Pulse Width Modulation DC Motor Controls

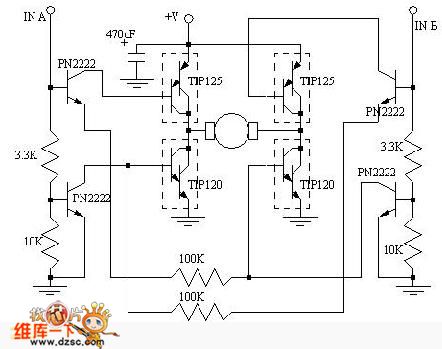
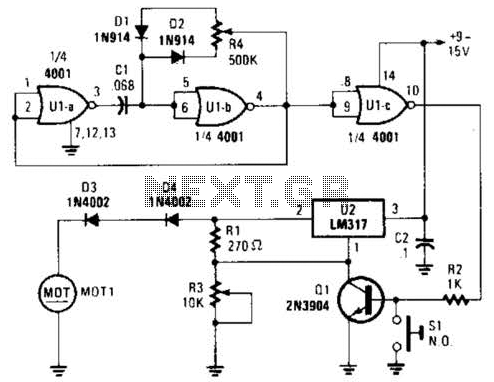
This simple pulse width modulation (PWM) DC motor control addresses common issues by regulating motor speed through the application of short pulses. The duration of these pulses is varied to adjust the motor speed; longer pulses result in faster motor operation, while shorter pulses reduce speed. The motor (M1) can be any DC motor that operates at 6V and does not exceed the maximum current rating of transistor Q1. Additionally, the voltage can be increased by connecting a higher voltage source to the switch instead of the 6V supply for the oscillator, ensuring that the power rating of Q1 is not exceeded.
The described PWM control circuit offers an efficient method for regulating DC motor speed by utilizing a switching mechanism that modulates the power delivered to the motor. The circuit consists of a PWM generator, typically implemented with a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller, which produces a square wave signal. This signal is fed into a power transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control the current flowing to the motor (M1).
The duty cycle of the PWM signal—defined as the ratio of the ON time to the total time period—determines the average voltage and current supplied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle, the effective power delivered to the motor can be finely tuned, allowing for precise speed control.
In this configuration, the motor should be rated for a maximum operating voltage of 6V, and care must be taken to ensure that the current drawn by the motor does not exceed the maximum current rating of the transistor Q1. If a higher voltage is desired for the motor operation, it is permissible to connect a higher voltage source to the switch. However, it is critical to ensure that the power dissipation in Q1 remains within safe limits to prevent damage to the transistor.
The PWM control circuit is particularly beneficial in applications where variable speed control is necessary, such as in robotics, fans, or other automated systems. It provides a simple yet effective solution for controlling the speed of DC motors while maintaining efficiency and minimizing heat generation compared to linear control methods. Proper selection of components, including the transistor and motor, along with careful design of the PWM signal, will lead to optimal performance of the motor control system.This simple pulse width modulation DC motor control eliminates these problems. It controls the motor speed by driving the motor with short pulses. Thesepulses vary in duration to change the speed of the motor. The longer the pulses, the faster the motor turns, and vice versa. 2. M1 can be any DC motor that operates from 6V and does not draw more than the maximum current of Q1. The voltage can be increased by connecting the higher voltage to the switch instead of the 6V that powers the oscillator. Be sure not to exceed the power rating of Q1 if you do this. 🔗 External reference
The described PWM control circuit offers an efficient method for regulating DC motor speed by utilizing a switching mechanism that modulates the power delivered to the motor. The circuit consists of a PWM generator, typically implemented with a 555 timer IC or a microcontroller, which produces a square wave signal. This signal is fed into a power transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control the current flowing to the motor (M1).
The duty cycle of the PWM signal—defined as the ratio of the ON time to the total time period—determines the average voltage and current supplied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle, the effective power delivered to the motor can be finely tuned, allowing for precise speed control.
In this configuration, the motor should be rated for a maximum operating voltage of 6V, and care must be taken to ensure that the current drawn by the motor does not exceed the maximum current rating of the transistor Q1. If a higher voltage is desired for the motor operation, it is permissible to connect a higher voltage source to the switch. However, it is critical to ensure that the power dissipation in Q1 remains within safe limits to prevent damage to the transistor.
The PWM control circuit is particularly beneficial in applications where variable speed control is necessary, such as in robotics, fans, or other automated systems. It provides a simple yet effective solution for controlling the speed of DC motors while maintaining efficiency and minimizing heat generation compared to linear control methods. Proper selection of components, including the transistor and motor, along with careful design of the PWM signal, will lead to optimal performance of the motor control system.This simple pulse width modulation DC motor control eliminates these problems. It controls the motor speed by driving the motor with short pulses. Thesepulses vary in duration to change the speed of the motor. The longer the pulses, the faster the motor turns, and vice versa. 2. M1 can be any DC motor that operates from 6V and does not draw more than the maximum current of Q1. The voltage can be increased by connecting the higher voltage to the switch instead of the 6V that powers the oscillator. Be sure not to exceed the power rating of Q1 if you do this. 🔗 External reference