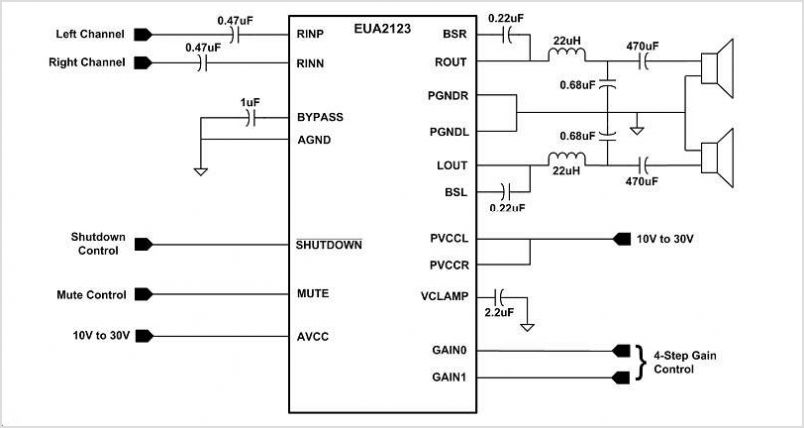
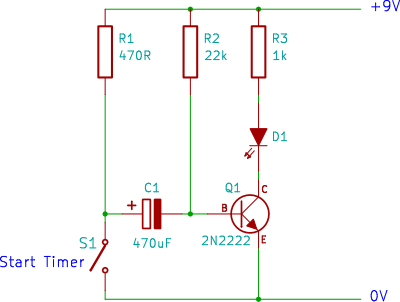
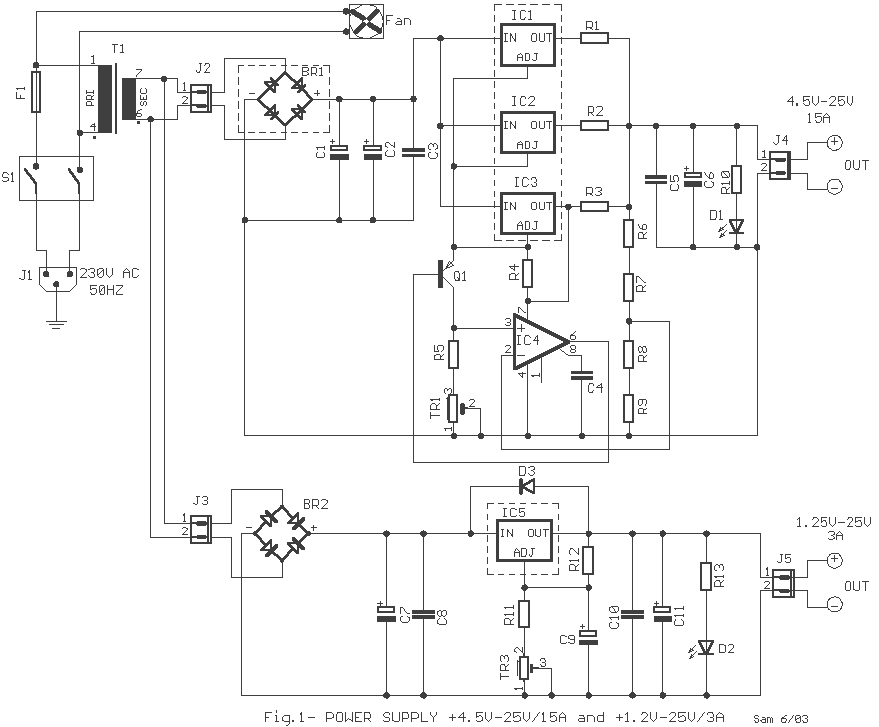
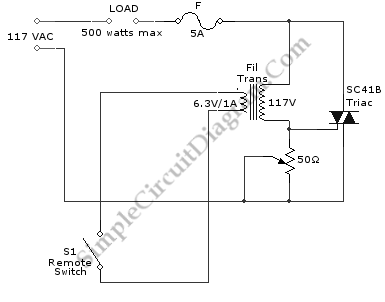
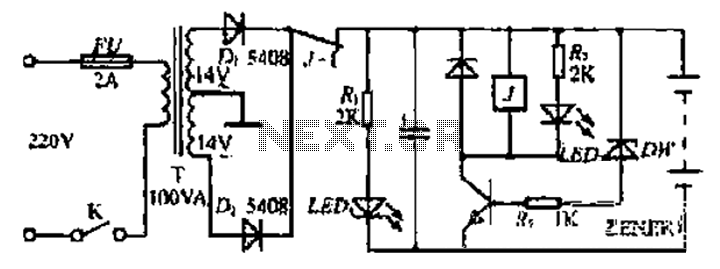
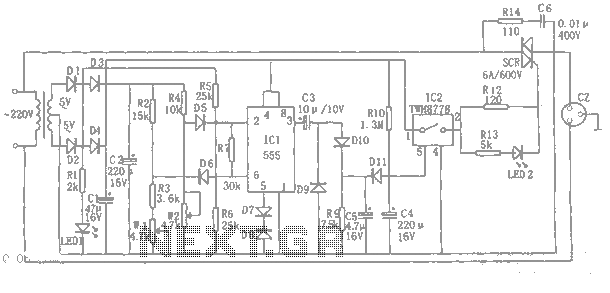
power off time delay relay
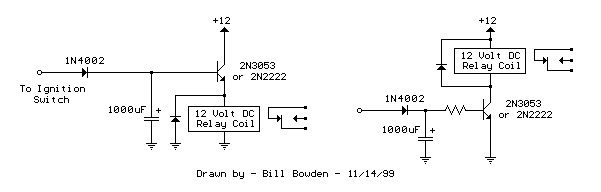
The two circuits demonstrate the process of opening a relay contact shortly after the ignition or light switch is turned off. The capacitor becomes charged, and the relay remains closed until the voltage at the diode anode reaches +12 volts.
The described circuits utilize a relay and a capacitor to create a delayed opening mechanism for the relay contacts. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the voltage supply to the circuit is interrupted. Initially, the capacitor holds a charge, which keeps the relay in a closed state. The relay operates as a switch that controls the flow of current to a load, such as lights or other electrical devices.
As the circuit operates, the diode plays a crucial role by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking reverse current. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the voltage at the anode of the diode begins to decrease. The capacitor discharges through the relay coil, maintaining the relay in the closed position for a brief period. This delay allows for a controlled shutdown of the connected load, preventing abrupt disconnection and potential damage to sensitive components.
The time it takes for the voltage at the diode anode to drop to +12 volts is determined by the capacitance value of the capacitor and the resistance in the circuit. A larger capacitance will result in a longer delay, while a smaller capacitance will reduce the delay time. The values of these components should be selected based on the specific application requirements, ensuring that the relay opens at the desired moment after the switch is turned off.
This circuit configuration is commonly used in automotive applications where it is beneficial to keep lights on for a short duration after the vehicle is turned off, enhancing safety and convenience. Proper implementation of these circuits can improve user experience and protect electrical components from voltage spikes or sudden disconnections.The two circuits illustrate opening a relay contact a short time after the ignition or ligh switch is turned off. The capacitor is charged and the relay is closed when the voltage at the diode anode rises to +12 volts..
🔗 External reference
The described circuits utilize a relay and a capacitor to create a delayed opening mechanism for the relay contacts. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the voltage supply to the circuit is interrupted. Initially, the capacitor holds a charge, which keeps the relay in a closed state. The relay operates as a switch that controls the flow of current to a load, such as lights or other electrical devices.
As the circuit operates, the diode plays a crucial role by allowing current to flow in one direction while blocking reverse current. When the ignition or light switch is turned off, the voltage at the anode of the diode begins to decrease. The capacitor discharges through the relay coil, maintaining the relay in the closed position for a brief period. This delay allows for a controlled shutdown of the connected load, preventing abrupt disconnection and potential damage to sensitive components.
The time it takes for the voltage at the diode anode to drop to +12 volts is determined by the capacitance value of the capacitor and the resistance in the circuit. A larger capacitance will result in a longer delay, while a smaller capacitance will reduce the delay time. The values of these components should be selected based on the specific application requirements, ensuring that the relay opens at the desired moment after the switch is turned off.
This circuit configuration is commonly used in automotive applications where it is beneficial to keep lights on for a short duration after the vehicle is turned off, enhancing safety and convenience. Proper implementation of these circuits can improve user experience and protect electrical components from voltage spikes or sudden disconnections.The two circuits illustrate opening a relay contact a short time after the ignition or ligh switch is turned off. The capacitor is charged and the relay is closed when the voltage at the diode anode rises to +12 volts..
🔗 External reference