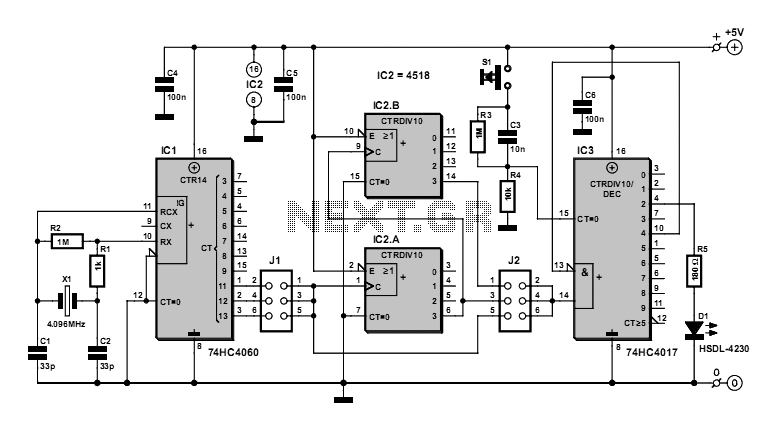
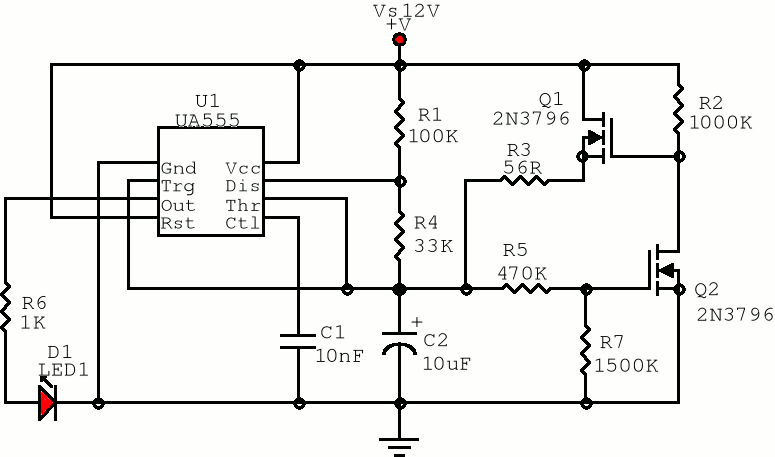
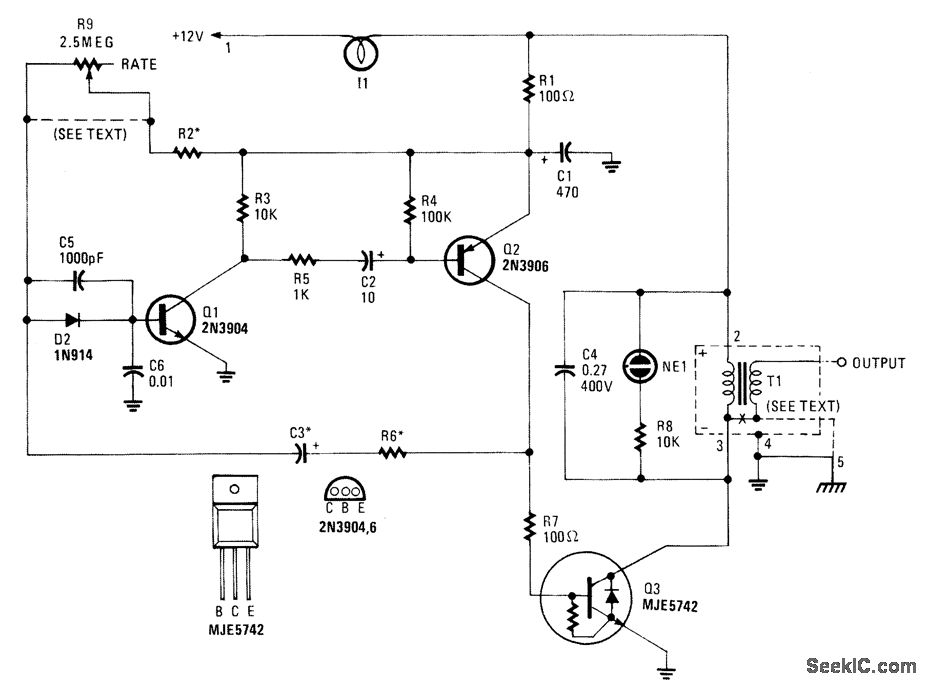
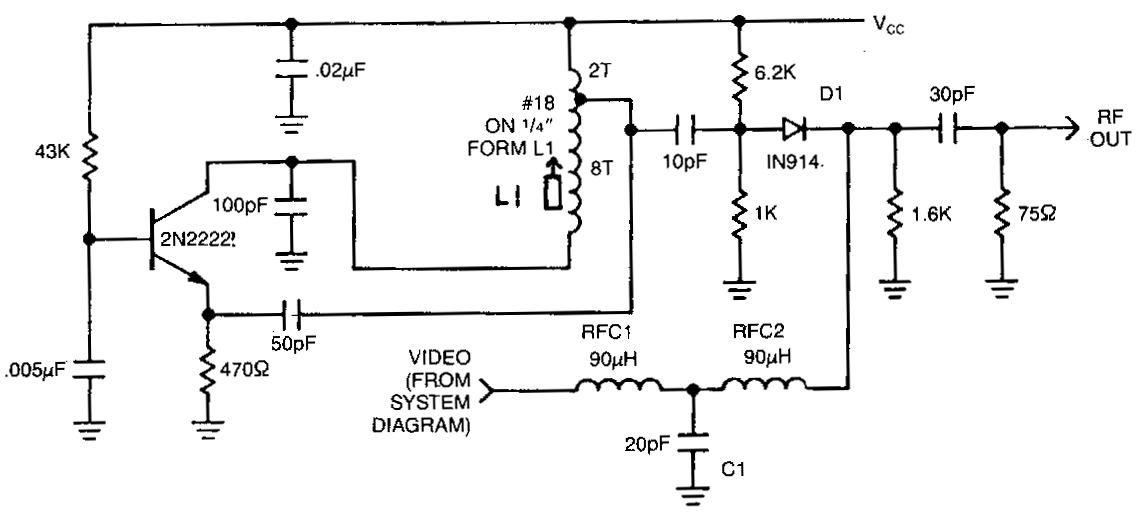
Pulse Width Modulator Using 555 IC
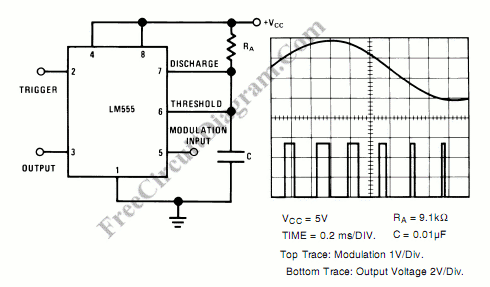
A pulse width modulator generates a PWM signal, which consists of pulses with a constant frequency while the duty cycle varies according to a modulating signal.
A pulse width modulator (PWM) is an essential component in various electronic applications, particularly in motor control, power regulation, and signal processing. The PWM signal is characterized by its ability to maintain a fixed frequency while adjusting the duration of the high state (duty cycle) based on an input modulating signal. This modulation allows for efficient control of power delivery to devices, enabling precise control over performance characteristics such as speed and torque in motors or brightness in LED lighting.
In a typical PWM circuit, the core components include a comparator, a reference voltage source, and a timing circuit. The comparator compares the modulating signal, which can be a sinusoidal waveform or any other varying signal, against a triangular or sawtooth waveform generated by the timing circuit. When the modulating signal exceeds the reference waveform, the output of the comparator switches high, creating a pulse. The width of this pulse is determined by the amplitude of the modulating signal at the moment of comparison, effectively varying the duty cycle.
The frequency of the PWM signal is determined by the timing circuit, which sets the rate at which the triangular or sawtooth waveform oscillates. The choice of frequency is critical and should be tailored to the specific application, balancing factors such as response time and efficiency. For instance, in motor control applications, a lower frequency might be preferable to reduce audible noise, while higher frequencies may be used in applications requiring rapid response times.
Additionally, filtering components may be included in the circuit to smooth out the PWM signal, converting it into a more stable DC voltage if needed. This is particularly useful in applications where a steady voltage is required, such as in power supplies or when driving analog devices.
Overall, the design of a PWM circuit involves careful consideration of component selection, waveform characteristics, and operational requirements to achieve the desired control and efficiency in electronic systems.Pulse width modulator produce a PWM signal, a pulse with a constant frequency but with the duty cycle vary according to a modulating signal. Here is the. 🔗 External reference
A pulse width modulator (PWM) is an essential component in various electronic applications, particularly in motor control, power regulation, and signal processing. The PWM signal is characterized by its ability to maintain a fixed frequency while adjusting the duration of the high state (duty cycle) based on an input modulating signal. This modulation allows for efficient control of power delivery to devices, enabling precise control over performance characteristics such as speed and torque in motors or brightness in LED lighting.
In a typical PWM circuit, the core components include a comparator, a reference voltage source, and a timing circuit. The comparator compares the modulating signal, which can be a sinusoidal waveform or any other varying signal, against a triangular or sawtooth waveform generated by the timing circuit. When the modulating signal exceeds the reference waveform, the output of the comparator switches high, creating a pulse. The width of this pulse is determined by the amplitude of the modulating signal at the moment of comparison, effectively varying the duty cycle.
The frequency of the PWM signal is determined by the timing circuit, which sets the rate at which the triangular or sawtooth waveform oscillates. The choice of frequency is critical and should be tailored to the specific application, balancing factors such as response time and efficiency. For instance, in motor control applications, a lower frequency might be preferable to reduce audible noise, while higher frequencies may be used in applications requiring rapid response times.
Additionally, filtering components may be included in the circuit to smooth out the PWM signal, converting it into a more stable DC voltage if needed. This is particularly useful in applications where a steady voltage is required, such as in power supplies or when driving analog devices.
Overall, the design of a PWM circuit involves careful consideration of component selection, waveform characteristics, and operational requirements to achieve the desired control and efficiency in electronic systems.Pulse width modulator produce a PWM signal, a pulse with a constant frequency but with the duty cycle vary according to a modulating signal. Here is the. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713