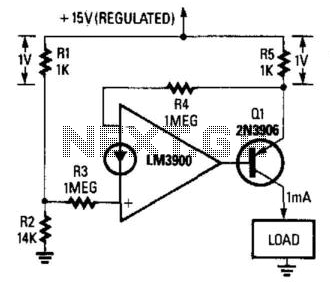
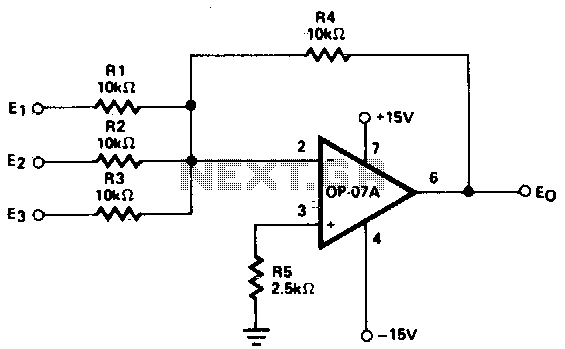
precision current loop thermocouple transmitter
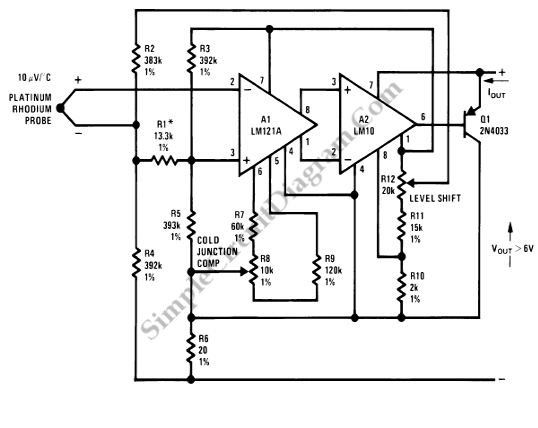
Current loop analog data transmission is utilized in industrial environments due to its robustness, offering good noise immunity and the capability for wiring fault detection.
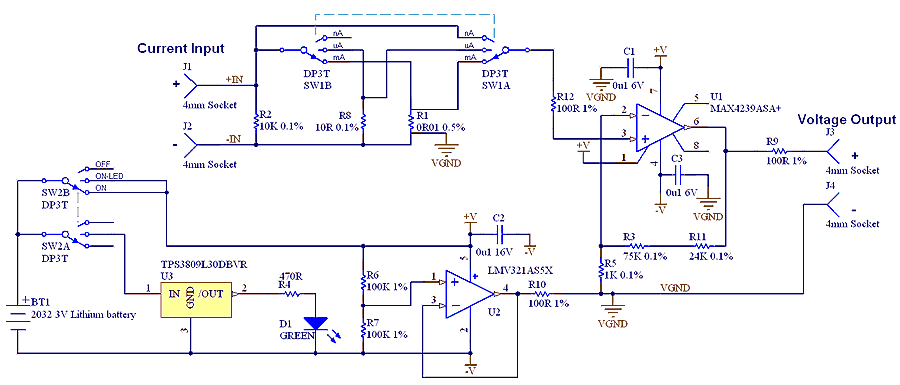
Current loop analog data transmission systems are widely employed in industrial applications due to their superior resilience to electromagnetic interference and noise, which is critical in environments with high levels of electrical noise. The typical configuration involves a 4-20 mA current loop, where the current level corresponds to the measurement of a physical parameter, such as temperature or pressure. This range is chosen because it allows for the detection of a zero signal (4 mA) and provides a clear indication of sensor failure when the current drops below the minimum threshold.
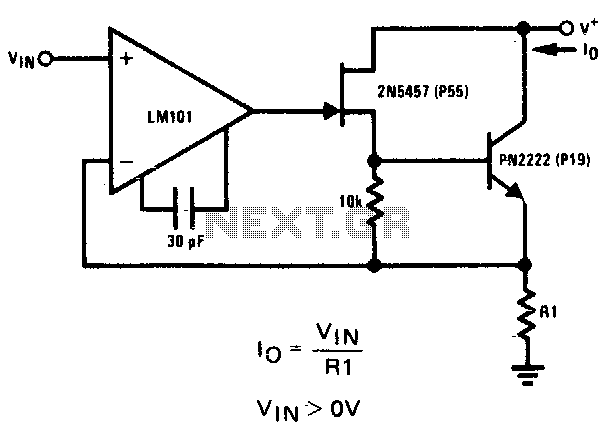
The system consists of a transmitter, which converts the physical measurement into a proportional current signal, and a receiver, which interprets the current signal to determine the corresponding value of the measured parameter. The robustness of the current loop is enhanced by the use of twisted pair wiring, which helps to further mitigate the effects of external noise sources.
In addition to noise immunity, current loop systems offer the advantage of wiring fault detection. If the loop current falls below the expected range, it can indicate issues such as a broken wire or a faulty sensor. This feature is particularly important in critical industrial processes where maintaining operational integrity is essential.
Overall, the current loop analog transmission method is favored for its reliability, ease of implementation, and effectiveness in ensuring accurate data transmission in challenging industrial settings.Current loop analog data transmission is used in industrial environment because of its robustness (good noise immunity), while providing wiring fault detection.. 🔗 External reference
Current loop analog data transmission systems are widely employed in industrial applications due to their superior resilience to electromagnetic interference and noise, which is critical in environments with high levels of electrical noise. The typical configuration involves a 4-20 mA current loop, where the current level corresponds to the measurement of a physical parameter, such as temperature or pressure. This range is chosen because it allows for the detection of a zero signal (4 mA) and provides a clear indication of sensor failure when the current drops below the minimum threshold.
The system consists of a transmitter, which converts the physical measurement into a proportional current signal, and a receiver, which interprets the current signal to determine the corresponding value of the measured parameter. The robustness of the current loop is enhanced by the use of twisted pair wiring, which helps to further mitigate the effects of external noise sources.
In addition to noise immunity, current loop systems offer the advantage of wiring fault detection. If the loop current falls below the expected range, it can indicate issues such as a broken wire or a faulty sensor. This feature is particularly important in critical industrial processes where maintaining operational integrity is essential.
Overall, the current loop analog transmission method is favored for its reliability, ease of implementation, and effectiveness in ensuring accurate data transmission in challenging industrial settings.Current loop analog data transmission is used in industrial environment because of its robustness (good noise immunity), while providing wiring fault detection.. 🔗 External reference