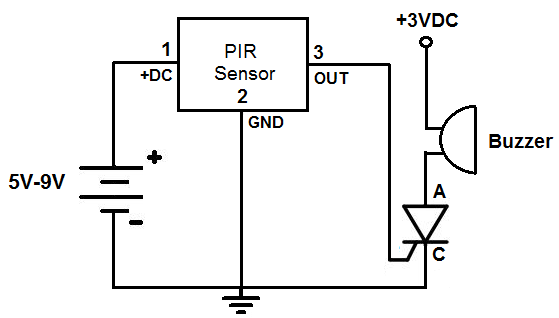
PIR motion detector circuit electronic project
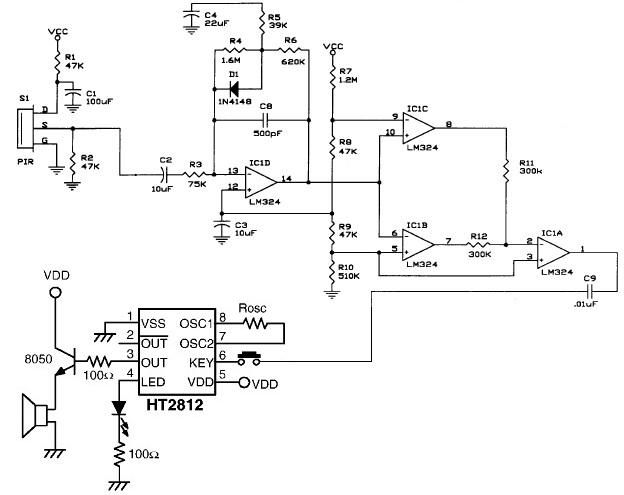
The operational amplifier IC1D modifies the frequency response to enhance the frequencies generated during motion detection while eliminating others, such as noise or gradual temperature variations. When the output voltage of IC1D exceeds 1.67V, it activates pins 8 and 2 of IC1, causing a high signal. This high signal results in a low output, allowing capacitor C9 to discharge through IC1A. The discharge of C9 subsequently pulls pin 6 of IC2 low, triggering the sound generator.
The circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) IC1D configured in a frequency shaping role, which is crucial for isolating the desired motion detection signals from unwanted noise. The op-amp's gain and frequency response are carefully set to ensure that only the relevant frequency components associated with motion are amplified. This is typically achieved through feedback networks that determine the bandwidth and gain characteristics of the op-amp.
When the output voltage of IC1D surpasses the threshold of 1.67V, it generates a high signal at pins 8 and 2 of the subsequent op-amp IC1. This high signal is significant as it triggers a state change in IC1, leading to a low output. The transition to a low output is essential for activating the discharge path for capacitor C9.
Capacitor C9 plays a critical role in timing and signal processing within the circuit. When C9 discharges through op-amp IC1A, it creates a rapid voltage drop that is sensed by pin 6 of IC2. This action initiates the sound generator, which is likely designed to produce an audible alert or notification in response to detected motion. The interaction between the various components—op-amps, capacitor, and sound generator—demonstrates a well-coordinated design aimed at achieving reliable motion detection and response.
In summary, this circuit effectively employs op-amps for signal processing, utilizes capacitive discharge for timing control, and integrates a sound-generating mechanism to provide feedback in the presence of motion. Each component is essential to the overall functionality, ensuring that the system is responsive to intended stimuli while minimizing interference from extraneous signals.The op-amp IC1D shapes the frequency response to amplify those frequencies produced when motion is detected and rejects all others, such as those due to noise or slow temperature changes. When IC1D outputs a voltage higher than 1. 67V, it forces pin 8 and pin 2 of IC1 to go high. A high in with one of these cases causes the output to go low and all ows C9 to discharge through IC1A. The discharging of C9 will pull pin 6 of IC2 low and trigger the sound generator. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes an operational amplifier (op-amp) IC1D configured in a frequency shaping role, which is crucial for isolating the desired motion detection signals from unwanted noise. The op-amp's gain and frequency response are carefully set to ensure that only the relevant frequency components associated with motion are amplified. This is typically achieved through feedback networks that determine the bandwidth and gain characteristics of the op-amp.
When the output voltage of IC1D surpasses the threshold of 1.67V, it generates a high signal at pins 8 and 2 of the subsequent op-amp IC1. This high signal is significant as it triggers a state change in IC1, leading to a low output. The transition to a low output is essential for activating the discharge path for capacitor C9.
Capacitor C9 plays a critical role in timing and signal processing within the circuit. When C9 discharges through op-amp IC1A, it creates a rapid voltage drop that is sensed by pin 6 of IC2. This action initiates the sound generator, which is likely designed to produce an audible alert or notification in response to detected motion. The interaction between the various components—op-amps, capacitor, and sound generator—demonstrates a well-coordinated design aimed at achieving reliable motion detection and response.
In summary, this circuit effectively employs op-amps for signal processing, utilizes capacitive discharge for timing control, and integrates a sound-generating mechanism to provide feedback in the presence of motion. Each component is essential to the overall functionality, ensuring that the system is responsive to intended stimuli while minimizing interference from extraneous signals.The op-amp IC1D shapes the frequency response to amplify those frequencies produced when motion is detected and rejects all others, such as those due to noise or slow temperature changes. When IC1D outputs a voltage higher than 1. 67V, it forces pin 8 and pin 2 of IC1 to go high. A high in with one of these cases causes the output to go low and all ows C9 to discharge through IC1A. The discharging of C9 will pull pin 6 of IC2 low and trigger the sound generator. 🔗 External reference