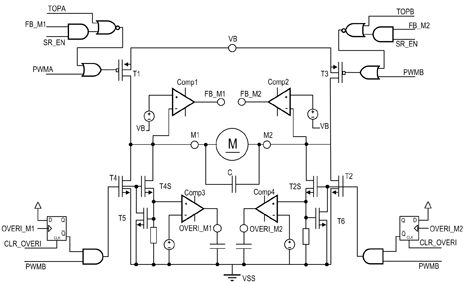
Power Path Management Battery Charger
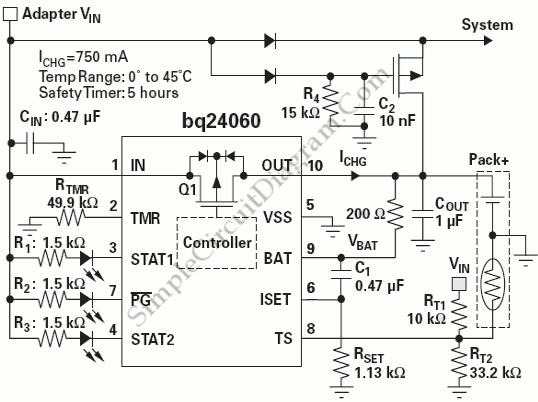
Powering the system is required by many applications while charging the battery simultaneously. Interaction between the system and charger may result in a...
Power management in electronic systems is critical, particularly in applications that necessitate simultaneous operation and battery charging. This dual functionality can lead to complex interactions between the system load and the charging circuit.
In a typical configuration, a power management integrated circuit (PMIC) is employed to oversee the power distribution between the system and the battery charger. The PMIC ensures that the system receives adequate power while the battery is being charged, preventing any interruptions in operation.
The schematic typically includes a battery management system (BMS) that monitors battery voltage, current, and temperature to optimize charging cycles and prolong battery life. The charger circuit can be a linear or switch-mode power supply, depending on the efficiency requirements of the application.
When the system is operational, the PMIC regulates the power drawn from the battery and the charger, allowing for seamless transitions between battery power and line power. This is often achieved through the use of power path management techniques, which ensure that the system can function without interruption even if the charger is disconnected.
Additionally, protection circuits are incorporated to safeguard against overvoltage, overcurrent, and thermal conditions, which could damage the battery or the system. These features are crucial in applications such as portable devices, where reliability and safety are paramount.
Overall, the design of a power management system that supports simultaneous operation and charging requires careful consideration of the interaction between the system load and the charging circuitry to ensure optimal performance and safety.Powering the system is required by many applications while charging the battery simultaneously. Interaction between the system and charger may result in a.. 🔗 External reference
Power management in electronic systems is critical, particularly in applications that necessitate simultaneous operation and battery charging. This dual functionality can lead to complex interactions between the system load and the charging circuit.
In a typical configuration, a power management integrated circuit (PMIC) is employed to oversee the power distribution between the system and the battery charger. The PMIC ensures that the system receives adequate power while the battery is being charged, preventing any interruptions in operation.
The schematic typically includes a battery management system (BMS) that monitors battery voltage, current, and temperature to optimize charging cycles and prolong battery life. The charger circuit can be a linear or switch-mode power supply, depending on the efficiency requirements of the application.
When the system is operational, the PMIC regulates the power drawn from the battery and the charger, allowing for seamless transitions between battery power and line power. This is often achieved through the use of power path management techniques, which ensure that the system can function without interruption even if the charger is disconnected.
Additionally, protection circuits are incorporated to safeguard against overvoltage, overcurrent, and thermal conditions, which could damage the battery or the system. These features are crucial in applications such as portable devices, where reliability and safety are paramount.
Overall, the design of a power management system that supports simultaneous operation and charging requires careful consideration of the interaction between the system load and the charging circuitry to ensure optimal performance and safety.Powering the system is required by many applications while charging the battery simultaneously. Interaction between the system and charger may result in a.. 🔗 External reference