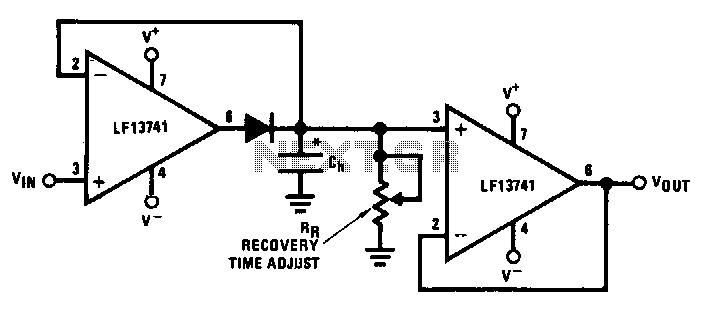
Phase detector with 10-bit accuracy
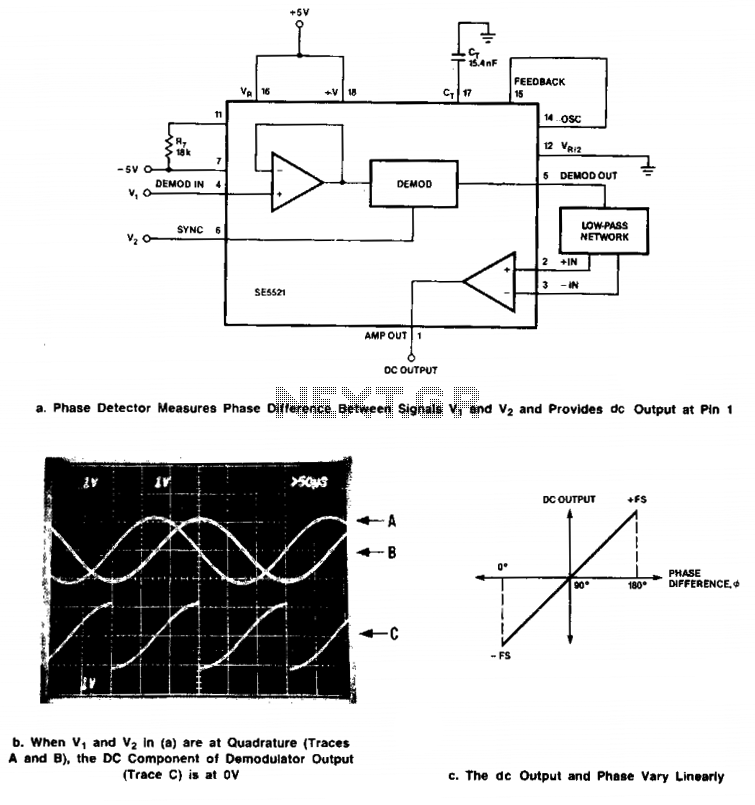
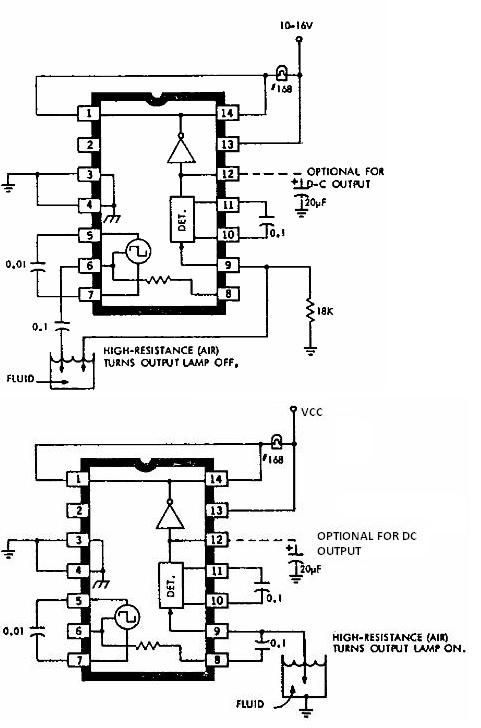
Signals of identical frequency are applied to the sync input (Pin 6) and to the demodulator input (Pin 4). The demodulator operates as a phase detector, with the output DC component being proportional to the phase difference between the two inputs. The signals must be referenced to 0 V for dual supply operation or to VR/2 for single supply operation. With ±5-V supplies, the demodulator can handle 7-V peak-to-peak signals. A low-pass network is configured with the uncommitted amplifier DC output at Pin 1 of the device. The DC output reaches its maximum (+ full-scale) when the inputs are 180° out of phase and minimum (- full-scale) when the signals are in phase.
The circuit described utilizes a phase detector configuration that is effective in applications requiring precise phase comparison between two signals of identical frequency. The demodulator's sync input (Pin 6) and demodulator input (Pin 4) are designed to accept signals that are synchronized in frequency, allowing for accurate detection of phase differences. The output DC voltage from the demodulator is directly related to the phase relationship of the input signals, providing a clear indication of whether the signals are in phase or out of phase.
For dual supply operation, the reference point is set to 0 V, ensuring that the signals remain within the operational limits of the demodulator. In single supply operation, the reference voltage is adjusted to VR/2, which effectively centers the input signals around a mid-scale point, allowing for optimal performance. The design accommodates ±5 V supply voltages, enabling the demodulator to process input signals with a peak-to-peak voltage of 7 V, making it suitable for a variety of signal types.
The low-pass filter network, connected to the uncommitted amplifier output at Pin 1, plays a crucial role in smoothing the output signal. This configuration helps to eliminate high-frequency noise and provides a cleaner DC output that accurately reflects the phase difference between the input signals. The behavior of the output is significant: the maximum output occurs when the two input signals are 180° out of phase, indicating a full-scale positive output, while a minimum output is produced when the signals are perfectly in phase, resulting in a full-scale negative output. This functionality is essential for applications such as phase-locked loops, frequency modulation demodulation, and other systems where phase information is critical.Signals of identical frequency are applied to sync input (Pin 6) and to the demodulator input (Pin 4), respectively, the demodulator functions as a phase detector with output dc component being proportional to phase difference between the two inputs. The signals must be referenced to 0 V for dual supply operation or to VR/2 for single supply operation.
At ± 5-V supplies, the demodulator can easily handle 7-V peak-to-peak signals. The low-pass network configured with the uncommitted amplifier dc output at Pin 1 of the device. The dc output is maximum (+ full-scale) when Vj and V2 are 180° out of phase and minimum (- full-scale) when the signals are in phase. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described utilizes a phase detector configuration that is effective in applications requiring precise phase comparison between two signals of identical frequency. The demodulator's sync input (Pin 6) and demodulator input (Pin 4) are designed to accept signals that are synchronized in frequency, allowing for accurate detection of phase differences. The output DC voltage from the demodulator is directly related to the phase relationship of the input signals, providing a clear indication of whether the signals are in phase or out of phase.
For dual supply operation, the reference point is set to 0 V, ensuring that the signals remain within the operational limits of the demodulator. In single supply operation, the reference voltage is adjusted to VR/2, which effectively centers the input signals around a mid-scale point, allowing for optimal performance. The design accommodates ±5 V supply voltages, enabling the demodulator to process input signals with a peak-to-peak voltage of 7 V, making it suitable for a variety of signal types.
The low-pass filter network, connected to the uncommitted amplifier output at Pin 1, plays a crucial role in smoothing the output signal. This configuration helps to eliminate high-frequency noise and provides a cleaner DC output that accurately reflects the phase difference between the input signals. The behavior of the output is significant: the maximum output occurs when the two input signals are 180° out of phase, indicating a full-scale positive output, while a minimum output is produced when the signals are perfectly in phase, resulting in a full-scale negative output. This functionality is essential for applications such as phase-locked loops, frequency modulation demodulation, and other systems where phase information is critical.Signals of identical frequency are applied to sync input (Pin 6) and to the demodulator input (Pin 4), respectively, the demodulator functions as a phase detector with output dc component being proportional to phase difference between the two inputs. The signals must be referenced to 0 V for dual supply operation or to VR/2 for single supply operation.
At ± 5-V supplies, the demodulator can easily handle 7-V peak-to-peak signals. The low-pass network configured with the uncommitted amplifier dc output at Pin 1 of the device. The dc output is maximum (+ full-scale) when Vj and V2 are 180° out of phase and minimum (- full-scale) when the signals are in phase. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713