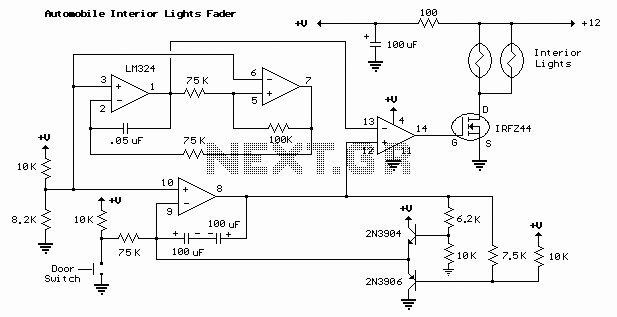
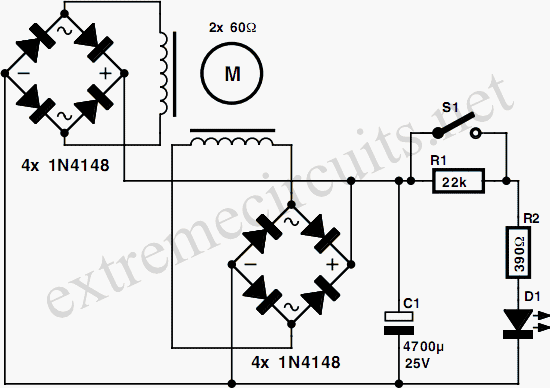
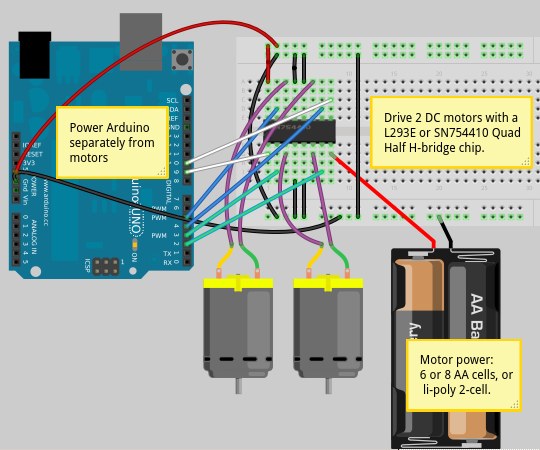
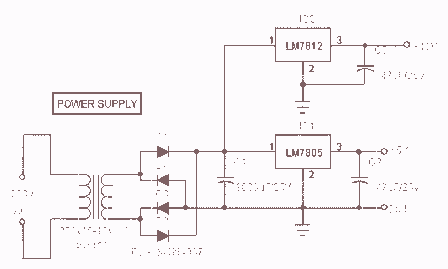
PWM Motor Speed Controller / DC Light Dimmer
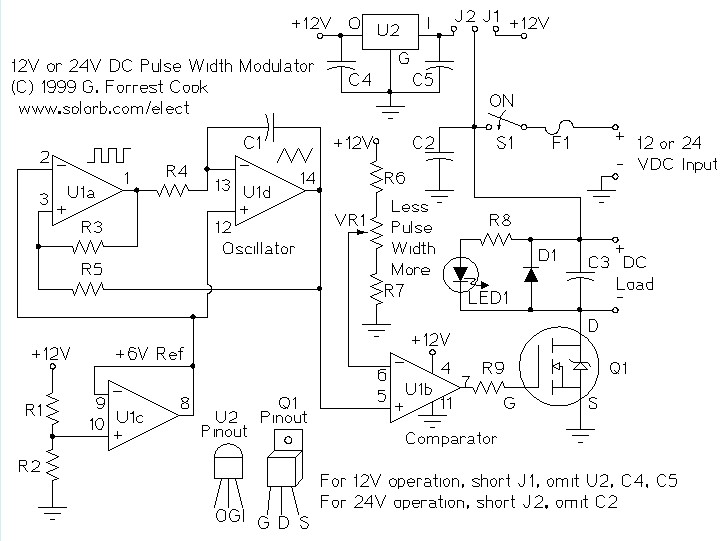
A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that can be utilized as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is intended for general-purpose applications, capable of controlling DC devices that draw up to a few amps of current. This circuit can operate in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only minor wiring modifications required.
The PWM circuit operates by varying the width of the pulses in a signal to control the amount of power delivered to a load. This is accomplished through a method known as duty cycle modulation, where the ratio of the "on" time to the total cycle time is adjusted. By changing the duration of the "on" state relative to the "off" state, the average voltage and current supplied to the load can be effectively controlled, resulting in dimming for lights or speed control for motors.
Typically, a PWM circuit consists of several key components: a microcontroller or timer IC to generate the PWM signal, a power transistor or MOSFET to switch the load, and additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability. The microcontroller is programmed to adjust the duty cycle based on user input or predefined settings, allowing for precise control over the output.
For a 12 or 24 Volt system, the circuit configuration will require appropriate selection of the power transistor to handle the maximum current load. For example, an N-channel MOSFET is often used due to its efficiency and fast switching capabilities. The gate of the MOSFET is driven by the PWM signal, which can be generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM IC.
In terms of wiring changes for different voltage systems, the primary consideration is ensuring that the components selected can handle the voltage and current levels without overheating or failing. The input voltage should be connected to the drain of the MOSFET, while the source connects to the load, which in turn connects to ground.
Additional components may include a flyback diode across inductive loads, such as motors, to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the load is switched off. Filtering capacitors may also be included to smooth out the output voltage and reduce electrical noise.
Overall, this PWM circuit provides a versatile solution for controlling DC devices, making it suitable for various applications in lighting and motor control, with the flexibility to adapt to different voltage systems with minimal modifications.A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is for a general purpose device that can control DC devices which draw up to a few amps of current.
The circuit may be used in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only a few minor wiring changes. This device has been.. 🔗 External reference
The PWM circuit operates by varying the width of the pulses in a signal to control the amount of power delivered to a load. This is accomplished through a method known as duty cycle modulation, where the ratio of the "on" time to the total cycle time is adjusted. By changing the duration of the "on" state relative to the "off" state, the average voltage and current supplied to the load can be effectively controlled, resulting in dimming for lights or speed control for motors.
Typically, a PWM circuit consists of several key components: a microcontroller or timer IC to generate the PWM signal, a power transistor or MOSFET to switch the load, and additional passive components such as resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability. The microcontroller is programmed to adjust the duty cycle based on user input or predefined settings, allowing for precise control over the output.
For a 12 or 24 Volt system, the circuit configuration will require appropriate selection of the power transistor to handle the maximum current load. For example, an N-channel MOSFET is often used due to its efficiency and fast switching capabilities. The gate of the MOSFET is driven by the PWM signal, which can be generated by a microcontroller or a dedicated PWM IC.
In terms of wiring changes for different voltage systems, the primary consideration is ensuring that the components selected can handle the voltage and current levels without overheating or failing. The input voltage should be connected to the drain of the MOSFET, while the source connects to the load, which in turn connects to ground.
Additional components may include a flyback diode across inductive loads, such as motors, to protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the load is switched off. Filtering capacitors may also be included to smooth out the output voltage and reduce electrical noise.
Overall, this PWM circuit provides a versatile solution for controlling DC devices, making it suitable for various applications in lighting and motor control, with the flexibility to adapt to different voltage systems with minimal modifications.A pulse width modulator (PWM) is a device that may be used as an efficient light dimmer or DC motor speed controller. The circuit described here is for a general purpose device that can control DC devices which draw up to a few amps of current.
The circuit may be used in either 12 or 24 Volt systems with only a few minor wiring changes. This device has been.. 🔗 External reference