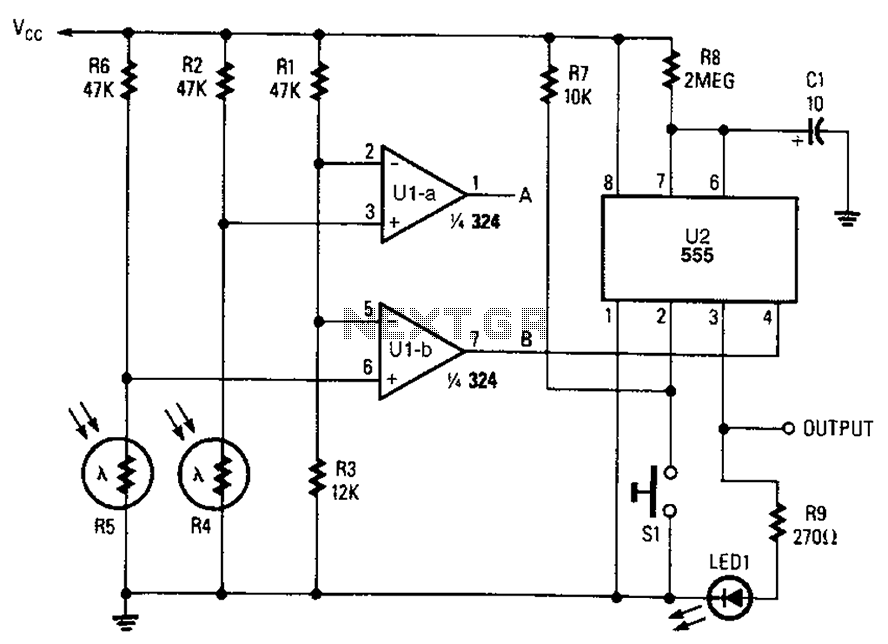
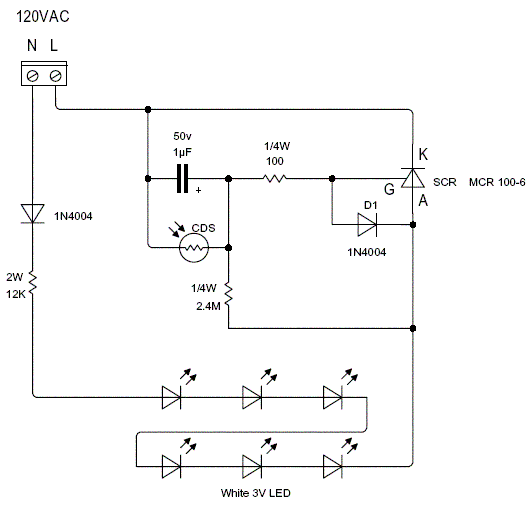
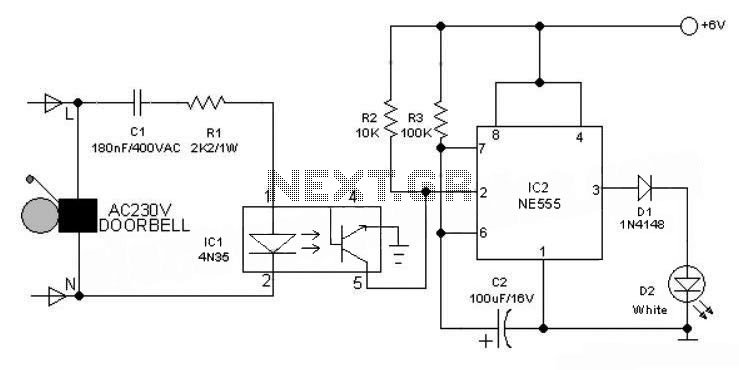
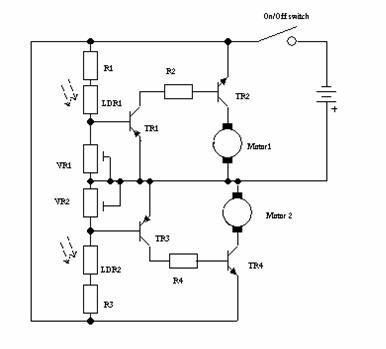
Pulse generation by interrupting a light beam
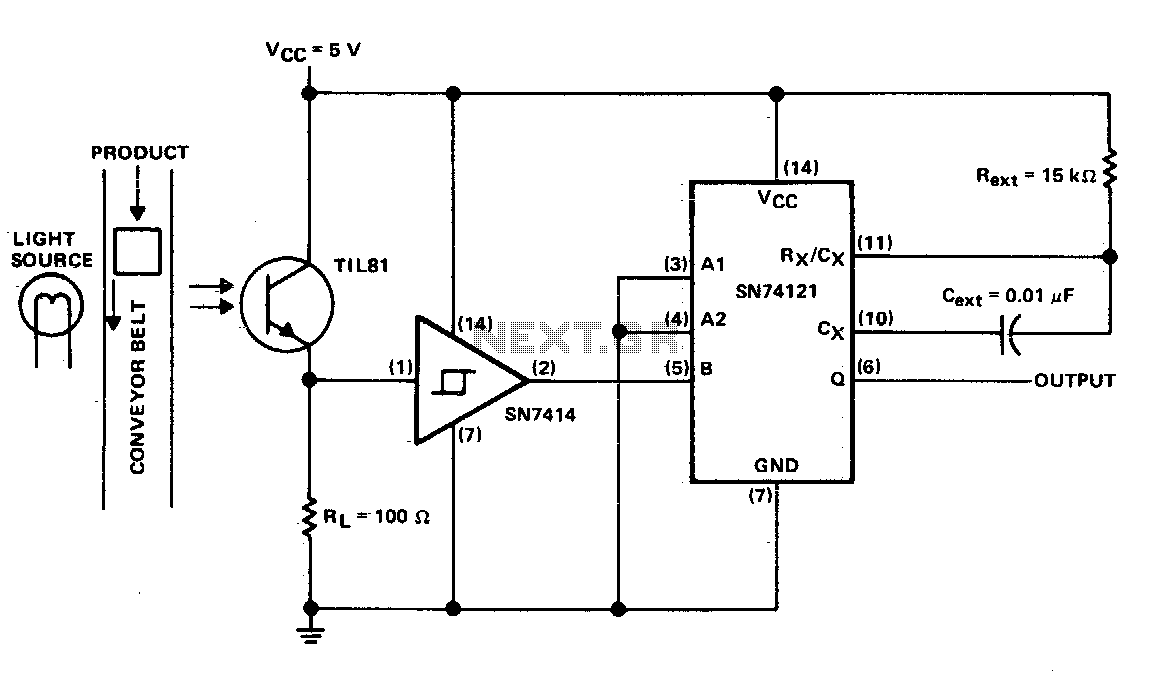
This circuit generates a pulse when an object on the conveyor belt obstructs the light source. The light source continuously keeps the phototransistor activated, resulting in a high logic level voltage at the Schmitt-trigger inverter and a TTL-compatible low logic level at pin 5 of the monostable. When an object blocks the light, the TIL81 turns off the Schmitt-trigger inverter, which in turn triggers the one-shot.
The described circuit operates on the principle of light interruption and pulse generation, making it suitable for object detection applications on conveyor systems. The light source, typically an LED, illuminates a path where a phototransistor is positioned. Under normal operating conditions, the phototransistor remains conductive due to the presence of light, allowing a high voltage signal to be fed into a Schmitt-trigger inverter. This inverter is designed to provide a clean transition between high and low logic levels, ensuring that noise does not affect the output signal.
The output from the Schmitt-trigger inverter serves two purposes: it maintains a stable high logic level when unobstructed and provides a TTL-compatible low logic level at pin 5 of a monostable multivibrator when the light path is blocked. The monostable multivibrator, often implemented with a 555 timer or a similar device, is configured to generate a single pulse of a specified duration when triggered.
When an object interrupts the light beam, the phototransistor turns off, causing the Schmitt-trigger inverter to switch to a low logic level. This transition triggers the monostable multivibrator, which then outputs a pulse. The pulse duration can be adjusted by changing the timing components (resistor and capacitor) associated with the monostable multivibrator, allowing for flexibility in applications where different pulse widths are required.
This circuit is particularly useful in automated systems for counting objects, detecting presence, or initiating further processing steps on a conveyor belt. The design is robust and can be adapted to various environments by selecting appropriate light sources and phototransistor types.This circuit puts out a pulse when an object on the conveyor belt blocks the light source. The light source keeps the phototran-sistor turned on. This produces a high-logic-level voltage at the Schmitt-trigger inverter and a TTL-compatible low logic level at pin 5 of the monostable When an object blocks the light, TIL81 turns off the Schmitt-trigger inverter to triggers the one shot.
The described circuit operates on the principle of light interruption and pulse generation, making it suitable for object detection applications on conveyor systems. The light source, typically an LED, illuminates a path where a phototransistor is positioned. Under normal operating conditions, the phototransistor remains conductive due to the presence of light, allowing a high voltage signal to be fed into a Schmitt-trigger inverter. This inverter is designed to provide a clean transition between high and low logic levels, ensuring that noise does not affect the output signal.
The output from the Schmitt-trigger inverter serves two purposes: it maintains a stable high logic level when unobstructed and provides a TTL-compatible low logic level at pin 5 of a monostable multivibrator when the light path is blocked. The monostable multivibrator, often implemented with a 555 timer or a similar device, is configured to generate a single pulse of a specified duration when triggered.
When an object interrupts the light beam, the phototransistor turns off, causing the Schmitt-trigger inverter to switch to a low logic level. This transition triggers the monostable multivibrator, which then outputs a pulse. The pulse duration can be adjusted by changing the timing components (resistor and capacitor) associated with the monostable multivibrator, allowing for flexibility in applications where different pulse widths are required.
This circuit is particularly useful in automated systems for counting objects, detecting presence, or initiating further processing steps on a conveyor belt. The design is robust and can be adapted to various environments by selecting appropriate light sources and phototransistor types.This circuit puts out a pulse when an object on the conveyor belt blocks the light source. The light source keeps the phototran-sistor turned on. This produces a high-logic-level voltage at the Schmitt-trigger inverter and a TTL-compatible low logic level at pin 5 of the monostable When an object blocks the light, TIL81 turns off the Schmitt-trigger inverter to triggers the one shot.