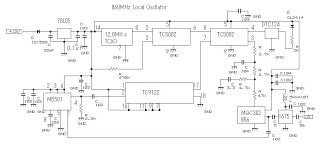
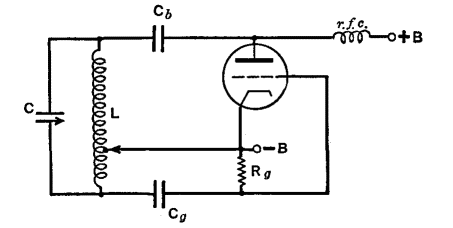
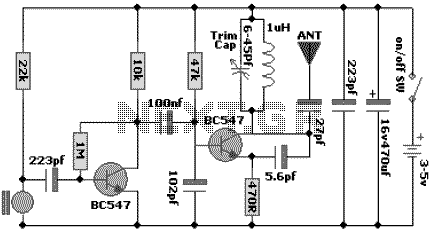
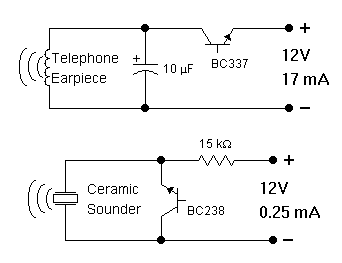
Quartz Crystal Oscillator and Quartz Crystals
Electronics tutorial about quartz crystal oscillators, including harmonic, overtone, Pierce oscillator, and crystal quartz oscillator circuits.
Quartz crystal oscillators are vital components in modern electronics, providing stable frequency references for a variety of applications. They utilize the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystals to generate oscillations at precise frequencies. The primary types of quartz crystal oscillators include harmonic, overtone, and Pierce oscillators, each with unique characteristics and applications.
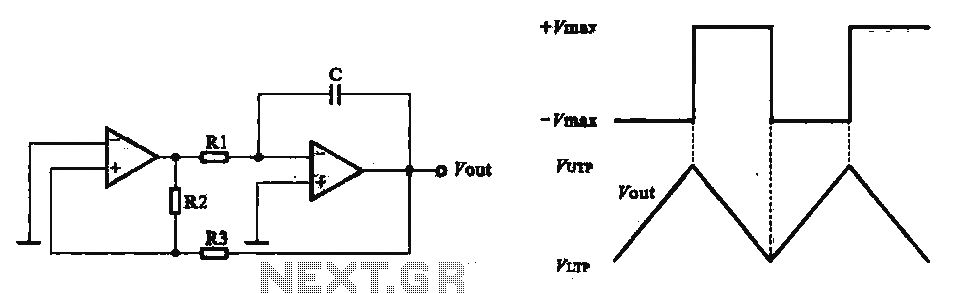
Harmonic oscillators operate by using the fundamental frequency of the crystal, where the oscillation is maintained by the crystal's mechanical resonance. This type is commonly used in applications requiring low noise and high stability, such as in clocks and frequency synthesizers.
Overtone oscillators, on the other hand, exploit higher harmonics of the fundamental frequency. By utilizing overtones, these oscillators can achieve higher frequencies without the need for larger crystals. This allows for compact designs in applications like RF transmitters and receivers.
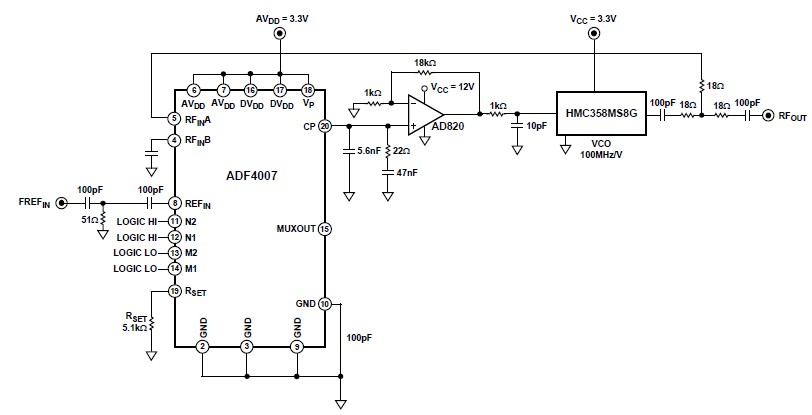
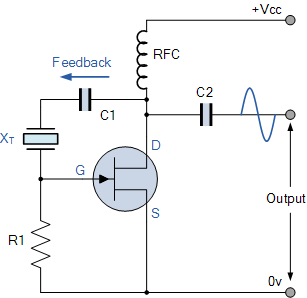
The Pierce oscillator is a specific configuration that employs a quartz crystal in a feedback loop with an amplifier. This design is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating stable oscillations. It is widely used in microcontroller applications and other digital circuits where precise timing is critical.
Crystal quartz oscillators can be integrated into circuits to provide clock signals for digital devices, ensuring synchronous operation. They are characterized by their small size, low power consumption, and high frequency stability, making them essential in telecommunications, computing, and consumer electronics.
In summary, quartz crystal oscillators are crucial for maintaining accurate timing and frequency control in electronic systems, with various configurations tailored to meet specific requirements across different applications.Electronics Tutorial about Quartz Crystal Oscillator including Harmonic, Overtone, Pierce Oscillator and Crystal Quartz Oscillator Circuits.. 🔗 External reference
Quartz crystal oscillators are vital components in modern electronics, providing stable frequency references for a variety of applications. They utilize the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystals to generate oscillations at precise frequencies. The primary types of quartz crystal oscillators include harmonic, overtone, and Pierce oscillators, each with unique characteristics and applications.
Harmonic oscillators operate by using the fundamental frequency of the crystal, where the oscillation is maintained by the crystal's mechanical resonance. This type is commonly used in applications requiring low noise and high stability, such as in clocks and frequency synthesizers.
Overtone oscillators, on the other hand, exploit higher harmonics of the fundamental frequency. By utilizing overtones, these oscillators can achieve higher frequencies without the need for larger crystals. This allows for compact designs in applications like RF transmitters and receivers.
The Pierce oscillator is a specific configuration that employs a quartz crystal in a feedback loop with an amplifier. This design is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in generating stable oscillations. It is widely used in microcontroller applications and other digital circuits where precise timing is critical.
Crystal quartz oscillators can be integrated into circuits to provide clock signals for digital devices, ensuring synchronous operation. They are characterized by their small size, low power consumption, and high frequency stability, making them essential in telecommunications, computing, and consumer electronics.
In summary, quartz crystal oscillators are crucial for maintaining accurate timing and frequency control in electronic systems, with various configurations tailored to meet specific requirements across different applications.Electronics Tutorial about Quartz Crystal Oscillator including Harmonic, Overtone, Pierce Oscillator and Crystal Quartz Oscillator Circuits.. 🔗 External reference