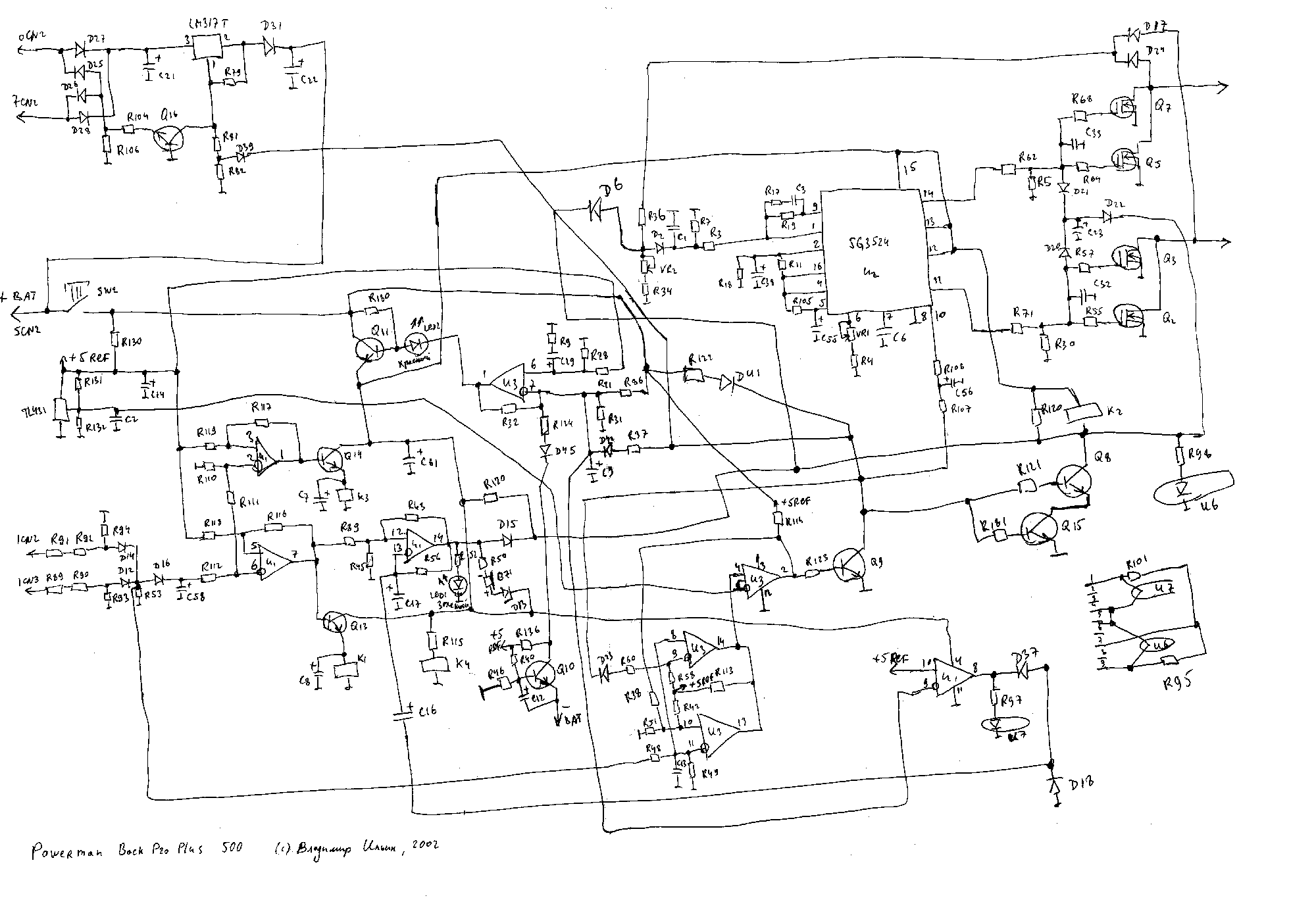
Power down function

This circuit adds a power down function to analog I/O ports (for example, the AD7769 and AD7774). Moreover, the diodes ordinarily needed to protect the devices against power-supply missequencing can be eliminated. Bringing the power down control high (+5V) applies power to the controlled circuit by turning on all MOSFETs. Specifically, raising the power down brings the output of U1C low, causing capacitor C1 to discharge VOL exponentially with time constant R1C1. As the voltage on C1 falls, two events occur. In the circuit, MOSFETs Q1 and Q2 switch the +5- and +12-V supplies, respectively, in a sequence controlled by two cross-coupled CD4001 CMOS NOR gates (U1C and U1D). The sequence in which power is applied is important: The controlled circuits may be damaged.
This circuit design employs a power management strategy to enhance the reliability and performance of analog I/O ports, specifically targeting devices such as the AD7769 and AD7774. The primary function of this circuit is to provide a controlled power-down capability while eliminating the need for protective diodes typically used to guard against power-supply missequencing.
The operation of the circuit hinges on a power-down control signal that, when asserted high at +5V, activates the power supply to the connected analog components by turning on the associated MOSFETs. The control mechanism involves two cross-coupled NOR gates (U1C and U1D), which orchestrate the switching of the +5V and +12V supplies through MOSFETs Q1 and Q2, respectively. This strategic sequencing is crucial, as improper power application can lead to damage of sensitive components.
Upon activating the power-down control, the output of U1C transitions to a low state, which initiates the discharge of capacitor C1 through resistor R1. The discharge follows an exponential decay characterized by the time constant R1C1. As the voltage across C1 decreases, it triggers additional events within the circuit, although these specific events are not detailed in the provided description.
The design effectively ensures that the power-up and power-down sequences are carefully managed to prevent any adverse effects on the controlled circuits, thereby enhancing the overall robustness of the system. This approach is particularly beneficial in applications where power sequencing is critical for the operational integrity of the devices involved. This circuit adds a power down function to analog I/O ports (for example, the AD7769 and AD7774). Moreover, the diodes ordinarily needed to protect the devices against power-supply missequencing can be eliminated Bringing the power down control high (+5V) applies power to the controlled circuit by turning on all MOSFETs. Specifically, raising the power down brings the output of U1C low, causing capacitor C1 to discharge VOL exponentially with time constant R1C1.
As the voltage on C1 falls, two events occur. In the circuit, MOSFETs Q1 and Q2 switch the +5- and +12-V supplies, respectively, in a sequence controlled by two cross-coupled CD4001 CMOS NOR gates (U1C and U1D). The sequence in which power isapplied is important: The controlled circuits may be dama 🔗 External reference
This circuit design employs a power management strategy to enhance the reliability and performance of analog I/O ports, specifically targeting devices such as the AD7769 and AD7774. The primary function of this circuit is to provide a controlled power-down capability while eliminating the need for protective diodes typically used to guard against power-supply missequencing.
The operation of the circuit hinges on a power-down control signal that, when asserted high at +5V, activates the power supply to the connected analog components by turning on the associated MOSFETs. The control mechanism involves two cross-coupled NOR gates (U1C and U1D), which orchestrate the switching of the +5V and +12V supplies through MOSFETs Q1 and Q2, respectively. This strategic sequencing is crucial, as improper power application can lead to damage of sensitive components.
Upon activating the power-down control, the output of U1C transitions to a low state, which initiates the discharge of capacitor C1 through resistor R1. The discharge follows an exponential decay characterized by the time constant R1C1. As the voltage across C1 decreases, it triggers additional events within the circuit, although these specific events are not detailed in the provided description.
The design effectively ensures that the power-up and power-down sequences are carefully managed to prevent any adverse effects on the controlled circuits, thereby enhancing the overall robustness of the system. This approach is particularly beneficial in applications where power sequencing is critical for the operational integrity of the devices involved. This circuit adds a power down function to analog I/O ports (for example, the AD7769 and AD7774). Moreover, the diodes ordinarily needed to protect the devices against power-supply missequencing can be eliminated Bringing the power down control high (+5V) applies power to the controlled circuit by turning on all MOSFETs. Specifically, raising the power down brings the output of U1C low, causing capacitor C1 to discharge VOL exponentially with time constant R1C1.
As the voltage on C1 falls, two events occur. In the circuit, MOSFETs Q1 and Q2 switch the +5- and +12-V supplies, respectively, in a sequence controlled by two cross-coupled CD4001 CMOS NOR gates (U1C and U1D). The sequence in which power isapplied is important: The controlled circuits may be dama 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713