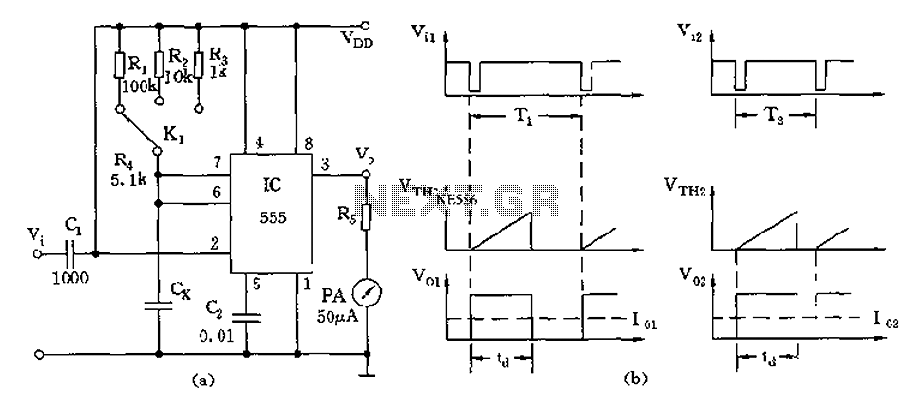
Preheat Ballast Schematic
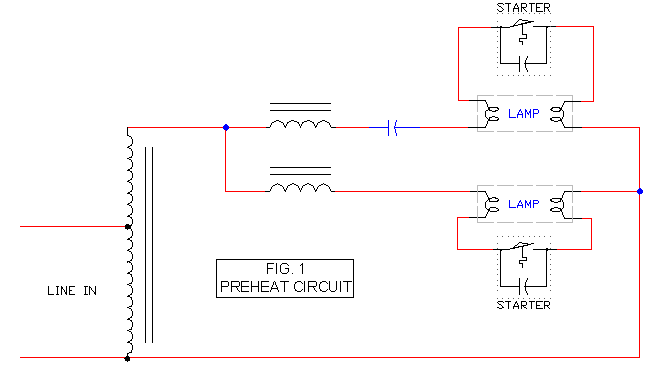
It includes a starter for each lamp that heats the filaments (cathodes) at both ends of the lamp before ignition. Once the lamp is lit, the heated filaments are no longer necessary. The heating serves solely as an ignition aid. During normal operation, the starter's contacts remain open, and the only current path through it is via the capacitor within the starter's casing. At this stage, current flows more freely through the lamp, which has a significantly lower impedance than the starter, resulting in minimal current passing through the starter's capacitor. When the arc is extinguished, the lamp's impedance increases compared to the starter, causing current to flow more readily through the filaments and the starter, while only a minimal current flows through the lamp.
The described circuit operates within a fluorescent lamp system, utilizing a starter mechanism to facilitate the initial ignition of the lamp. The starter is a crucial component that provides the necessary voltage to preheat the cathodes, ensuring that the gas within the lamp ionizes effectively. This preheating process is essential for reducing the initial breakdown voltage required to initiate the arc within the lamp.
In standard operation, after the lamp ignites, the starter's contacts open, effectively isolating the starter from the circuit. The capacitor within the starter maintains a minor current flow, which serves to stabilize the operation of the lamp. The lower impedance of the lamp compared to the starter allows for efficient current flow through the lamp, enhancing its brightness and performance.
When the lamp is turned off and the arc extinguishes, the circuit dynamics change. The lamp's impedance increases due to the lack of ionization, resulting in a higher resistance path compared to the starter. Consequently, this causes the current to preferentially flow through the starter and the filaments instead of the lamp. The circuit's design ensures that the system can effectively restart the lamp when necessary, maintaining the longevity and functionality of the fluorescent lighting system.
In summary, the starter's role is pivotal in managing the transition from the pre-ignition phase to normal operation and back to the off state, ensuring that the lamp operates efficiently while extending its lifespan. The balance of impedance between the starter and the lamp is critical for optimal performance, highlighting the importance of careful design in fluorescent lighting circuits.It incorporates a Starter for each lamp, which heats up the fillaments [Cathodes] at each end of the lamp prior to starting. Once the lamp has started, it no longer requires heated fillaments. The heating is only a starting aid. During normal operation, the starter`s contacts will be open, and the only circuit path through it will be the Capacitor inside the Starter`s case.
The currents will now flow easily through the lamp [much lower Impedance across the lamp than the starter], only a minimal amount of current flows through the starter`s Capacitor. Once the arc is extinguished, the lamp becomes a higher Impedance than the starter, so currents will now flow easier through the fillaments and the Starter, minimal current flows through the lamp.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates within a fluorescent lamp system, utilizing a starter mechanism to facilitate the initial ignition of the lamp. The starter is a crucial component that provides the necessary voltage to preheat the cathodes, ensuring that the gas within the lamp ionizes effectively. This preheating process is essential for reducing the initial breakdown voltage required to initiate the arc within the lamp.
In standard operation, after the lamp ignites, the starter's contacts open, effectively isolating the starter from the circuit. The capacitor within the starter maintains a minor current flow, which serves to stabilize the operation of the lamp. The lower impedance of the lamp compared to the starter allows for efficient current flow through the lamp, enhancing its brightness and performance.
When the lamp is turned off and the arc extinguishes, the circuit dynamics change. The lamp's impedance increases due to the lack of ionization, resulting in a higher resistance path compared to the starter. Consequently, this causes the current to preferentially flow through the starter and the filaments instead of the lamp. The circuit's design ensures that the system can effectively restart the lamp when necessary, maintaining the longevity and functionality of the fluorescent lighting system.
In summary, the starter's role is pivotal in managing the transition from the pre-ignition phase to normal operation and back to the off state, ensuring that the lamp operates efficiently while extending its lifespan. The balance of impedance between the starter and the lamp is critical for optimal performance, highlighting the importance of careful design in fluorescent lighting circuits.It incorporates a Starter for each lamp, which heats up the fillaments [Cathodes] at each end of the lamp prior to starting. Once the lamp has started, it no longer requires heated fillaments. The heating is only a starting aid. During normal operation, the starter`s contacts will be open, and the only circuit path through it will be the Capacitor inside the Starter`s case.
The currents will now flow easily through the lamp [much lower Impedance across the lamp than the starter], only a minimal amount of current flows through the starter`s Capacitor. Once the arc is extinguished, the lamp becomes a higher Impedance than the starter, so currents will now flow easier through the fillaments and the Starter, minimal current flows through the lamp.
🔗 External reference