PJRC MP3 Player Schematic Diagrams
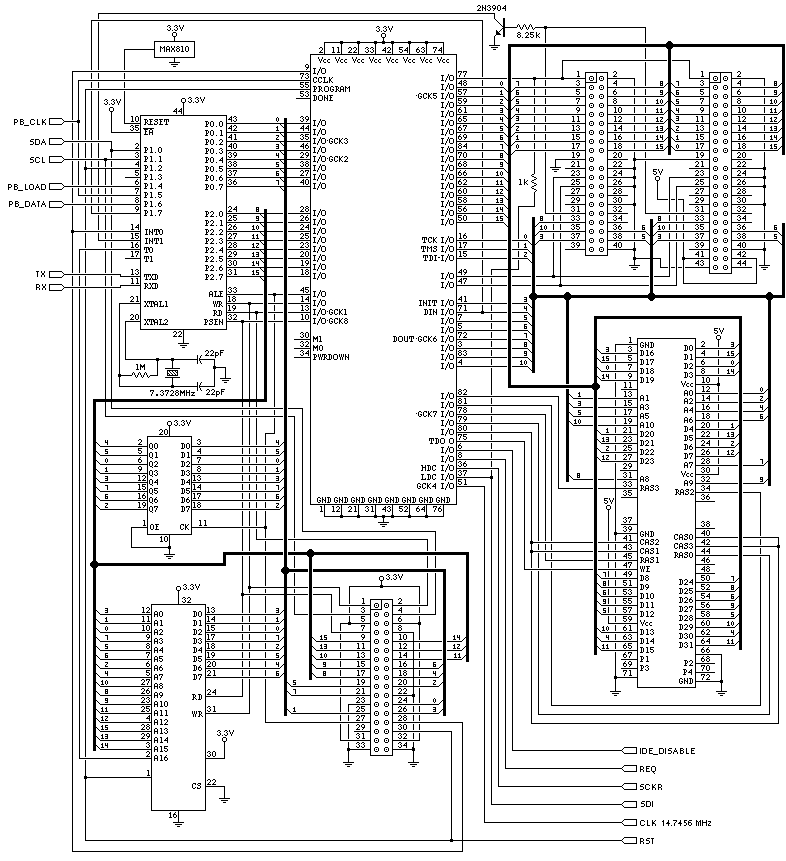
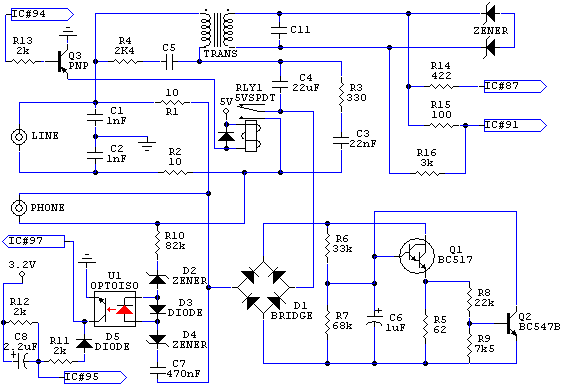
The two unspecified polarized capacitors (one directly above the transformer and one directly to the right of the transformer) are actually each a pair of 470 µF capacitors in parallel (for a total of four 470 µF capacitors). These capacitors must be Low-ESR types for the power supply to function properly. The two 100 µF 16V capacitors were changed to 33 µF. PJRC provides these as Low-ESR capacitors to reduce noise. Standard capacitors, from 22 µF to 220 µF, are likely to work. The 3.3 µF capacitors attached to pin 5 should be 2.2 µF (either value will work, but 2.2 µF has been used on the assembled boards and unassembled kits). This capacitor sets the time constant before the power supply will automatically shut off when the output is shorted or the input voltage is too low. The diodes shown connected between the source and drain on the two MOSFET transistors are the diode structures inside transistors. These two diode symbols do not represent actual diode components soldered to the circuit board.
The circuit features a combination of polarized capacitors strategically placed to ensure optimal performance of the power supply system. Specifically, there are four 470 µF capacitors arranged in parallel, with two located above and to the right of the transformer. These capacitors are essential for maintaining low equivalent series resistance (Low-ESR) to enhance the efficiency of the power supply, particularly under varying load conditions. The selection of Low-ESR capacitors helps in minimizing voltage ripple and improving transient response, which is critical for stable operation.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates capacitors that were modified from 100 µF 16V to 33 µF, sourced from PJRC, which are also Low-ESR types. This change is aimed at further reducing noise in the power supply, thus enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. The use of standard capacitors ranging from 22 µF to 220 µF is permissible, providing flexibility in component selection while still maintaining functionality.
A notable component in the circuit is the 2.2 µF capacitor connected to pin 5. This component is crucial as it determines the time constant for the power supply's automatic shut-off feature. In scenarios where the output is shorted or the input voltage drops below a certain threshold, this capacitor ensures that the power supply responds appropriately by shutting down to prevent damage.
Moreover, the schematic includes diodes represented between the source and drain of two MOSFET transistors. It is important to note that these diode symbols correspond to the intrinsic diode structures found within the MOSFETs themselves, rather than indicating separate diode components that are physically mounted on the circuit board. This design choice simplifies the layout and reduces the number of discrete components, thereby optimizing space and potentially lowering costs in manufacturing.
In summary, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of component selection, particularly with respect to capacitor types and values, to ensure reliable and efficient power supply operation. The integration of Low-ESR capacitors, alongside careful consideration of timing components and internal diode structures, reflects a thoughtful approach to circuit design in electronic applications.The two unspecified polarized capacitors (one directly above the transformer and one directly to the right of the transformer) are actually each a pair of 470 µF capacitors in parallel (for a total of four 470 µF capacitors). These capacitors MUST be Low-ESR types for the power supply to function properly. Figure 4: The two 100 µF 16V capacitors were changed to 33 µF. PJRC provides these as Low-ESR capacitors to reduce noise. Standard capacitors, from 22 µF to 220 µF are likely to work. Figure 4: The 3. 3 µF capacitors attached to pin 5 should be 2. 2 µF (either value will work, but we have been using 2. 2 µF on the assembled boards and unassembled kits). This capacitor sets the time constant before the power supply will automatically shut off when the output is shorted or the input voltage is too low. Figure 4: The diodes shown connected between the source and drain on the two MOSFET transistors are the diode structures inside transistors.
These two diode symbols do not represent actual diode components soldered to the circuit board. 🔗 External reference
The circuit features a combination of polarized capacitors strategically placed to ensure optimal performance of the power supply system. Specifically, there are four 470 µF capacitors arranged in parallel, with two located above and to the right of the transformer. These capacitors are essential for maintaining low equivalent series resistance (Low-ESR) to enhance the efficiency of the power supply, particularly under varying load conditions. The selection of Low-ESR capacitors helps in minimizing voltage ripple and improving transient response, which is critical for stable operation.
Additionally, the circuit incorporates capacitors that were modified from 100 µF 16V to 33 µF, sourced from PJRC, which are also Low-ESR types. This change is aimed at further reducing noise in the power supply, thus enhancing the overall performance of the circuit. The use of standard capacitors ranging from 22 µF to 220 µF is permissible, providing flexibility in component selection while still maintaining functionality.
A notable component in the circuit is the 2.2 µF capacitor connected to pin 5. This component is crucial as it determines the time constant for the power supply's automatic shut-off feature. In scenarios where the output is shorted or the input voltage drops below a certain threshold, this capacitor ensures that the power supply responds appropriately by shutting down to prevent damage.
Moreover, the schematic includes diodes represented between the source and drain of two MOSFET transistors. It is important to note that these diode symbols correspond to the intrinsic diode structures found within the MOSFETs themselves, rather than indicating separate diode components that are physically mounted on the circuit board. This design choice simplifies the layout and reduces the number of discrete components, thereby optimizing space and potentially lowering costs in manufacturing.
In summary, the circuit design emphasizes the importance of component selection, particularly with respect to capacitor types and values, to ensure reliable and efficient power supply operation. The integration of Low-ESR capacitors, alongside careful consideration of timing components and internal diode structures, reflects a thoughtful approach to circuit design in electronic applications.The two unspecified polarized capacitors (one directly above the transformer and one directly to the right of the transformer) are actually each a pair of 470 µF capacitors in parallel (for a total of four 470 µF capacitors). These capacitors MUST be Low-ESR types for the power supply to function properly. Figure 4: The two 100 µF 16V capacitors were changed to 33 µF. PJRC provides these as Low-ESR capacitors to reduce noise. Standard capacitors, from 22 µF to 220 µF are likely to work. Figure 4: The 3. 3 µF capacitors attached to pin 5 should be 2. 2 µF (either value will work, but we have been using 2. 2 µF on the assembled boards and unassembled kits). This capacitor sets the time constant before the power supply will automatically shut off when the output is shorted or the input voltage is too low. Figure 4: The diodes shown connected between the source and drain on the two MOSFET transistors are the diode structures inside transistors.
These two diode symbols do not represent actual diode components soldered to the circuit board. 🔗 External reference