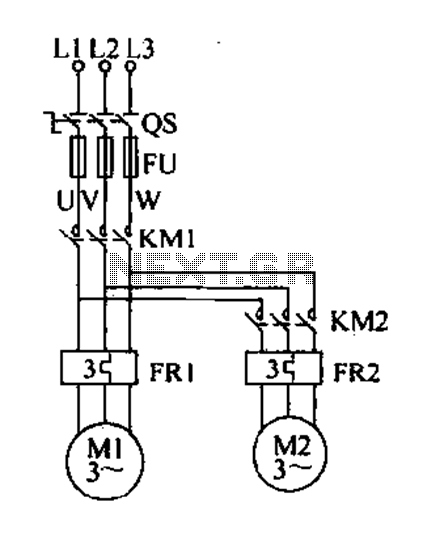
pololu high current motor driver
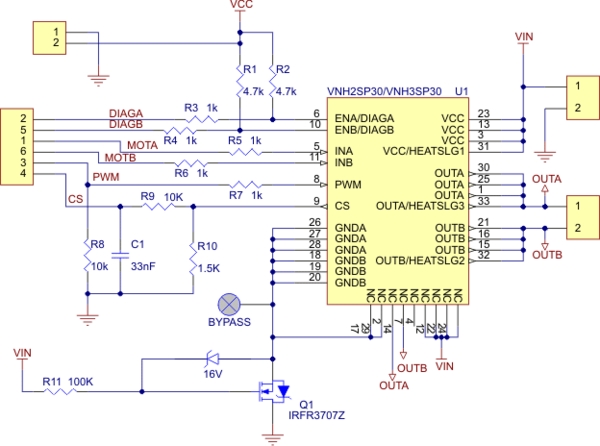
Need more current? If you have a larger motor ready for use, the Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board 14A 6V-16V is the ideal solution. Connect three digital lines to your microcontroller (five if error condition feedback is desired), and you are set to go! The Pololu High Current motor driver board is a compact solution utilizing the VNH2SP30 motor driver integrated circuit. The board includes most components from the typical application diagram found on page 7 of the VNH2SP30 datasheet, such as pull-up and current-limiting resistors, along with a FET for reverse battery protection. A microcontroller or other control circuit is required to turn the H-Bridge on and off. In a typical setup, the motor power supply connects at the bottom of the board, the motor on the right side, and the control connections on the left side. The diagnostic pins can remain disconnected if monitoring fault conditions of the motor driver chip is not desired. INA and INB control the motor's direction, while the PWM pin toggles the motor on or off. The motor driver has a maximum current rating of 30 A continuous; however, the chip may overheat at much lower currents. Thus, it is recommended to operate it at 14 A continuous. The actual current delivery capability will depend on the cooling efficiency of the motor driver. Tests have shown that short bursts of 30 A and a few seconds at 20 A can be achieved without overheating. At 14 A, the chip remains only slightly warm to the touch. For higher currents, a heat sink is recommended. It is also advisable to solder the motor and power supply wires directly rather than using terminal blocks, which are rated for up to 15 A. Many motor controllers or speed controllers may have peak current ratings significantly higher than the continuous current rating; however, this is not applicable to the VNH2SP30, which has a continuous rating of 30 A and over-current protection that can engage as low as 30 A (typically 45 A). Therefore, the stall current of the motor should not exceed 30 A. Even if the average current is expected to be lower, high currents can still occur during startup or when employing low duty cycle PWM to maintain the average current. The motor driver board features an N-channel MOSFET for reverse-battery protection, preventing damage to the motor driver if the input power is connected in reverse. However, this component slightly increases the total resistance between the battery and motor and limits the operating voltage to a maximum of 20 V. For enhanced performance or higher-voltage applications, the MOSFET can be bypassed by connecting the negative battery terminal to the bypass pin, which must also be connected to the logic supply ground.
The Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board is designed for high-performance applications requiring precise control of larger motors. Its compact design integrates essential components for efficient operation, making it suitable for various projects. The board's layout facilitates straightforward connections, with clearly defined positions for power supply, motor, and control interfaces.
The control mechanism utilizes a standard H-Bridge configuration, allowing for bi-directional motor control. The INA and INB pins provide the capability to reverse motor direction, while the PWM input allows for speed modulation through pulse-width modulation techniques. This versatility makes the board ideal for robotics and automation applications where precise motor control is crucial.
Thermal management is a critical aspect of the design, as the VNH2SP30 chip is sensitive to overheating. The recommendation to operate at 14 A continuous is a safety measure to ensure reliability and longevity of the device. The inclusion of a heat sink is advisable for applications that may demand higher current outputs, ensuring that the chip remains within safe operating temperatures.
The reverse-battery protection feature enhances the reliability of the motor driver, safeguarding it against accidental miswiring. However, users should be mindful of the slight increase in resistance and the voltage limitations imposed by this feature.
Overall, the Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board 14A 6V-16V represents a robust solution for controlling high-current motors, combining ease of use, safety features, and the ability to handle demanding applications.Need more current If you`ve got a larger motor waiting to be used, the Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board 14A 6V-16V is just what you need. Connect three digital lines to your microcontroller (five if you want error condition feedback), and you`re ready to go!
The Pololu High Current motor driver board is a compact solution for using the VNH2SP30 motor driver integrated circuit. The board incorporates most of the components of the typical application diagram on page 7 of the VNH2SP30 datasheet, including pull-up and current-limiting resistors and a FET for reverse battery protection. All you need to add is a microcontroller or other control circuit to turn the H-Bridge on and off. In a typical application, the motor power supply is connected at the bottom of the board, the motor on the right side of the board, and the control connections to the left side of the board.
The diagnostic pins can be left disconnected if you do not want to monitor the fault conditions of the motor driver chip. INA and INB control the direction of the motor, and the PWM pin turns the motor on or off. The motor driver has a maximum current rating of 30 A continuous. However, the chip by itself will overheat at much lower currents. That is why it is suggested that you use it at 14A continuous. The actual current you can deliver will depend on how well you can keep the motor driver cool. In our tests, we were able to deliver short durations (on the order of milliseconds) of 30 A and a few seconds of 20 A without overheating.
At 14 A, the chip gets just barely noticeably warm to the touch. For higher currents, a heat sink will be necessary. The motor and power supply wires should also be soldered directly instead of going through the terminal blocks, which are rated for up to 15 A. Manymotor controllers or speed controllers can have peak current ratings that are substantially higher than the continuous current rating; this is not the case with the VNH2SP30, which has a 30 A continuous rating and a over-current protection that can kick in as low as 30 A (45 A typical).
Therefore, the stall current of your motor should not be more than 30 A. (Even if you expect to run at a much lower average current, the motor can still draw high currents when it is starting or if you use low duty cycle PWM to keep the average current down. ) The motor driver board includes an N-channel MOSFET for reverse-battery protection. This component keeps the motor driver from destroying itself if the input power is accidentally connected backwards.
However, this component does slightly increase the total resistance between your battery and your motor, and it limits the operating voltage to a maximum of 20 V. For slightly improved performance or for higher-voltage applications, the MOSFET can be bypassed by connecting the negative battery terminal to the bypass pin.
(This terminal will also need to be connected to your logic supply ground. ) 🔗 External reference
The Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board is designed for high-performance applications requiring precise control of larger motors. Its compact design integrates essential components for efficient operation, making it suitable for various projects. The board's layout facilitates straightforward connections, with clearly defined positions for power supply, motor, and control interfaces.
The control mechanism utilizes a standard H-Bridge configuration, allowing for bi-directional motor control. The INA and INB pins provide the capability to reverse motor direction, while the PWM input allows for speed modulation through pulse-width modulation techniques. This versatility makes the board ideal for robotics and automation applications where precise motor control is crucial.
Thermal management is a critical aspect of the design, as the VNH2SP30 chip is sensitive to overheating. The recommendation to operate at 14 A continuous is a safety measure to ensure reliability and longevity of the device. The inclusion of a heat sink is advisable for applications that may demand higher current outputs, ensuring that the chip remains within safe operating temperatures.
The reverse-battery protection feature enhances the reliability of the motor driver, safeguarding it against accidental miswiring. However, users should be mindful of the slight increase in resistance and the voltage limitations imposed by this feature.
Overall, the Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board 14A 6V-16V represents a robust solution for controlling high-current motors, combining ease of use, safety features, and the ability to handle demanding applications.Need more current If you`ve got a larger motor waiting to be used, the Pololu High Current Motor Driver Board 14A 6V-16V is just what you need. Connect three digital lines to your microcontroller (five if you want error condition feedback), and you`re ready to go!
The Pololu High Current motor driver board is a compact solution for using the VNH2SP30 motor driver integrated circuit. The board incorporates most of the components of the typical application diagram on page 7 of the VNH2SP30 datasheet, including pull-up and current-limiting resistors and a FET for reverse battery protection. All you need to add is a microcontroller or other control circuit to turn the H-Bridge on and off. In a typical application, the motor power supply is connected at the bottom of the board, the motor on the right side of the board, and the control connections to the left side of the board.
The diagnostic pins can be left disconnected if you do not want to monitor the fault conditions of the motor driver chip. INA and INB control the direction of the motor, and the PWM pin turns the motor on or off. The motor driver has a maximum current rating of 30 A continuous. However, the chip by itself will overheat at much lower currents. That is why it is suggested that you use it at 14A continuous. The actual current you can deliver will depend on how well you can keep the motor driver cool. In our tests, we were able to deliver short durations (on the order of milliseconds) of 30 A and a few seconds of 20 A without overheating.
At 14 A, the chip gets just barely noticeably warm to the touch. For higher currents, a heat sink will be necessary. The motor and power supply wires should also be soldered directly instead of going through the terminal blocks, which are rated for up to 15 A. Manymotor controllers or speed controllers can have peak current ratings that are substantially higher than the continuous current rating; this is not the case with the VNH2SP30, which has a 30 A continuous rating and a over-current protection that can kick in as low as 30 A (45 A typical).
Therefore, the stall current of your motor should not be more than 30 A. (Even if you expect to run at a much lower average current, the motor can still draw high currents when it is starting or if you use low duty cycle PWM to keep the average current down. ) The motor driver board includes an N-channel MOSFET for reverse-battery protection. This component keeps the motor driver from destroying itself if the input power is accidentally connected backwards.
However, this component does slightly increase the total resistance between your battery and your motor, and it limits the operating voltage to a maximum of 20 V. For slightly improved performance or for higher-voltage applications, the MOSFET can be bypassed by connecting the negative battery terminal to the bypass pin.
(This terminal will also need to be connected to your logic supply ground. ) 🔗 External reference