Power Amplifier Speaker Protection Circuit Schematic

Power Amplifier Speaker Protection Circuit Schematic. When a power amplifier is switched on, a loud thump sound is often heard due to a sudden heavy discharge.
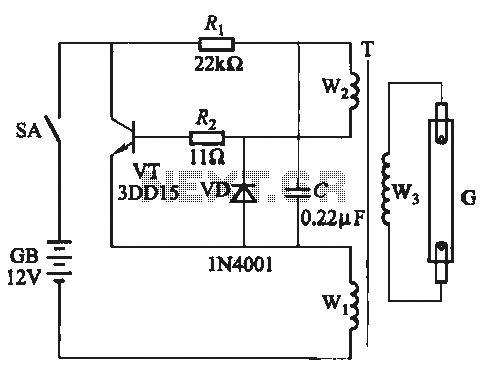
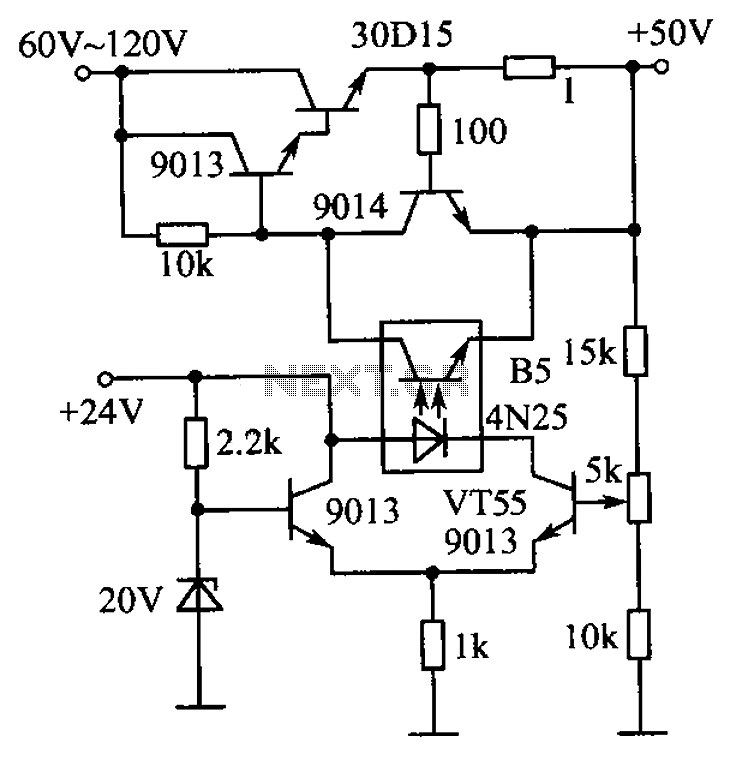
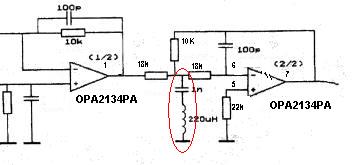
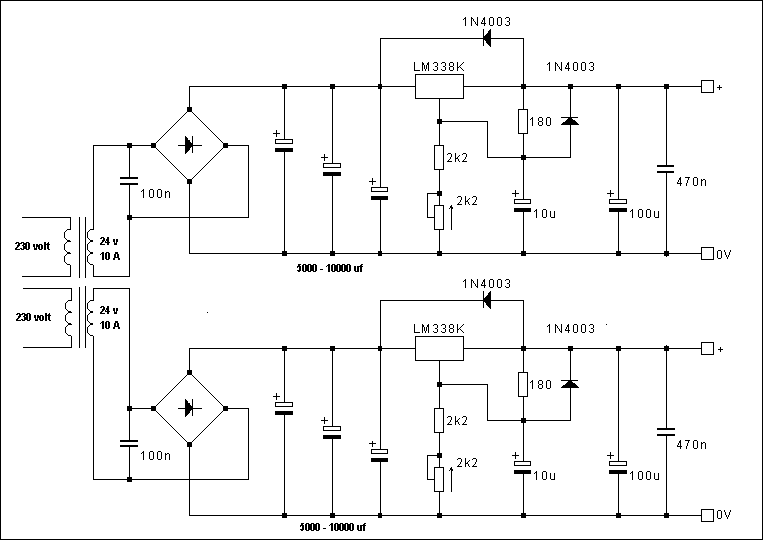
The power amplifier speaker protection circuit is designed to prevent loud thump sounds during the power-up sequence of an amplifier, which can potentially damage speakers. This circuit typically employs a relay-based design that disconnects the speakers from the amplifier output during the initial power-up phase.
The schematic generally includes the following components: a relay, which acts as a switch to connect or disconnect the speakers; a delay timer circuit, which ensures that the relay remains open for a brief period after the amplifier is powered on; and a protection diode that prevents back EMF from the relay coil from damaging other components in the circuit.
Upon powering the amplifier, the delay timer circuit is activated, allowing a short time for the amplifier to stabilize. During this period, the relay remains in the open position, isolating the speakers from the output. Once the timer completes its cycle, the relay is energized, closing the circuit and connecting the speakers to the amplifier output. This sequence effectively eliminates the loud thump sound, providing a safer operation for both the amplifier and the connected speakers.
The use of high-quality components is essential to ensure reliability and performance. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate indicator LEDs to show the status of the relay operation, enhancing user feedback. Overall, this protection circuit is a crucial addition to any power amplifier design, safeguarding against potential audio transients that could harm speaker systems.Power Amplifier Speaker Protection Circuit Schematic While switching a power amplifier on, a loud thump sound is heard to sudden heavy discharge.. 🔗 External reference
The power amplifier speaker protection circuit is designed to prevent loud thump sounds during the power-up sequence of an amplifier, which can potentially damage speakers. This circuit typically employs a relay-based design that disconnects the speakers from the amplifier output during the initial power-up phase.
The schematic generally includes the following components: a relay, which acts as a switch to connect or disconnect the speakers; a delay timer circuit, which ensures that the relay remains open for a brief period after the amplifier is powered on; and a protection diode that prevents back EMF from the relay coil from damaging other components in the circuit.
Upon powering the amplifier, the delay timer circuit is activated, allowing a short time for the amplifier to stabilize. During this period, the relay remains in the open position, isolating the speakers from the output. Once the timer completes its cycle, the relay is energized, closing the circuit and connecting the speakers to the amplifier output. This sequence effectively eliminates the loud thump sound, providing a safer operation for both the amplifier and the connected speakers.
The use of high-quality components is essential to ensure reliability and performance. Additionally, the circuit may incorporate indicator LEDs to show the status of the relay operation, enhancing user feedback. Overall, this protection circuit is a crucial addition to any power amplifier design, safeguarding against potential audio transients that could harm speaker systems.Power Amplifier Speaker Protection Circuit Schematic While switching a power amplifier on, a loud thump sound is heard to sudden heavy discharge.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713