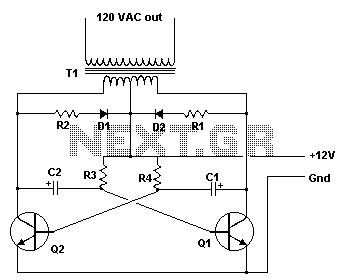
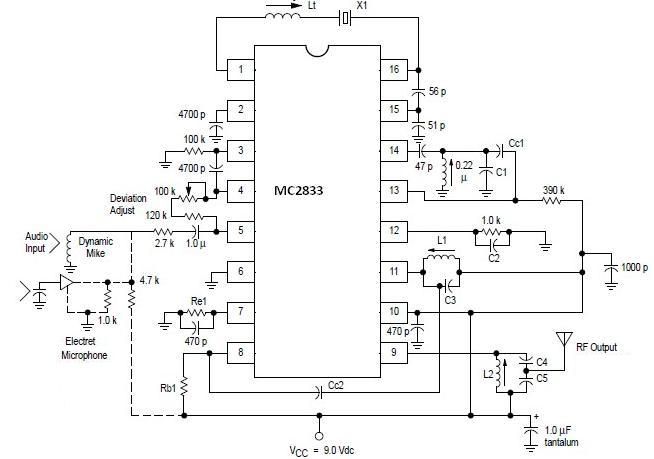
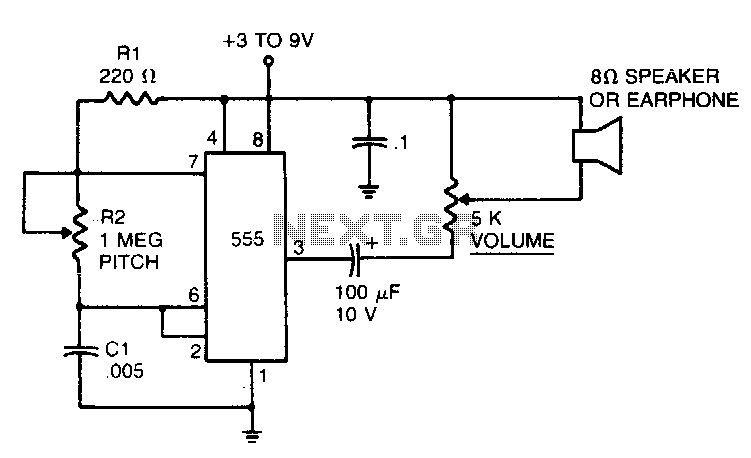
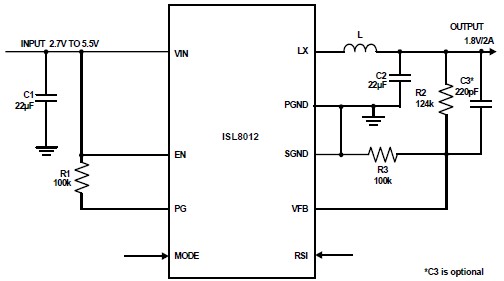
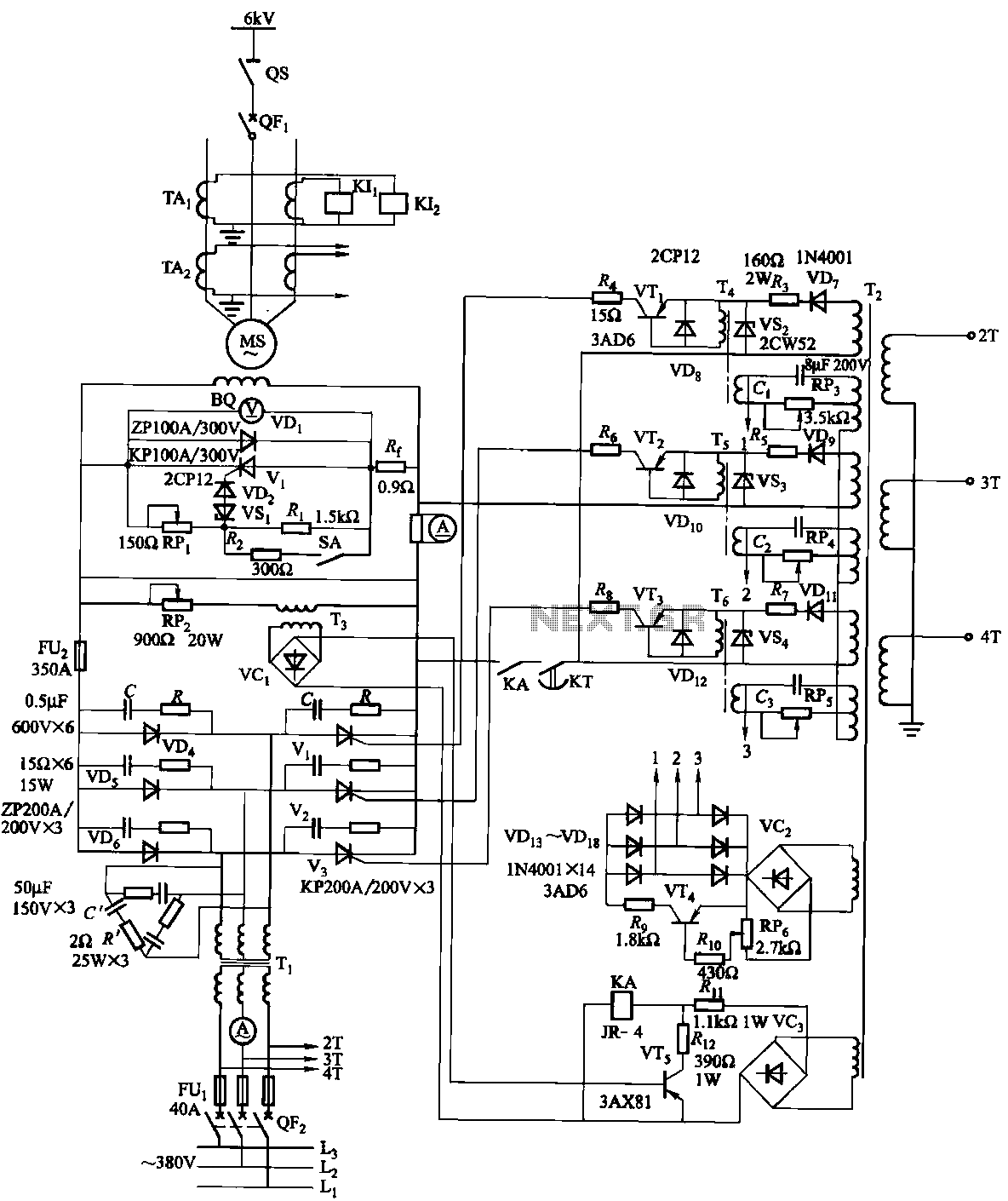
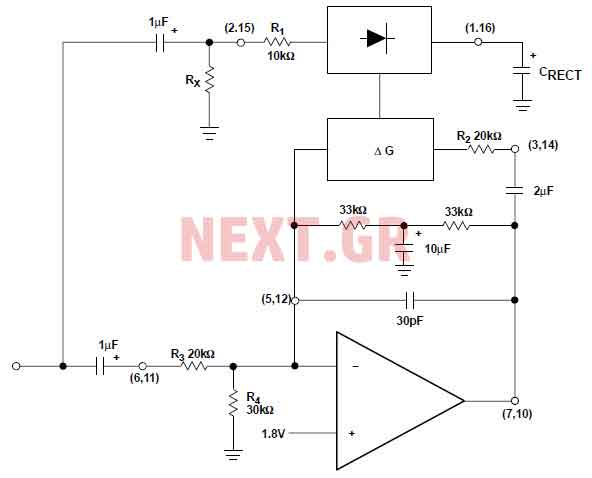
Practical sound level monitor circuit diagram
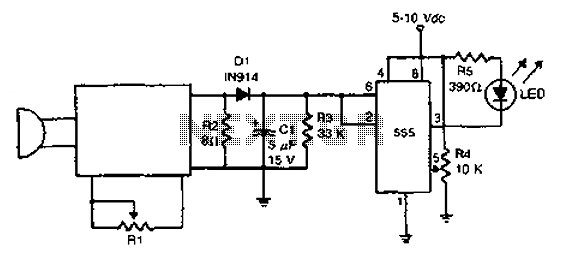
The acoustic detector consists of a Schmitt trigger IC555 connected to various components. When the input exceeds a certain voltage, the output will change state from high to low. R4 is used to set the threshold voltage.
The acoustic detector circuit utilizes the Schmitt trigger configuration of the IC555, which is known for its ability to provide hysteresis in switching applications. This characteristic is particularly useful in noise-sensitive environments, allowing the circuit to avoid false triggering due to small fluctuations in the input signal.
The primary function of the circuit is to detect acoustic signals that exceed a predefined threshold voltage. The input signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the Schmitt trigger. As the input voltage rises and crosses the threshold set by the resistor R4, the output of the IC555 transitions from a high state (logic 1) to a low state (logic 0). This transition can be utilized to activate further circuitry, such as alarms, indicators, or other control systems.
R4 plays a crucial role in defining the threshold voltage, and its value can be adjusted to tailor the sensitivity of the detector to specific acoustic levels. Additional components, such as capacitors and resistors, may be included in the circuit to filter out noise and stabilize the input signal, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this acoustic detector circuit is effective for applications requiring sound detection, such as security systems, sound-activated switches, and various automation tasks, where the precise detection of sound levels is critical.Acoustic detector consists of a Schmitt trigger IC555 connected components. Just input exceeds a certain voltage, its output will change state, from high to low. R4 to set the threshold voltage.
The acoustic detector circuit utilizes the Schmitt trigger configuration of the IC555, which is known for its ability to provide hysteresis in switching applications. This characteristic is particularly useful in noise-sensitive environments, allowing the circuit to avoid false triggering due to small fluctuations in the input signal.
The primary function of the circuit is to detect acoustic signals that exceed a predefined threshold voltage. The input signal is fed into the non-inverting input of the Schmitt trigger. As the input voltage rises and crosses the threshold set by the resistor R4, the output of the IC555 transitions from a high state (logic 1) to a low state (logic 0). This transition can be utilized to activate further circuitry, such as alarms, indicators, or other control systems.
R4 plays a crucial role in defining the threshold voltage, and its value can be adjusted to tailor the sensitivity of the detector to specific acoustic levels. Additional components, such as capacitors and resistors, may be included in the circuit to filter out noise and stabilize the input signal, ensuring reliable operation.
Overall, this acoustic detector circuit is effective for applications requiring sound detection, such as security systems, sound-activated switches, and various automation tasks, where the precise detection of sound levels is critical.Acoustic detector consists of a Schmitt trigger IC555 connected components. Just input exceeds a certain voltage, its output will change state, from high to low. R4 to set the threshold voltage.