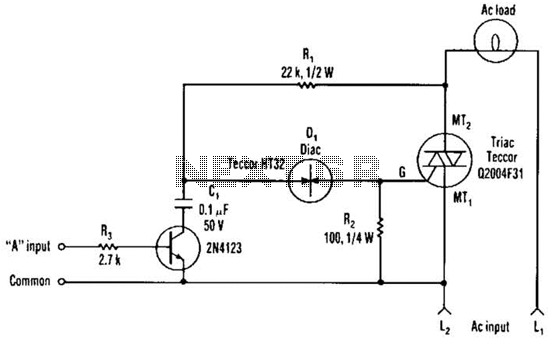
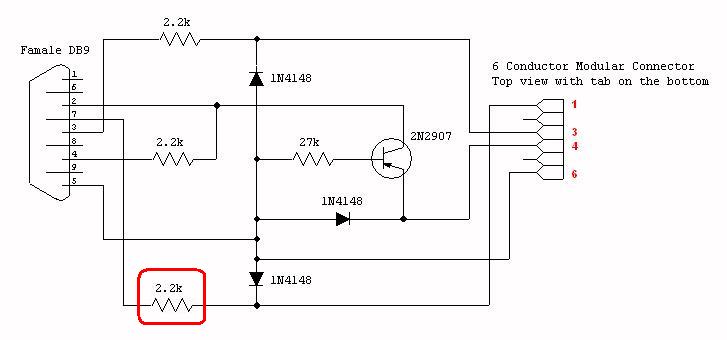
This is a schematic diagram of a Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit. This circuit is used to control the operation of a permanent magnet motor.
The Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit is designed to efficiently manage the performance of permanent magnet motors, which are widely used in various applications due to their high efficiency and compact size. The schematic typically includes key components such as a microcontroller, power transistors, and feedback mechanisms to regulate motor speed and torque.
At the core of the circuit is the microcontroller, which processes input signals from sensors or user interfaces to determine the desired motor performance. The microcontroller sends control signals to power transistors or MOSFETs, which act as electronic switches to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the motor. This allows for precise control over the motor's speed and direction.
Feedback mechanisms, such as encoders or Hall effect sensors, are often integrated into the circuit to monitor the motor's actual speed and position. This data is fed back to the microcontroller, enabling closed-loop control that adjusts the input signals based on real-time performance, ensuring optimal operation and preventing issues such as stalling or overheating.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering, diodes for protection against back EMF, and resistors for current limiting. The layout of the circuit is crucial for minimizing electromagnetic interference and ensuring stable operation. Proper grounding and component placement are essential to enhance the overall reliability and performance of the Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit.This is a schematic diagram of Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit. This circuit is used to control the permanent magnet control. This circuit uses. 🔗 External reference
The Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit is designed to efficiently manage the performance of permanent magnet motors, which are widely used in various applications due to their high efficiency and compact size. The schematic typically includes key components such as a microcontroller, power transistors, and feedback mechanisms to regulate motor speed and torque.
At the core of the circuit is the microcontroller, which processes input signals from sensors or user interfaces to determine the desired motor performance. The microcontroller sends control signals to power transistors or MOSFETs, which act as electronic switches to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the motor. This allows for precise control over the motor's speed and direction.
Feedback mechanisms, such as encoders or Hall effect sensors, are often integrated into the circuit to monitor the motor's actual speed and position. This data is fed back to the microcontroller, enabling closed-loop control that adjusts the input signals based on real-time performance, ensuring optimal operation and preventing issues such as stalling or overheating.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering, diodes for protection against back EMF, and resistors for current limiting. The layout of the circuit is crucial for minimizing electromagnetic interference and ensuring stable operation. Proper grounding and component placement are essential to enhance the overall reliability and performance of the Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit.This is a schematic diagram of Permanent Magnet Motor Control circuit. This circuit is used to control the permanent magnet control. This circuit uses. 🔗 External reference